Method for simultaneously realizing linear optimization and power periodic fading compensation in analog photon down-conversion link
A linear optimization and frequency conversion link technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, electromagnetic wave transmission systems, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of transmission signal fading, inability to extract useful signals at the receiving end, different time delays, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings: this embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operating procedures are provided, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following the described embodiment.
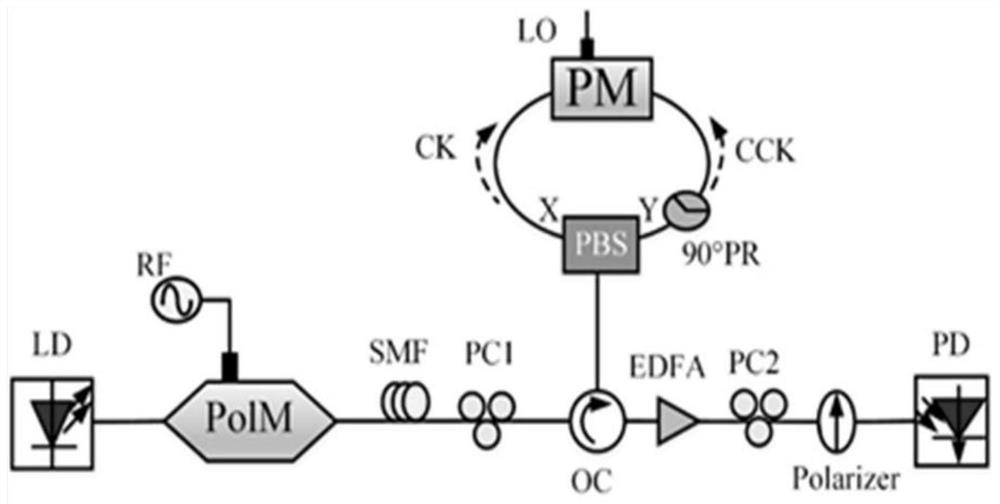
[0033] As attached in the manual figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, the device includes: laser LD, polarization modulator PolM, single-mode fiber SMF, polarization controller PC, Sagnac ring, erbium-doped fiber amplifier EDFA, polarizer Polarizer and photodetector PD. The Sagnac ring is composed of an optical circulator OC, a polarization beam splitter PBS, a phase modulator PM and a 90° polarization rotator 90°PR.
[0034] In this example, the specific implementation steps of the method are:
[0035] Step 1: The laser generates a continuous light wave with a w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com