Preparation method of cu-ag/la@hap catalyst and its catalytic oxidation of 1,2-propanediol to prepare lactic acid
A catalyst, propylene glycol technology, applied in the field of catalysis, can solve the problem of 1,2-propanediol market surplus and achieve high application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Preparation of metal lanthanum-doped HAP support La@HAP: 10mL Ca(NO 3 ) 2 (1mol / L), 10mL H 3 PO 4 (0.6mol / L) and 2mL La(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O (1mol / L) aqueous solution was added in the there-necked flask, after adding dropwise 25% ammoniacal liquor to adjust the pH of the solution to 10, reacted for 8 hours under stirring conditions, then transferred the gained solution to a polytetrafluoroethylene autoclave, The reaction was continued for 8 hours at 100°C. After the reaction, the obtained powder was washed and filtered several times with deionized water, and then dried in an oven at 100°C for 12 hours to obtain the La@HAP carrier.
[0028] (2) Preparation of Cu-Ag bimetallic nanoparticle colloid: 0.07g Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 O, 0.05g AgNO 3 Dissolve in 13mL of 1% polyvinyl alcohol solution, then add 30mL of 0.1mol / L NaBH 4 aqueous solution. After aging for 30 minutes at room temperature, the Cu-Ag bimetal nanoparticle colloid can be obtained.
[0029] (3) Prepar...
Embodiment 2
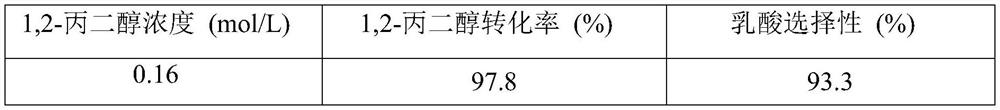
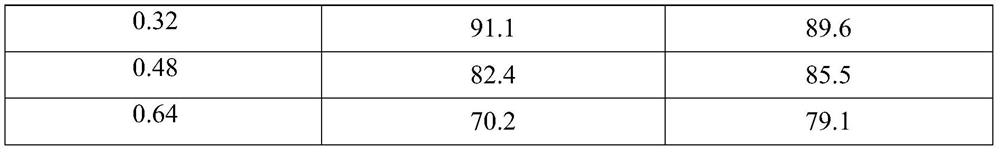
[0033]Steps (1) to (3) are the same as in Example 1, and step (4) only changes the concentration of 1,2-propanediol in Example 1 to 0.16mol / L, 0.48mol / L, and 0.64mol / L, and the resulting 1,2- The results of propylene glycol conversion and lactic acid selectivity are shown in Table 1. The results showed that with the increase of the concentration of 1,2-propanediol, the conversion rate decreased gradually, and the selectivity of lactic acid also decreased gradually.
[0034] The impact of different 1,2-propanediol concentrations on the conversion rate of the final raw material and the selectivity of the reaction product in table 1
[0035]
[0036]
Embodiment 3
[0038] Steps (1) to (3) are the same as in Example 1, and step (4) only changes the concentration of sodium hydroxide used in Example 1 to be 0.16mol / L, 0.32mol / L, and 0.64mol / L respectively. The obtained 1,2-propanediol conversion rate and lactic acid selectivity results are shown in Table 2. Result shows, along with the increase of sodium hydroxide concentration, 1,2-propanediol conversion rate increases gradually, is 0.48mol / L in sodium hydroxide concentration, and promptly sodium hydroxide concentration and 1,2-propanediol concentration ratio are 1.5: At 1, the conversion rate of 1,2-propanediol reached 91.1%, while the selectivity of lactic acid reached the highest 89.6%.
[0039] The impact of the different sodium hydroxide concentrations of table 2 on the conversion rate of final raw material and the selectivity of reaction product
[0040] Sodium hydroxide concentration (mol / L) 1,2-propanediol conversion rate (%) Lactic acid selectivity (%) 0.16 81.5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com