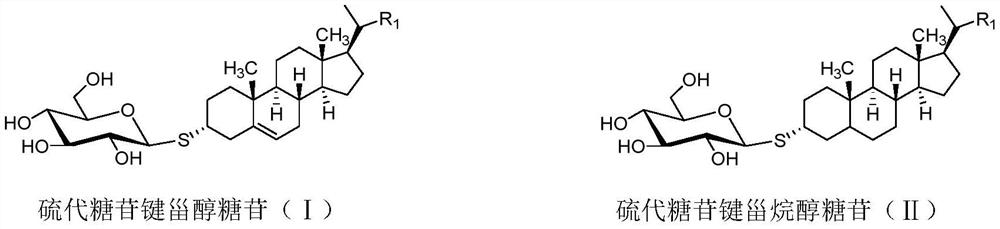Thioglycosidic bond sterol glucoside and thioglycosidic bond stanol glucoside as well as preparation method and application of thioglycosidic bond sterol glucoside and thioglycosidic bond stanol glucoside
A technology of thioglycosidic bond stanol glycosides and thioglycosidic bond sterol glycosides is applied in the directions of metabolic diseases, steroids, antitoxic agents, etc., and can solve the problems of lack of access means, short drug half-life, and uneven structure, etc. Achieving the effect of simplifying experimental protocols, achieving productivity, and increasing flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
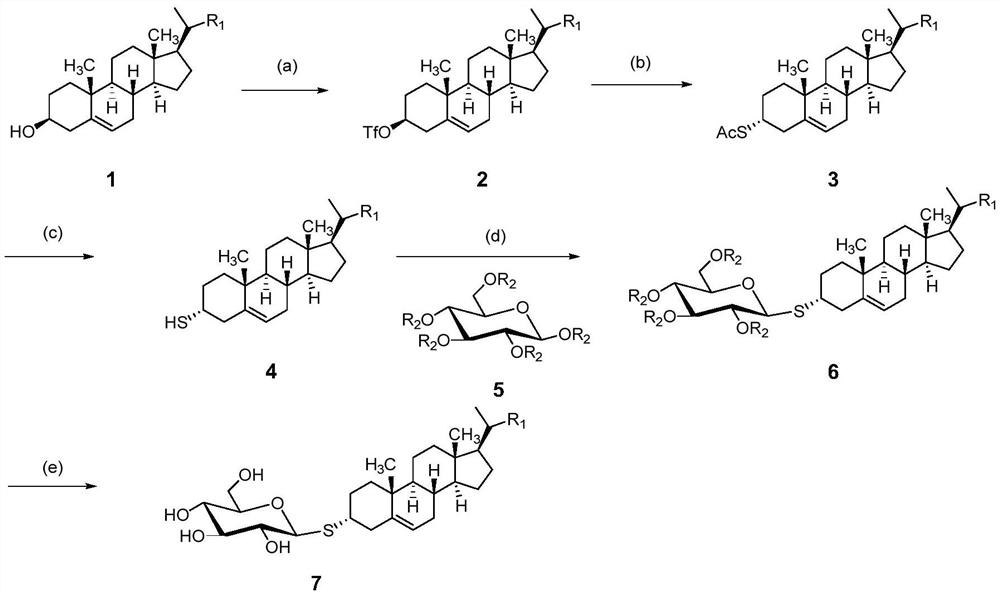
[0046] Using brassicasterol (compound 1) as the raw material and fully acetyl-protected glucose (compound 5) as the glycosyl donor
[0047] Synthesis of compound 2
[0048] Natural sterol crude compound 1 (brassicasterol, 0.7g, 1.68mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous DCM (10mL) and anhydrous pyridine (0.24mL) pre-cooled to 0°C, and then trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride ( 1.422g (2.8mmol) of anhydrous DCM (3.5mL) solution was slowly added dropwise to the solution of the above compound 1, the time for the addition was more than 30 minutes, and when adding DCM, it was necessary to ensure that the system was at 0°C, and the reaction was completed after the addition The system needs to continue to react at 0°C for 1 hour. After the reaction, wash with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution (50 mL), wash with magnesium sulfate (MgSO 4 ), filtered and concentrated by evaporation to obtain compound 2 (0.752g, 83%) substituted by trifluoromethanesulfonyl at the C-3 position, 1H NMR (30...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Using campestanol (compound 1) as raw material, perbenzoyl-protected glucose (compound 5) as glycosyl donor
[0059] Synthesis of compound 2
[0060] Crude natural stanol Compound 1 (0.7 g, 1.68 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous DCM (10 mL) and anhydrous pyridine (0.24 mL) pre-cooled to 0 °C, followed by trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride (1.422 g 2.8 mmol) of anhydrous DCM (3.5mL) solution was slowly added dropwise to the solution of Compound 1, the time for the addition was more than 30min, and when DCM was added, it was necessary to ensure that the system was at 0°C. After the addition, the reaction system needed to be at 0 The reaction was continued for 1 hour at °C. After the reaction, wash with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution (50mL), wash with magnesium sulfate (MgSO 4 ) was dried, filtered and concentrated by evaporation to obtain compound 2 (0.730g, 81%) substituted by trifluoromethanesulfonyl at the C-3 position, 1H NMR (300MHz, DMSO) δ1.24 (m, 3H), 1.90...
Embodiment 3
[0070] The preparation method of embodiment 3 is the same as that of embodiment 1, and the difference is that compound 1 is campesterol, and the consumption of trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride in step (1) is 1 times of the molar number of compound 1; Reaction is at -10 ℃ Carry out; the consumption of potassium thioacetate in step (2) is 1 times of compound 2 moles; Reaction is carried out at-20 ℃; Reaction solvent used in step (3) is ethyl acetate; Reagent used is potassium hydroxide , the basic reagent consumption is 5 times of compound 3 moles; Reaction solvent used in step (4) is toluene, and used Lewis acid catalyst is trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, and the consumption of Lewis acid catalyst is 0.5 times of compound 3 moles; The inert protective gas is helium; in the step (5), the compound 6 is hydrolyzed and deprotected with a base, the base is potassium hydroxide (KOH), the reaction solvent used is ether, and the amount of the alkaline reagent is 0.5 times the mole numb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com