A method of joint treatment of black and odorous water by using indigenous microbial film and microalgae
A microbial membrane and combined treatment technology, applied in biological water/sewage treatment, filtration treatment, sedimentation treatment, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in maintaining stable water quality, low treatment efficiency, and power consumption in operation, and achieve manpower saving and strong treatment capacity , The effect of improving the removal rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] A method for jointly treating black and odorous water using indigenous microbial film and microalgae, comprising the following steps:
[0024] 1) Collect black and odorous water, use potassium dichromate method to test the COD content in the black and odorous water is 210mg / L; The content of TP in the black and odorous water is 5.8 mg / L by ammonium acid spectrophotometry; the NH in the black and odorous water is tested by Nessler's reagent spectrophotometry 3 -N content is 143.2mg / L;
[0025] 2) Put the black and odorous water after the test in step 1) into the adjustment tank 1 for precipitation, and then pump it into the contact oxidation tank 3 with sediment through the inlet pump 2, and carry out biological oxidation in the biological contact oxidation tank 3. Co-cultivation of indigenous microbial film pretreatment by contact oxidation method. In the pretreatment process of co-cultivation of indigenous microbial film by biological contact oxidation method, rice wa...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: except following difference, other is the same as embodiment 1.
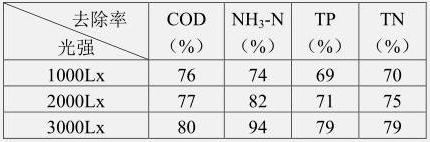
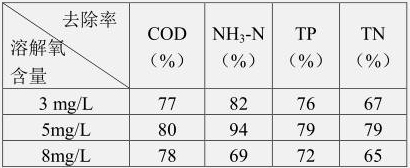
[0033] Haematococcus pluvialis was inoculated in the solution in the photobioreactor, and the inoculated amount of Haematococcus pluvialls was 125,000 cells / mL. The dissolved oxygen concentration of the solution in the gas-controlled photobioreactor was 3mg / L, 5mg / L, 8mg / L, and the light intensity of the LED lamp was 3000Lx. Analyze the effect of UV-induced Haematococcus pluvialis on TN, TP under different dissolved oxygen concentrations. removal rate.
[0034] It has been tested that under the condition of light intensity of 3000Lx and inoculation volume of 125,000 cells / mL, high dissolved oxygen concentration promotes the growth of aerobic microorganisms in water. A large number of aerobic bacteria carry out aerobic respiration and use molecular oxygen as the electron acceptor in the biological oxidation process. Therefore, the growth and reproduction of bacteria lead to an increase in th...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: except following difference, other is with embodiment 1.
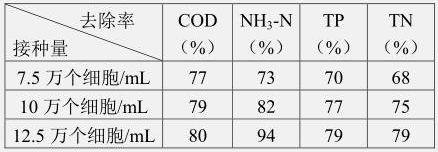
[0039] Haematococcus pluvialis was inoculated in the solution in the photobioreactor. During the intensive experiment, the dissolved oxygen concentration in the photobioreactor solution was controlled to be 5mg / L by intermittent aeration with the gas pump and the aeration head b, and the light intensity of the LED lamp was 3000Lx. The removal rate of algae to TN and TP.
[0040] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the inoculation amount is large, and the high cell density will reduce the concentration of nutrients in the medium, resulting in the transformation of bacteria and microalgae from a symbiotic relationship to a competitive relationship. At the same time, excessive bacterial toxins cause a large number of microalgae to die, and assimilated macromolecular compounds such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and organic matter are released. For microalgae with too small cell density, high concentration of med...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com