Gene editing system for constructing high-quality porcine nuclear transplantation donor cells with high fecundity and resistance to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome and series diarrhea diseases and application of gene editing system
A gene editing and gene technology, applied in the direction of receptor/cell surface antigen/cell surface determinant, plant gene improvement, genetically modified cells, etc., can solve the problems of receptor protein inactivation, pig infectivity reduction, etc., to achieve High fecundity, low cloning efficiency, low cloning and feeding costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Embodiment 1, the construction of plasmid
[0090] 1.1 Construction of plasmid pU6gRNA eEF1a-mNLS-hSpCas9-EGFP-PURO (plasmid pKG-GE3 for short)
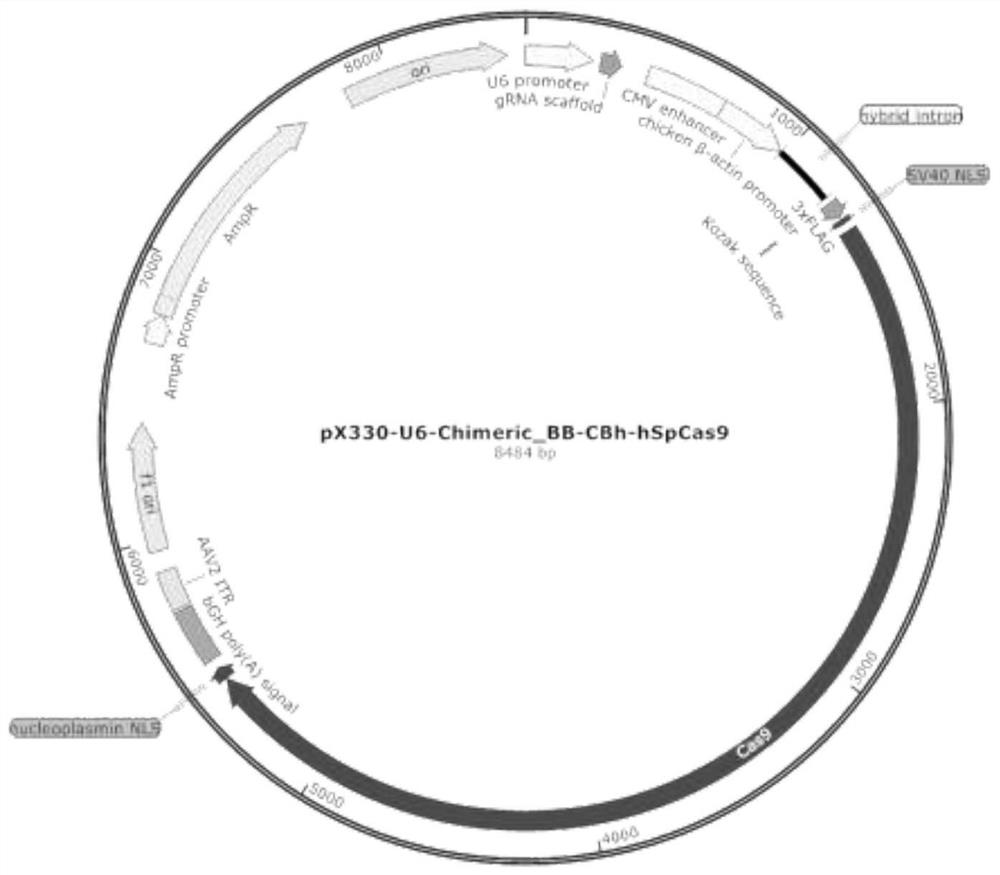
[0091] The sequence of the original plasmid pX330-U6-Chimeric_BB-CBh-hSpCas9 (abbreviated as plasmid pX330) is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The schematic diagram of the structure of plasmid pX330 is shown in figure 1 . In SEQ ID NO.1, the 440-725 nucleotides form the CMV enhancer, the 727-1208 nucleotides form the chicken β-actin promoter, and the 1304-1324 nucleotides encode the SV40 nuclear localization signal ( NLS), the 1325-5449th nucleotide encodes the Cas9 protein, and the 5450-5497th nucleotide encodes the nucleoplasmin nuclear localization signal (NLS).
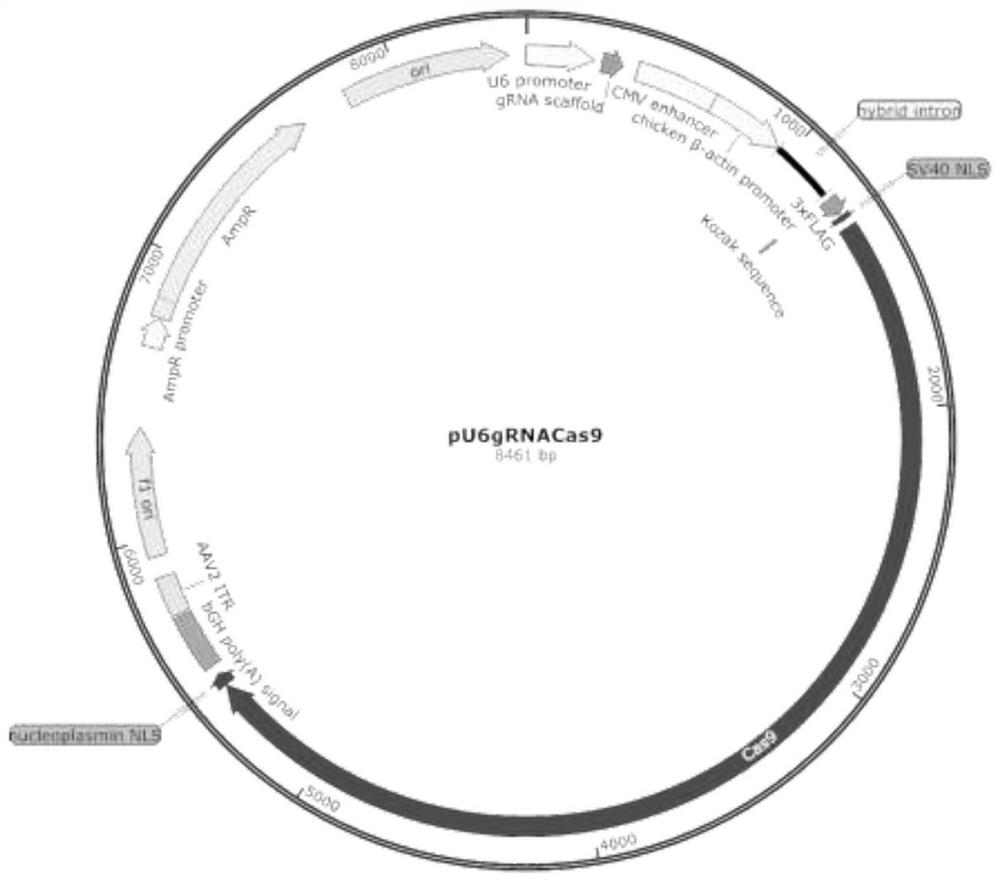
[0092] Plasmid pU6gRNA eEF1a-mNLS-hSpCas9-EGFP-PURO ( Figure 5 ), referred to as plasmid pKG-GE3, the nucleotide is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Compared with the plasmid pX330, the plasmid pKG-GE3 has been mainly modified as follows: ① Remove the residual gRNA backbone sequ...
Embodiment 2
[0105] Example 2 Plasmid Proportion Optimization and Effect Comparison of Plasmid pX330 and Plasmid pKG-GE3
[0106] 2.1 Target gRNA design and construction
[0107] 2.1.1 Using Benchling to design target gRNA for RAG1 gene
[0108] RAG1-g4: AGTTATGGCAGAACTCAGTG (SEQ ID NO. 9)
[0109] Synthesize complementary DNA Oligo for the insertion sequence of the above-mentioned RAG1 gene target as follows:
[0110] RAG1-gRNA4S: caccgAGTTATGGCAGAACTCAGTG (SEQ ID NO.10)
[0111] RAG1-gRNA4A: aaacCACTGAGTTCTGCCATAACTc (SEQ ID NO.11)
[0112] Both RAG1-gRNA4S and RAG1-gRNA4A are single-stranded DNA molecules.
[0113] 2.1.2 Primers designed to amplify and detect fragments containing the RAG1 gRNA target
[0114] RAG1-nF126: CCCCATCCAAAGTTTTTAAAGGA
[0115] RAG1-nR525: TGTGGCAGATGTCACAGTTTAGG
[0116] 2.1.3 Construction and cloning of gRNA recombinant vector
[0117] 1) Digest 1ug pKG-U6gRNA plasmid with restriction endonuclease BbsI;
[0118] 2) run the digested pKG-U6gRNA plasmid...
Embodiment 3
[0165] Example 3 Screening of efficient INHA gene gRNA targets
[0166]Pig INHA gene information: encodes inhibin subunit alpha protein; located on pig chromosome 5; GeneID is 397386, Sus scrofa. The protein encoded by the pig INHA gene is shown in GENBANK ACCESSION NO.XP_020930352.1 (linear CON 12-JAN-2018), and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.13. In the genomic DNA, the porcine INHA gene has two exons, wherein the second exon and its upstream and downstream sequences of 100 bp are shown in SEQ ID NO.14.
[0167] 3.1 INHA gene knockout predetermined target and conservation analysis of adjacent genome sequences
[0168] 18 newborn Congjiang pigs, including 10 females (named 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10) and 8 males (named A, B, C, D , E, F, G, H).
[0169] Using the genomic DNA of 18 pigs as a template, PCR amplification was performed using primer pairs (the target sequence of the primer pair includes exon 2 of the pig INHA gene), and then electrophoresis was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com