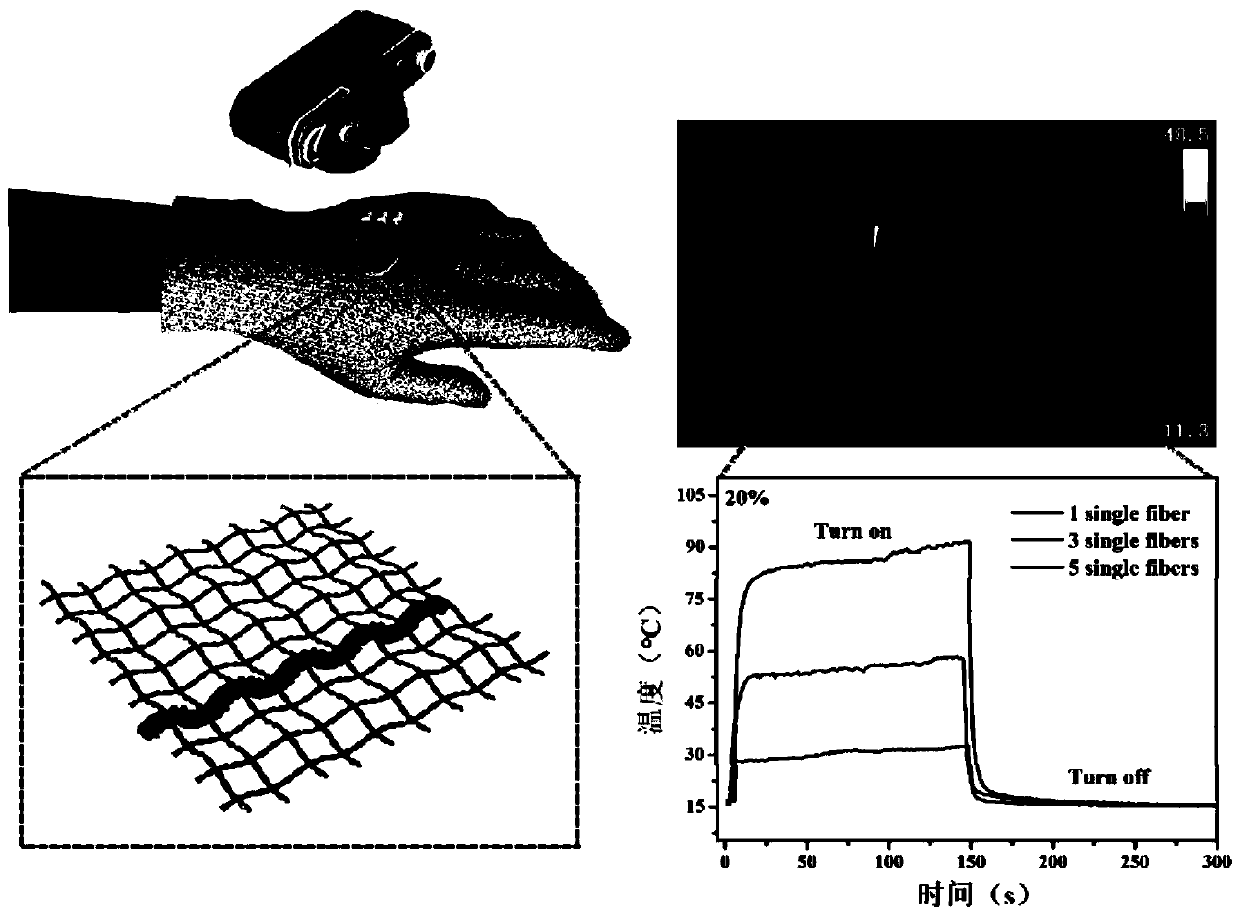
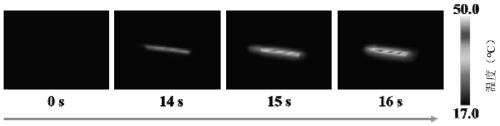
Electric heating wire based on cellulose-dopamine/carbon nanotube conductive fibers and application of electric heating wire
A technology of carbon nanotubes and conductive fibers, which is applied in the field of flexible polymer conductive materials, can solve the problems affecting the commercialization process of CNTs and the difficulty of uniform dispersion, and achieve the effects of strong implementability, fast heating speed, and abundant raw material sources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] (1) Preparation of dopamine-modified cellulose aqueous solution
[0039] Weigh 100 g of carboxymethyl cellulose sodium salt (molecular weight 700 kDa, degree of substitution 0.9), and prepare 0.5 wt % carboxymethyl cellulose aqueous solution. Add 0.96g of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride into the above aqueous solution and stir mechanically for 1h, use 0.1mol L -1 Dilute hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value of the solution to 4.5-5, continue to add 0.58g N-hydroxysuccinimide and 0.95g dopamine hydrochloride, in N 2 Under ambient conditions, mechanically stir for 24 hours at a speed of 1000 rad min -1 . Using a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3kDa, dialyze at room temperature for 5 days, and replace distilled water every 12 hours. Subsequently, a 2wt% DACMC light yellow transparent solution was obtained by suction filtration, and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C.
[0040] (2) Preparation of cellulose-dopamine / carbon nanot...
Embodiment 2
[0049] (1) Preparation of dopamine-modified cellulose aqueous solution
[0050] Weigh 100 g of carboxymethyl cellulose sodium salt (molecular weight 700 kDa, degree of substitution 0.9), and prepare 0.5 wt % carboxymethyl cellulose aqueous solution. Add 0.96g of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride into the above aqueous solution and stir mechanically for 1h, use 0.1mol L -1 Dilute hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value of the solution to 4.5-5, continue to add 0.58g N-hydroxysuccinimide and 0.95g dopamine hydrochloride, in N 2 Under ambient conditions, mechanically stir for 24 hours at a speed of 1000 rad min -1 . Using a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3kDa, dialyze at room temperature for 5 days, and replace distilled water every 12 hours. Subsequently, a 2wt% DACMC light yellow transparent solution was obtained by suction filtration, and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C.
[0051] (2) Preparation of cellulose-dopamine / carbon nanot...
Embodiment 3
[0057] (1) Preparation of dopamine-modified cellulose aqueous solution
[0058] Weigh 100 g of carboxymethyl cellulose sodium salt (molecular weight 700 kDa, degree of substitution 0.9), and prepare 0.5 wt % carboxymethyl cellulose aqueous solution. Add 0.96g of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride into the above aqueous solution and stir mechanically for 1h, use 0.1mol L -1 Dilute hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value of the solution to 4.5-5, continue to add 0.58g N-hydroxysuccinimide and 0.95g dopamine hydrochloride, in N 2 Under ambient conditions, mechanically stir for 24 hours at a speed of 1000 rad min -1 . Using a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3kDa, dialyze at room temperature for 5 days, and replace distilled water every 12 hours. Subsequently, a 2wt% DACMC light yellow transparent solution was obtained by suction filtration, and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C.
[0059] (2) Preparation of cellulose-dopamine / carbon nanot...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com