Catalytic cracking catalyst, preparation method and applications thereof
A catalytic cracking and catalyst technology, used in catalyst activation/preparation, physical/chemical process catalysts, molecular sieve catalysts, etc., can solve the problem that ultra-stable molecular sieves cannot meet the requirements of processing hydrogenation LCO catalytic cracking catalysts, and zeolite crystal retention is low. , poor selectivity, etc., to achieve good catalytic cracking catalytic performance, high LCO conversion efficiency, and less non-framework aluminum content.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
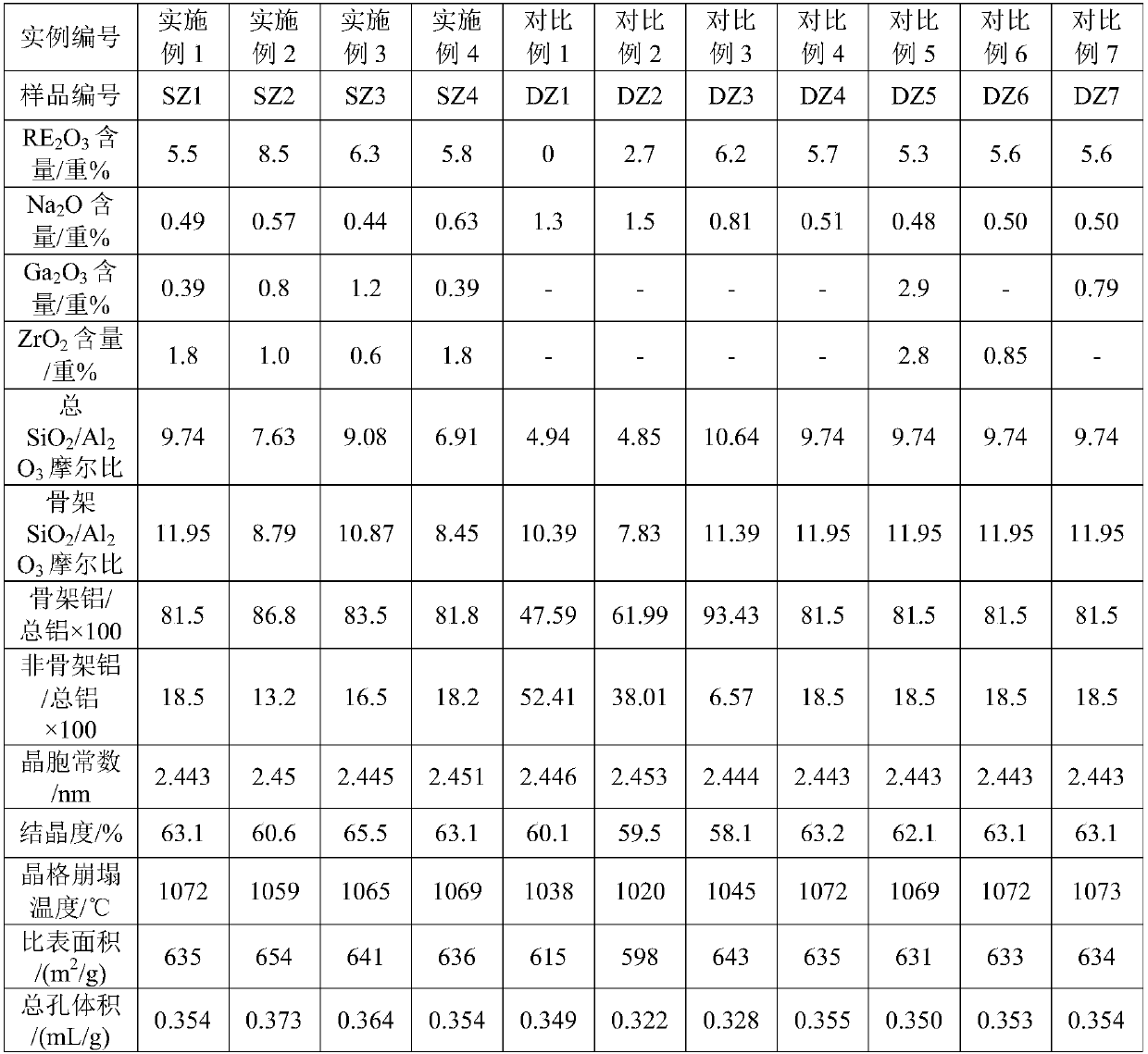
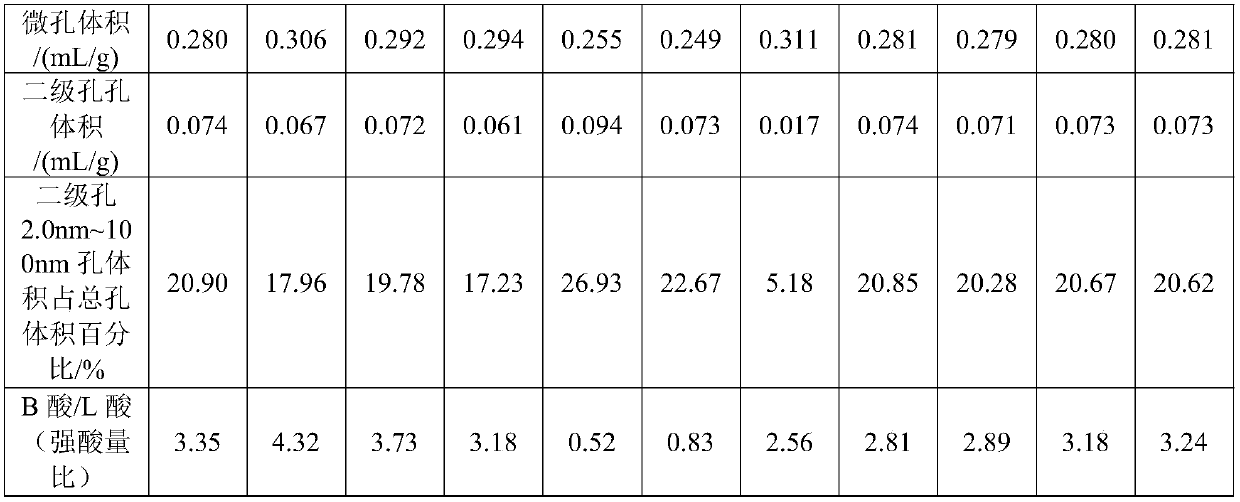
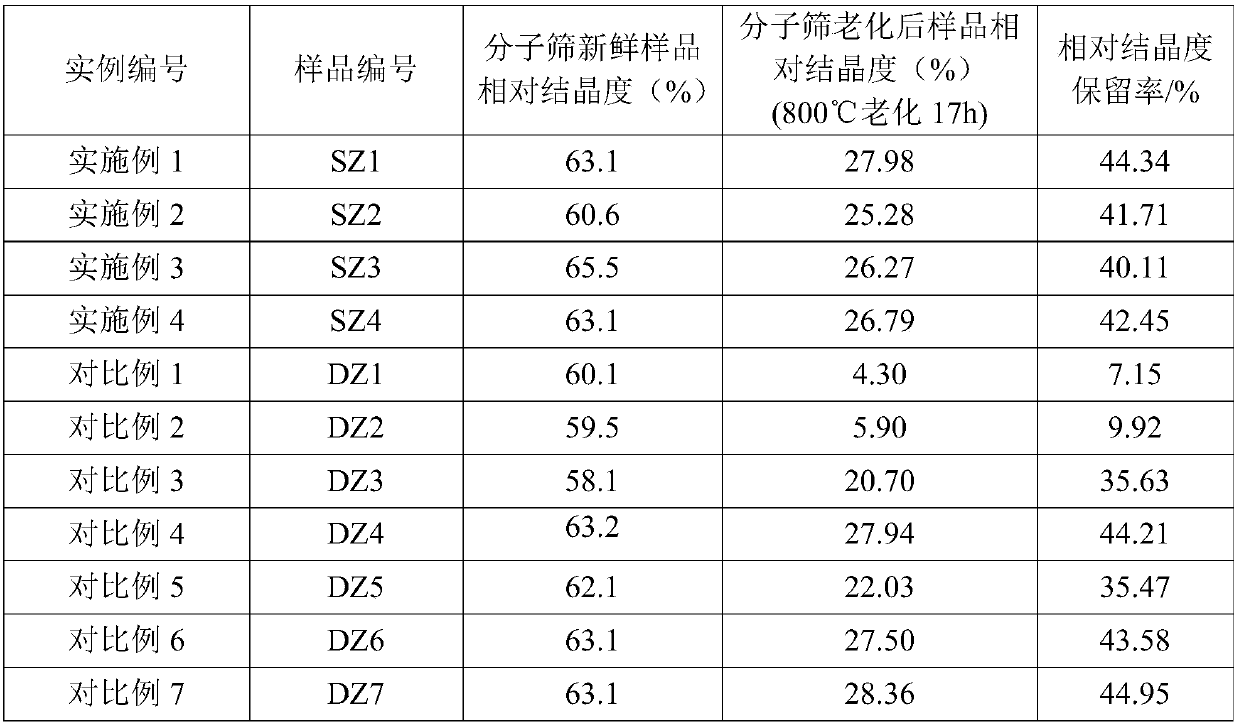
[0067] The preparation method of the catalyst described in the present disclosure can refer to existing methods, for example, according to the methods disclosed in patents CN1098130A and CN1362472A. Typically comprising the steps of forming a slurry comprising modified Y molecular sieve, binder, clay and water, spray drying, optionally washing and drying. Spray drying, washing, and drying are prior art, and there is no special requirement in this disclosure.
[0068] The second aspect of the present disclosure provides a method for preparing the catalytic cracking catalyst described in the first aspect of the present disclosure. The method includes: preparing a modified Y-type molecular sieve, forming a modified Y-type molecular sieve comprising the modified Y-type molecular sieve, alumina binder, clay and water slurry, and spray drying to obtain the catalytic cracking catalyst;
[0069] Wherein, the preparation of modified Y-type molecular sieve comprises the following steps...
Embodiment 1
[0106] Take 2000g NaY molecular sieve (calculated on a dry basis) and add it to 20L decationized aqueous solution and stir to make it evenly mixed, add 600mL of RE(NO 3 ) 3 Solution (rare earth solution concentration is RE 2 o 3 Calculated as 319g / L), stirred, heated up to 90-95°C and kept for 1h, then filtered, washed, and the filter cake was dried at 120°C to obtain a unit cell constant of 2.471nm and a sodium oxide content of 7.0% by weight. 2 o 3 A Y-type molecular sieve with a total rare earth content of 8.8% by weight; then bake it for 6 hours at a temperature of 390°C in an atmosphere containing 50% by volume of water vapor and 50% by volume of air to obtain a Y-type molecular sieve with a unit cell constant of 2.455nm, and then dry it Treated so that its water content is less than 1% by weight; then according to SiCl 4 : Y-type molecular sieve (dry basis) = 0.5: 1 weight ratio, feed SiCl vaporized by heating 4 Gas, at a temperature of 400°C, react for 2 hours, aft...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Take 2000g NaY molecular sieve (on a dry basis) and add it to 25L decationized aqueous solution and stir to make it evenly mixed, add 800mL of RECl 3 solution (in RE 2 o 3 The calculated solution concentration is: 319g / L), stirred, heated up to 90-95°C and maintained for 1h, then filtered and washed, and the filter cake was dried at 120°C to obtain a unit cell constant of 2.471nm and a sodium oxide content of 5.5% by weight. with RE 2 o 3 A Y-type molecular sieve with a total rare earth content of 11.3% by weight is then calcined at a temperature of 450° C. under 80 volume percent water vapor for 5.5 hours to obtain a Y-type molecular sieve with a unit cell constant of 2.461 nm. Afterwards, it is dried to make its water content Below 1 wt%, then follow SiCl 4 : Y-type zeolite = 0.6:1 weight ratio, feed SiCl vaporized by heating 4 Gas, at a temperature of 480°C, react for 1.5h, after that, wash with 20L decationized water, then filter, and then add the filter cake t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cell constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Cell constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com