Method for producing acetone-ethanol-butanol (ABE) by fermentation with straw hydrolysate as raw material
A technology of hydrolyzate and straw, applied in the field of biomass energy preparation, can solve the problems of lack of ability to synthesize glutathione, few research reports on anaerobic bacteria, etc., achieve good practical value and promotion and application significance, and improve fermentation yield The effect of rate and dosage optimization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The method for producing ABE by fermenting the straw hydrolyzate provided in this example with fresh corncobs as the raw material for fermentation is as follows.
[0044] (1) Preparation of straw hydrolyzate
[0045] When preparing the straw hydrolyzate, steps such as straw pretreatment and biological enzymolysis are included, specifically:
[0046] (1) Straw pretreatment
[0047] After drying the fresh corncobs, crush them through a 40-mesh sieve, put 20g of corncobs into a 500mL conical flask, add 200mL of 0.75% dilute sulfuric acid, and treat them at 121°C for 60min, Ca(OH) 2 Adjust the pH to 4.8.
[0048] (2) Biological enzymatic hydrolysis
[0049] Add biological enzymes to the sterilized straw mixture in step (1), mix well, enzymatically treat at 55°C for 48h, then centrifuge at 3000r / min for 5min to remove solid sediment, and the supernatant is the hydrolyzed straw to be fermented liquid;
[0050] The biological enzyme is a mixture of cellulase, xylanase, an...
Embodiment 2
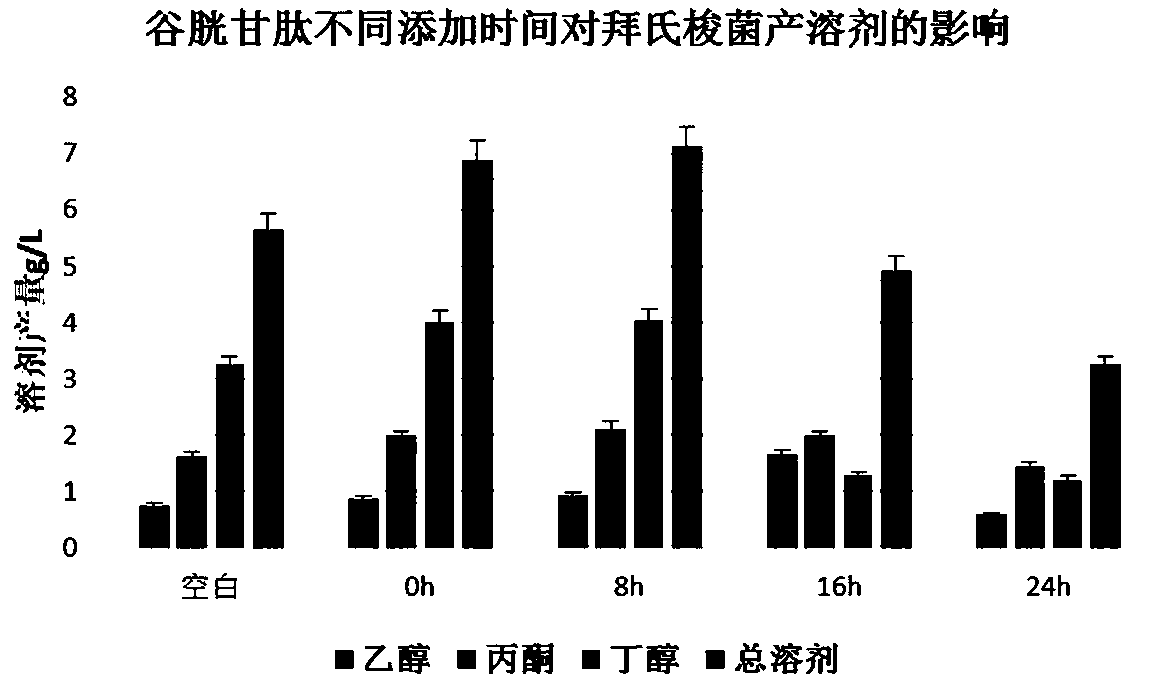
[0066] In this example, fresh corncobs were taken as an example to conduct a fermentation experiment. The specific operation was the same as in Example 1, only the strain was adjusted to Clostridium acetobutylicum (the preparation method of the seed liquid was the same as in Example 1), and the addition of glutathione was set. The time node is added after 8 hours of fermentation (the amount added is the same as in Example 1).
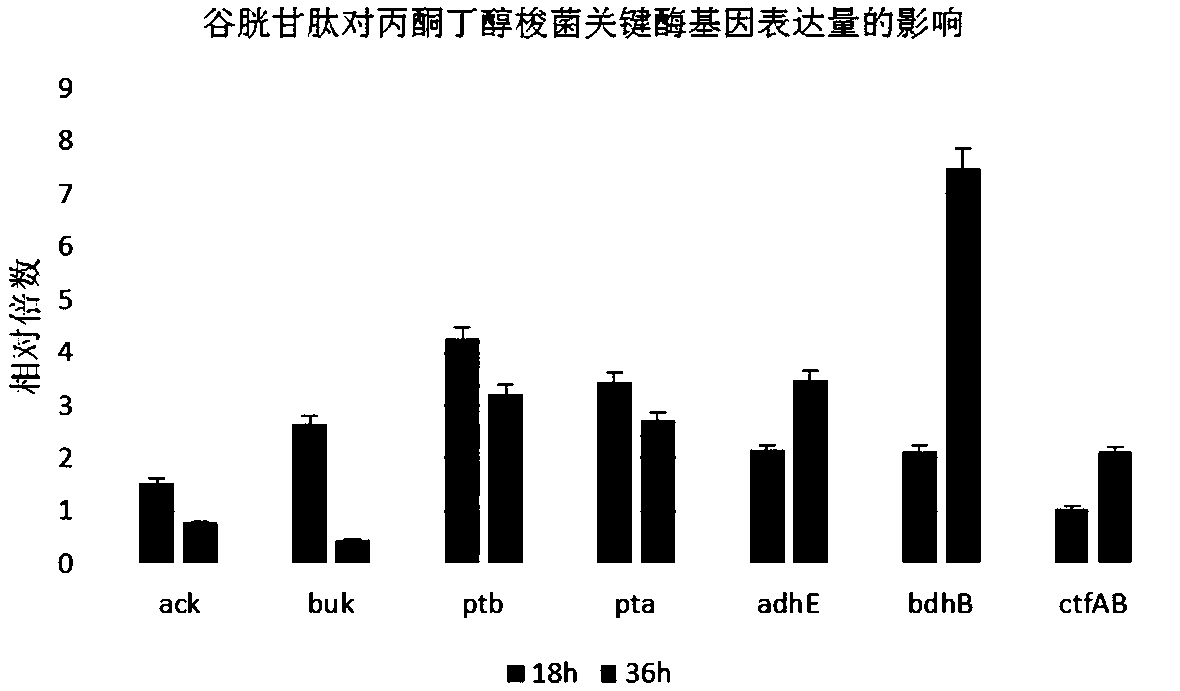
[0067] The total RNA was extracted at 18h in the acidogenic period and 36h in the solventogenic period, and the difference in gene expression of key enzymes in the solvent metabolism pathway was analyzed by fluorescent quantitative PCR method. The fluorescent quantitative results were as follows: figure 2 Shown (specific key enzyme genes and corresponding enzyme names are: ack acetate kinase; buk butyrate kinase; ptb phosphotransbutyrylase; pta phosphotransacetylase; adhE alcohol dehydrogenase; ctfAB CoA transferase; bdhB butanol dehydrogenase Hydrogen...
Embodiment 3
[0073] In this example, taking fresh wheat straw as an example, a fermentation experiment was carried out. The specific operation is the same as that in Example 1. Clostridium acetobutylicum and Clostridium beijerinckii were used for fermentation respectively, and the time node for adding glutathione was set as after 8 hours of fermentation Add (the amount added is the same as in Example 1). the result shows:
[0074] When inoculating Clostridium acetobutylicum alone for fermentation, in the fermentation broth: ethanol content 1.25g / L, acetone content 3.17g / L, butanol content 4.89g / L, total solvent content 9.31g / L;
[0075] When inoculated with Clostridium beijerinckii for fermentation alone, in the fermentation broth: ethanol content 1.03g / L, acetone content 2.64g / L, butanol content 4.32g / L, total solvent content 7.99g / L.
[0076] As a control, if glutathione is not added (other related operations are the same), after 72 hours of fermentation, when Clostridium acetobutylicum...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com