Method for removing organic matters through cooperation of electrochemistry and hydrogen peroxide
A hydrogen peroxide and organic matter technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption of oxidants, large amounts of iron sludge, etc., and achieve short reaction time and high utilization rate , the effect of saving energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
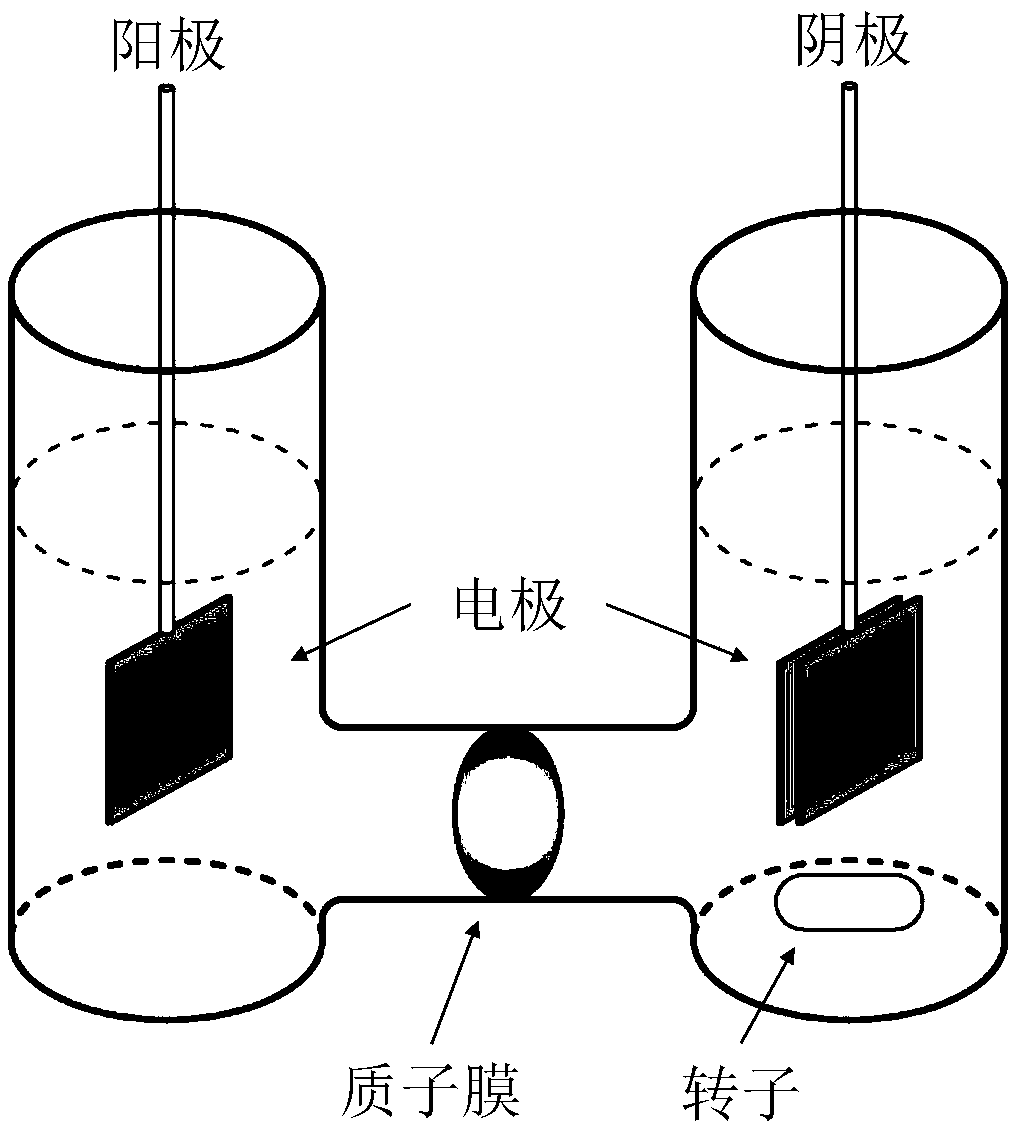
[0059] In this example the cathode / H 2 o 2 / Fe 3+ The effect of the system on the removal of phenol in aqueous solution. The results showed that during the reaction, phenol was polymerized in the cathode chamber and a black solid precipitate was formed. After reacting for 20 minutes, the cathode reaction liquid was separated from solid and liquid, and the removal rate of phenol reached 84%, and the removal rate of COD reached 30%. figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of the reactor in Example 1.
[0060] Operating conditions:
[0061] Anode: a 2cm×2cm platinum plate electrode
[0062] Cathode: two 2cm×2cm platinum plate electrodes connected in parallel
[0063] Phenol solution concentration: 4mmol / L
[0064] Phenol solution volume: 100mL
[0065] Sulfate concentration: 50mmol / L sodium sulfate
[0066] Catholyte volume: 100mL
[0067] h 2 o 2 Concentration: 10mmol / L
[0068] Fe 3+ Concentration: 1mmol / L
[0069] h 2 o 2 with Fe 3+ The molar ratio: 10:1 ...
Embodiment 2
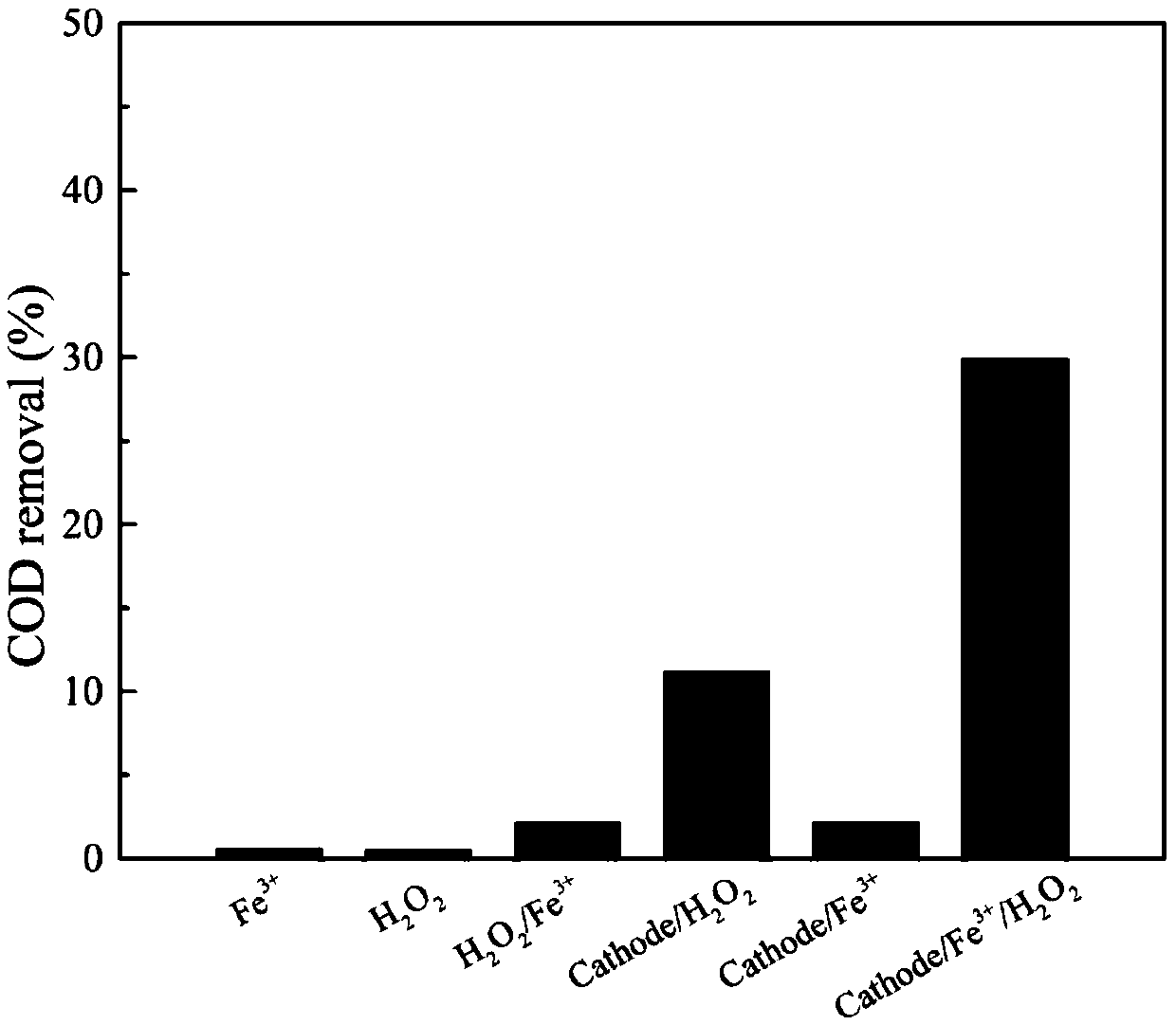
[0075] In this example, the removal effect of several different systems on phenol in aqueous solution was compared, including (1) Fe 3+ Acting alone, (2)H 2 o 2 Acting alone, (3)H 2 o 2 / Fe 3+ system, (4) cathode / H 2 o 2 system, (5) cathode / Fe 3+ system. Among them, the concentration of the phenol solution is 4mmol / L, and the amount and reaction conditions of the corresponding dosing substances in each system are consistent with those in Example 1. After the cathode reaction liquid is separated from solid and liquid, its COD removal rate is respectively 0.6%, 0.5%, 2.2%, 11%, 2.2%, which is far lower than the COD removal rate in Example 1, indicating that the cathode, H 2 o 2 , Fe 3+ The combined action of the three can generate obvious organic solid polymers and significantly improve the COD removal efficiency.
[0076] image 3 It is the comparison figure of the COD removal rate in the phenol aqueous solution and the COD removal rate in the embodiment 1 of differ...
Embodiment 3
[0078] In this example, different Fe 3+ The effect of concentration on the removal efficiency of phenol in aqueous solution, Fe 3+ The dosages are respectively 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5mmol / L, and all the other reaction conditions are consistent with those in Example 1. The results show that with the Fe in the system 3+ As the concentration increases, the side reactions in the system gradually increase, resulting in differences in the degree of polymerization of phenol; when Fe 3+ When the concentration was 1mmol / L, an obvious black solid precipitate was formed. After 20 minutes of reaction, the solution in the cathodic chamber was separated into solid and liquid, and the removal rate of phenol reached 84%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com