Arthrobacter capable of degrading n-eicosane and application thereof
A n-eicosane and degradable technology, applied in the field of microbial remediation of organic pollutants, can solve the problems of application limitations, inconsistent application conditions of strains, and poor stability of bacterial flora, so as to avoid high costs, stable performance, and low requirements for experimental conditions Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
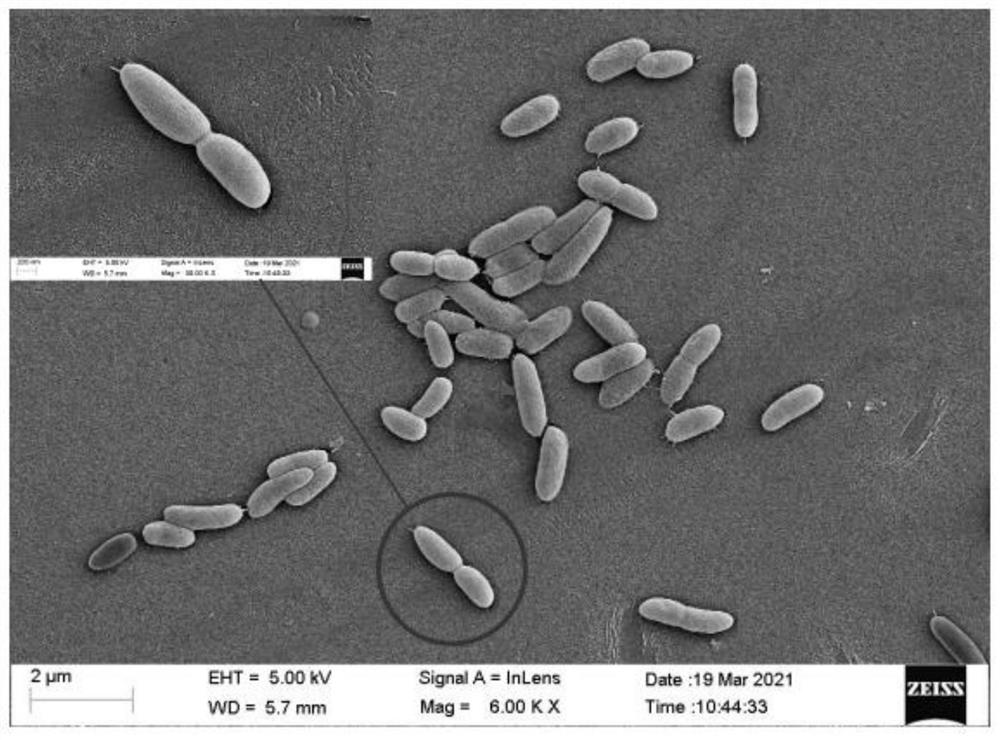
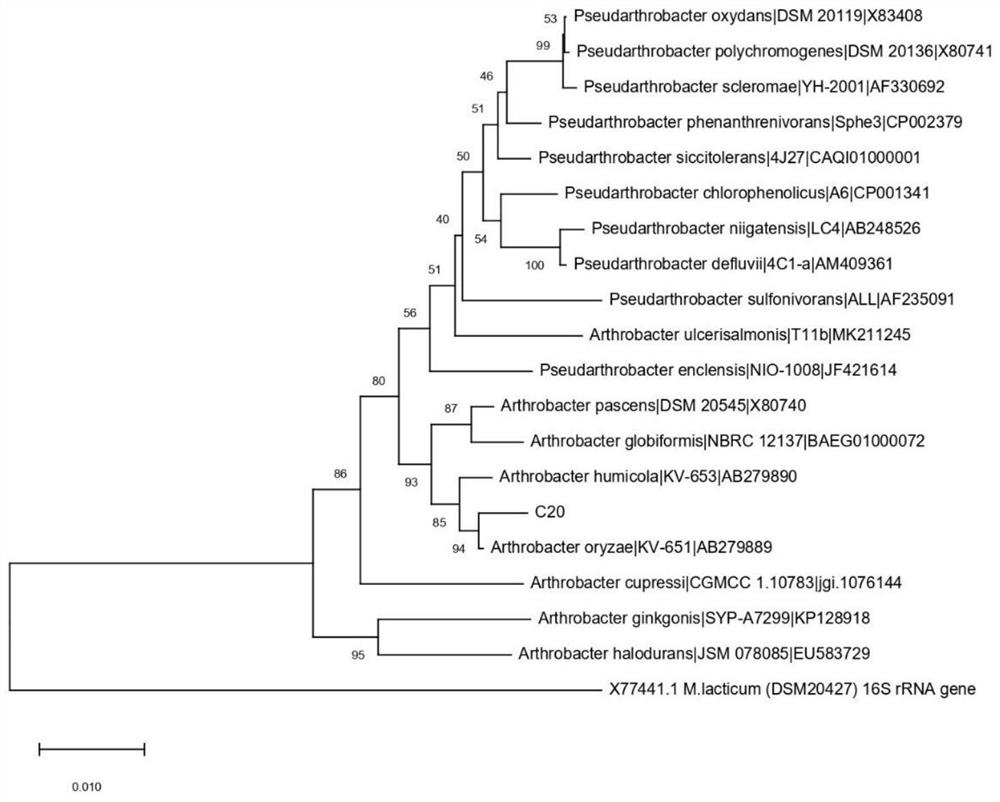
[0028] Screening, isolation and purification and identification of embodiment 1 bacterial strain C20
[0029] One, the screening method of a n-eicosane degrading bacterial strain C20
[0030] 1. Material preparation
[0031] Soil source for strain screening: Taken from the polluted soil of a coking plant in Huangshi City, Hubei Province, the soil samples were sealed with sampling bags, and brought back to the laboratory at 4°C for storage and later use.
[0032] LB medium: peptone 10.0g / L, yeast extract 5.0g / L, NaCl 10.0g / L, pH 7.0-7.2. Add 1.5% agar powder to the solid medium. Autoclave at 121°C for 20 minutes.
[0033] Mineral salt medium (MSM): KH 2 PO 4 338.8mg / L, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 234.0mg / L, Na 2 CO 3 100.0mg / L, CaCl 2 3.9mg / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 59.3mg / L, Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O 890.7mg / L, FeSO 4 0.3mg / L, 1.0mL / L, tryptone 500mg / L, trace element solution (FeCl 2 4H 2 O 1500.0mg / L, CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O190.0mg / L, MnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 100.0mg / L; ZnCl 2 70mg / L, NiCl 2...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2 Degradation of n-Eicosane by Bacterial Strain C20 in Inorganic Salt Liquid Medium Using n-Eicosane as the Only Carbon Source
[0048] 1. Degradation and recovery of n-eicosane
[0049] (1) After streaking the strain C20 on the LB plate, pick a single colony and inoculate it in the LB liquid medium, and culture it in a shaker at 30°C and 200rpm for 24h;
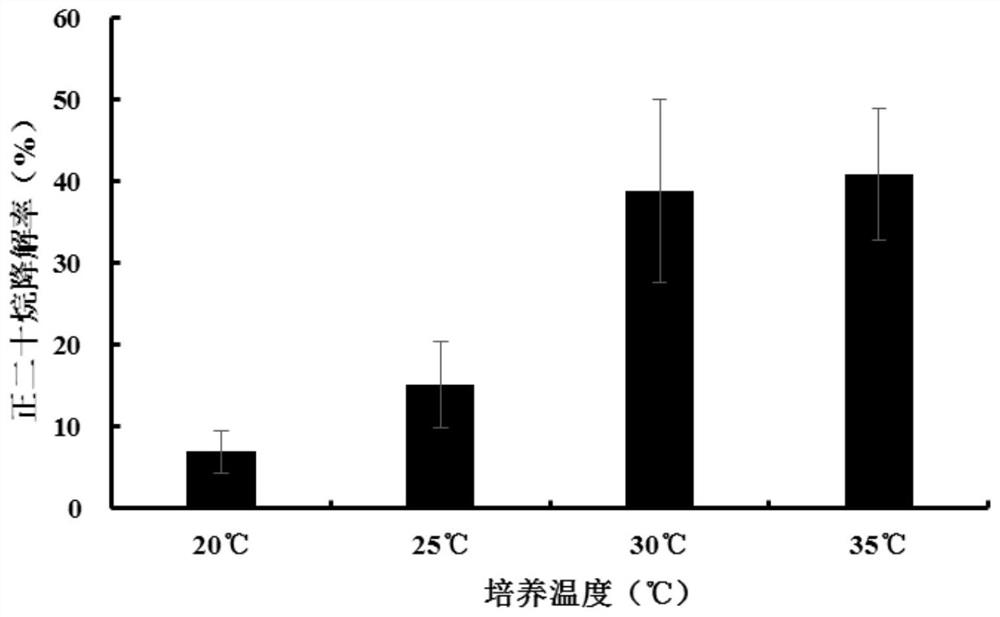
[0050] (2) Centrifuge the bacterial solution after 24 hours of cultivation, discard the culture medium, resuspend it with sterile water, centrifuge again, discard the supernatant and resuspend it with sterile water, repeat this process three times; The solution was adjusted to OD with sterile water 600 = 1.0, transferred to 50mL eicosane as the only carbon source of MSM liquid medium for 7 days, 200rpm shaking culture for 7 days; without adding bacterial strain C20 as a control; control single factor variables, explore environmental factors: temperature, initial bottom The most suitable environment for the d...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3 Application of strain C20 in the aerobic pool test device of the actual discharge of coking wastewater A / A / O treatment process containing n-eicosane
[0066] (1) After streaking the strain C20 on the LB plate, pick a single colony and inoculate it in the LB liquid medium, and culture it in a shaker at 30°C and 200rpm for 24h;
[0067](2) Centrifuge the bacterial solution after 24 hours of cultivation, discard the culture medium, resuspend with sterile water, centrifuge again, discard the supernatant and resuspend with sterile water, repeat this process three times; The solution was adjusted to OD with sterile water 600 = 1.0, transferred to the water body after the wastewater in the operating device was resuspended, and the method of stuffy exposure was used to make it grow and adapt. The effluent water sample 7 days before the addition of the bacteria was used as the control group, and the 7 days after the addition of the bacteria suffocated, the effluent wa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com