Genetically engineered bacterium for producing ferulic acid and biosynthesis method of ferulic acid
A genetically engineered bacteria and biosynthesis technology, applied in the field of biological applications, can solve the problem of high production cost, and achieve the effects of low cost, simple and clean process, and short process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] The construction of embodiment 1 genetically engineered bacteria
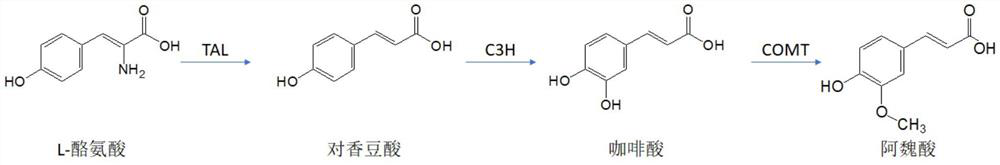
[0060] Referring to the biosynthetic pathway of ferulic acid in plants, and according to the protein sequence reported in NCBI, the codon optimization of the gene sequence was carried out to adapt it to the E. coli expression system. Artificially synthesized gene fragments of tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL), S-adenosylmethionine synthetase 5 (Sam5), and caffeic acid-3-O-methyltransferase (COMT) were sequentially ligated into pBR322 or pET21d vector, and transformed into JM109, BL21(DE3) or Rosetta competent cells, and positive clones were screened. The recombinant strains screened out were subjected to enzyme digestion verification, and sequenced to confirm that the sequence was correct, and the expected production strain was obtained. Specifically, the following methods are used:
[0061] According to the protein sequences of TAL, Sam5 and COMT, the codons were optimized, and three genes were artificiall...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2 Shake flask conversion produces ferulic acid
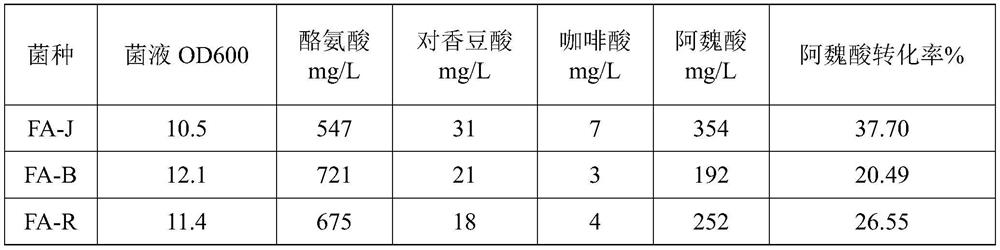
[0064] After thawing the strains prepared by the method of Example 1 stored at -80°C, they were streaked on LB agar plates and cultured overnight at 37°C. Pick a single clone, inoculate in 20mL LB broth medium containing antibiotics, and culture in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask at 37°C and 200rpm for 12h to obtain seed liquid. Take another 5 mL and inoculate in 100 mL M9 medium (ammonium chloride 1 g / L, disodium hydrogen phosphate 6 g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 3 g / L, yeast extract 0.5 g / L, magnesium sulfate 2 mM, calcium chloride 0.1 mM , glycerol 20g / L, L-tyrosine 1g / L, L-methionine 1g / L, IPTG 0.1mM, antibiotic 100mg / L), 25 ℃ 200rpm cultivated for 3 days, obtained the fermented liquid containing ferulic acid.
[0065] The conversion rate was determined as follows:
[0066] Extract 5-10 mL of fermentation broth with an equal volume of ethyl acetate three times, combine the extracts, concentrate and dry, th...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3 fermentation tank produces ferulic acid
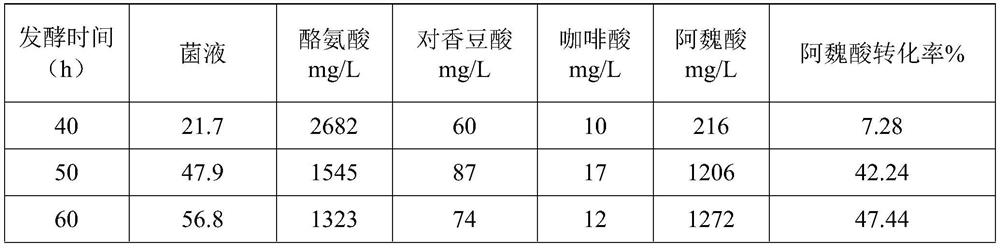
[0071] After the FA-J strains prepared by the method in Example 1 were thawed, they were streaked on an agar plate and cultured overnight at 37°C. Single clones were picked, inoculated in 150 mL LB broth medium, and cultured at 37°C for 10 h. Then inoculated in 3L TB medium (24g / L yeast extract, 12g / L peptone, 2.31g / L sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 17.4g / L disodium hydrogen phosphate, 20g / L glucose, 3g L-tyrosine / L, L-methionine 3g / L, IPTG 0.1mM, antibiotic 100mg / L, feeding 400g / L glucose) in a 5L fermenter, cultivated at 28°C, pH control 7.0, ventilation 3L / min, controlled dissolved oxygen It is not lower than 30%, the tank pressure is not more than 0.07MPa, the dissolved oxygen is controlled by the rotating speed and feeding speed, and the tank is put into the tank after culturing for 60 hours to obtain a ferulic acid-containing fermented liquid. The conversion results are shown in Table 2.
[0072] Table 2
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com