Structure of antimonide quantum well CMOS device and preparation method thereof
An antimonide and quantum well technology, applied in the field of microelectronics, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of epitaxial material growth and process preparation, large differences in lattice constant, polarity and thermal expansion coefficient, and low hole mobility, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
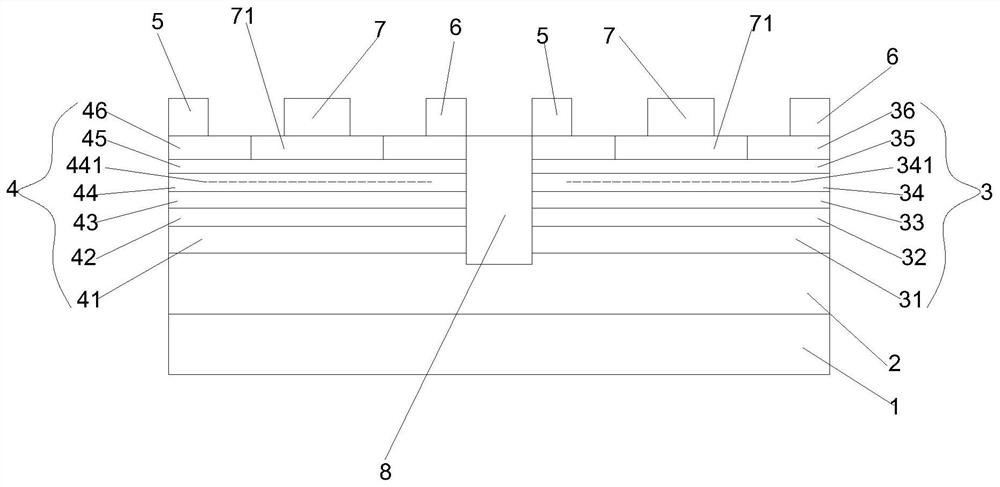
[0066] A kind of antimonide quantum well CMOS device structure, see figure 1 shown, including:
[0067] Using GaAs as the substrate 1;
[0068] A buffer layer 2 is provided on the substrate 1, and the thickness of the buffer layer is 1.0 μm;
[0069] The buffer layer 2 is relatively independently provided with a p-channel antimonide quantum well layer 3 and an n-channel antimonide quantum well layer 4;
[0070] The p-channel antimonide quantum well layer 3 includes:
[0071] Laminated on the buffer layer 2 sequentially from bottom to top
[0072] The first lower barrier layer 31 is made of AlGaSb material with a thickness of 50nm,
[0073] The first channel layer 32 is made of InGaSb material with a thickness of 10nm.
[0074] The first isolation layer 33 is made of AlGaSb material with a thickness of 2nm.
[0075] The first upper barrier layer 34 is made of AlGaSb material with a thickness of 5nm,
[0076] The first interface control layer 35 is made of InAs material w...
Embodiment 2
[0124] A kind of antimonide quantum well CMOS device structure, same as embodiment 1, difference is:
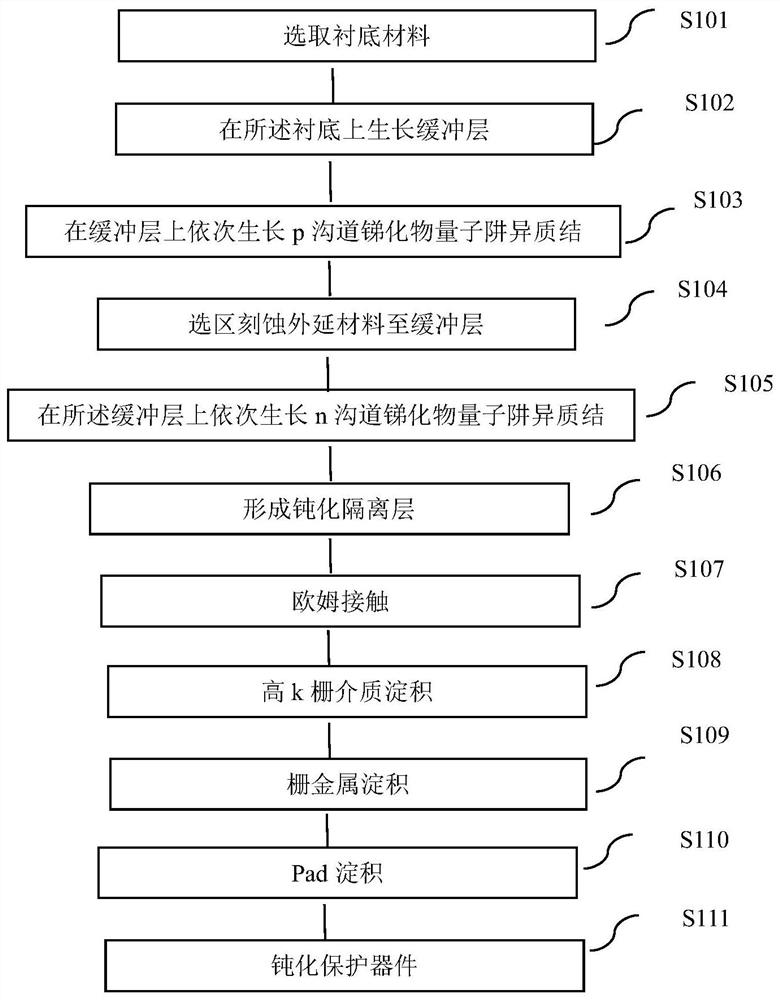
[0125] The preparation method of above-mentioned antimonide quantum well CMOS device structure, see image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0126] S201 Select GaAs substrate
[0127] S202 using molecular beam epitaxy to grow a buffer layer of 1 μm AlGaSb on the GaAs substrate.
[0128]S203 Using molecular beam epitaxy technology on the buffer layer, sequentially grow n-channel antimonide quantum well layers to form a heterojunction; grow a second lower barrier layer AlInSb on the surface of the buffer layer; grow the second lower barrier layer on the second lower barrier layer growing a second channel layer InAsSb on the top; growing a second isolation layer AlInSb on the second channel layer; growing a second upper barrier layer AlInSb on the second isolation layer; growing a second upper barrier layer AlInSb on the second upper barrier Doping Si in the layer to ...
Embodiment 3
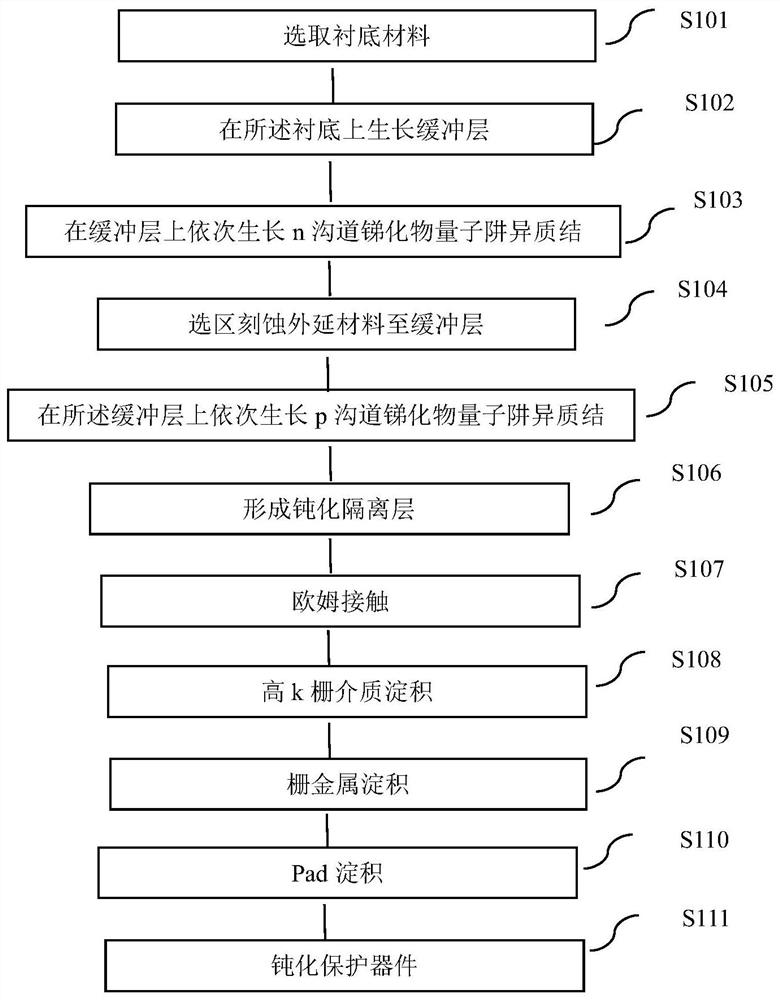
[0153] Same as Example 1, the difference is that
[0154] The p-channel antimonide quantum well layer on the buffer layer, the n-channel antimonide quantum well layer and the passivation isolation layer between the p-channel antimonide quantum well layer and the n-channel antimonide quantum well layer are according to the following steps be made of,
[0155] After the preparation of the p-channel antimonide quantum well layer is completed, the epitaxial material of the p-channel antimonide quantum well layer is selectively etched to the buffer layer to form a trench area where the n-channel antimonide quantum well layer can grow, and the p-channel is formed by PECVD. The etched side of the antimonide quantum well layer is passivated, and the passivation layer SiO is deposited 2 , forming a passivation isolation layer, and then growing an n-channel antimonide quantum well layer on the buffer layer to realize a passivation isolation region between the n-channel antimonide quant...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com