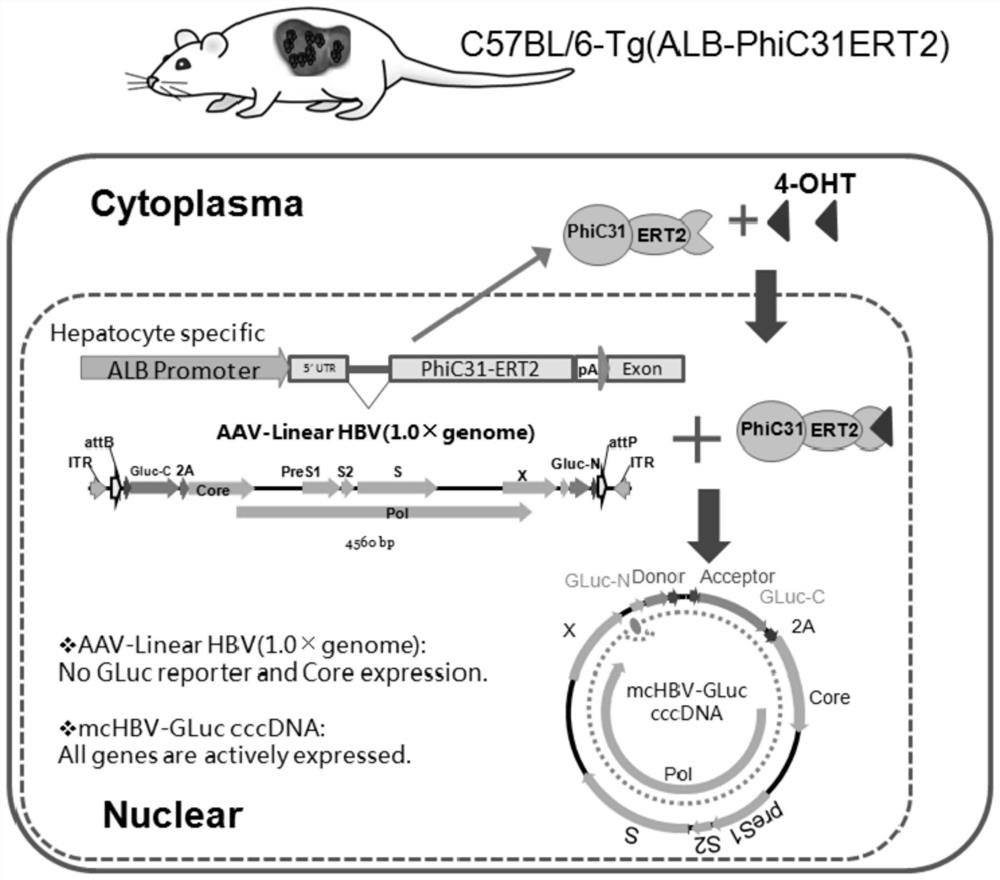
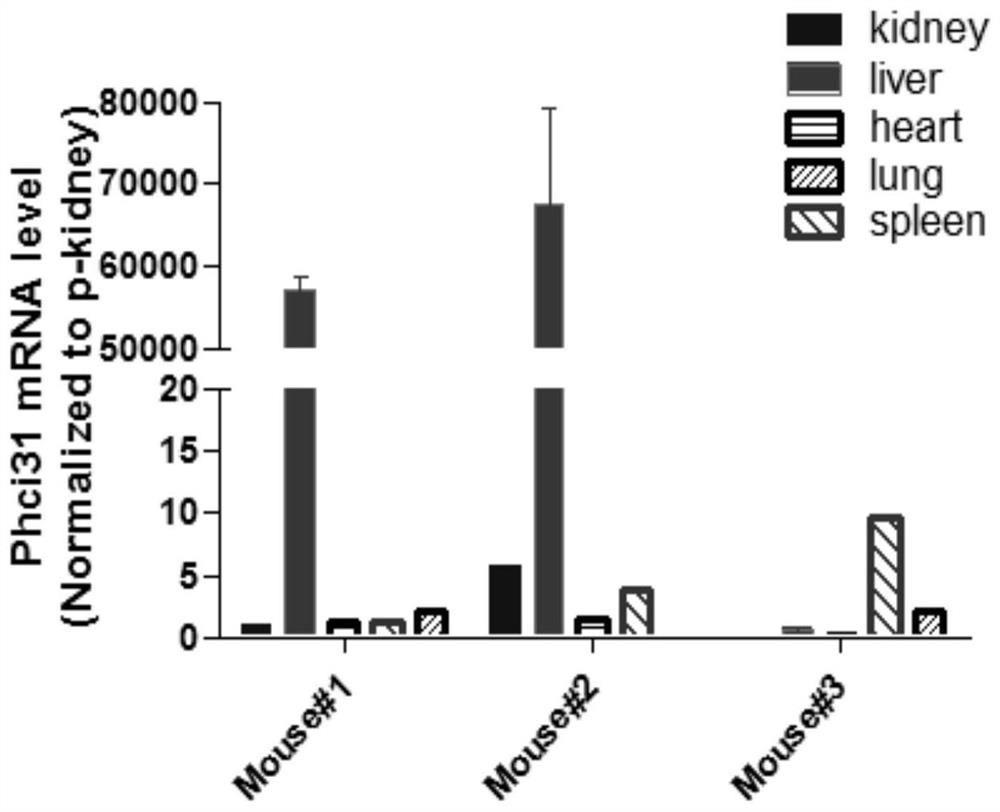
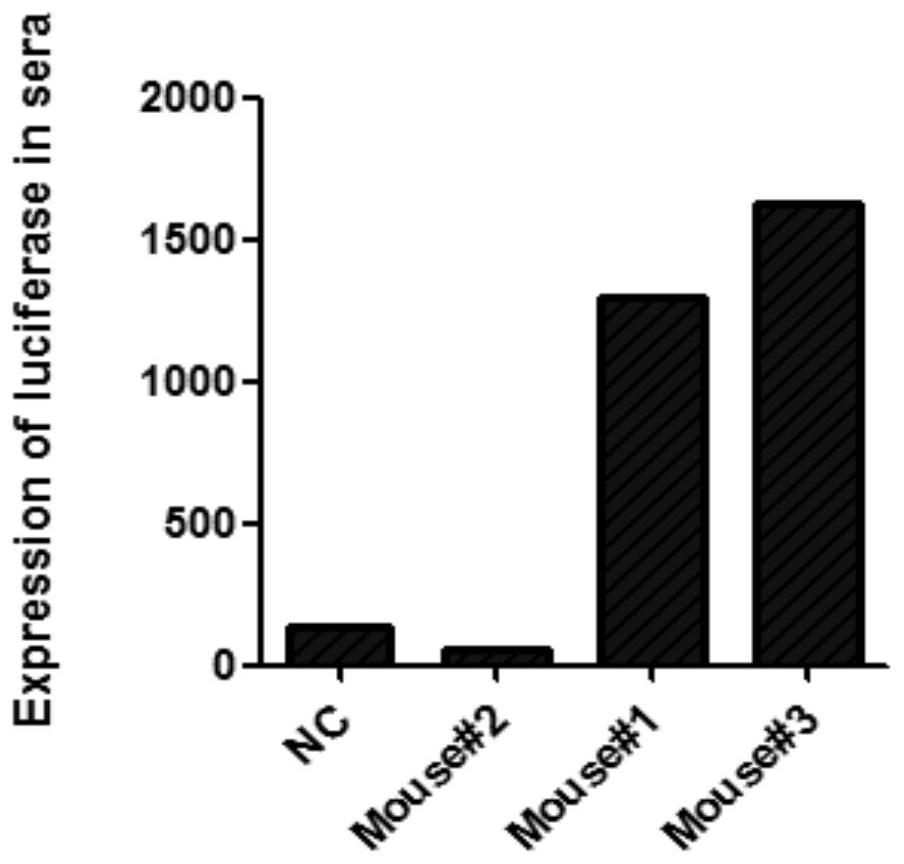
Construction method for hepatitis B virus (HBV) non-human animal model and application of HBV non-human animal model
A non-human animal and construction method technology, applied in the fields of botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, applications, etc., can solve the problems of no cccDNA, can not reflect the biological characteristics of cccDNA, can not simulate the life cycle of HBV, etc., to achieve easily detectable effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0061] 1. Obtaining Genomic DNA from Patient Samples
[0062] 1. Use the nucleic acid extraction or purification kit (Da'an Gene, Sun Yat-Sen University) to extract the hepatitis B virus DNA from the patient sample. The operation is as follows:
[0063] 1) Take 200ul sample and add it to a centrifuge tube, add 50ul proteinase K
[0064] 2) Add 200ul lysate, vortex for 15sec, centrifuge for 10sec, 72°C for 10min
[0065] 3) Add 250ul absolute ethanol, vortex for 15 seconds
[0066] 4) Aspirate the mixture to the spin column, centrifuge at 12,000g for 1min at room temperature, transfer the spin column to a new collection tube
[0067] 5) Add 500ul inhibitor removal solution to the spin column, centrifuge at 12,000g for 1min at room temperature, and transfer the spin column to a new collection tube
[0068] 6) Add 500ul deionized solution to the spin column, centrifuge at 12,000g for 1min at room temperature, and transfer the spin column to a new collection tube
[0069] 7) R...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com