Method for regulating and controlling alkalinity of red mud through pyrolysis of agricultural biomass waste
A technology for biomass waste and agricultural production, which is applied in the field of regulating the alkalinity of red mud by pyrolysis of agricultural biomass waste, can solve the problems of poor economy and alkalinity control effect, environmental pollution, long adjustment time, etc. The effect of comprehensive utilization is difficult, raw materials and methods are simple and easy to achieve
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The stalks of agricultural waste were cleaned with deionized water, dried at 60°C for 24 hours, crushed with a pulverizer, and passed through a 20-mesh sieve. Place the red mud in a ventilated place to dry naturally for 72 hours and pass through a 100-mesh sieve. Then the treated straw and red mud were mixed and stirred evenly according to the mass ratio of 1:1, and put into the muffle furnace at 10°C·min. -1 After the heating rate was increased to 400 °C, it was pyrolyzed for 2 h. After the pyrolyzed product was cooled to room temperature, 10 g was dispersed in 50 ml of aqueous solution, and the pH value of the supernatant was measured.
[0035] How to measure pH:
[0036] Weigh 10 g of the pyrolyzed product, add 100 ml of distilled water, stir and mix evenly, seal with plastic wrap, stir with a magnetic stirrer (150 rpm) for 1 h, and the supernatant obtained by suction filtration is used for pH determination.
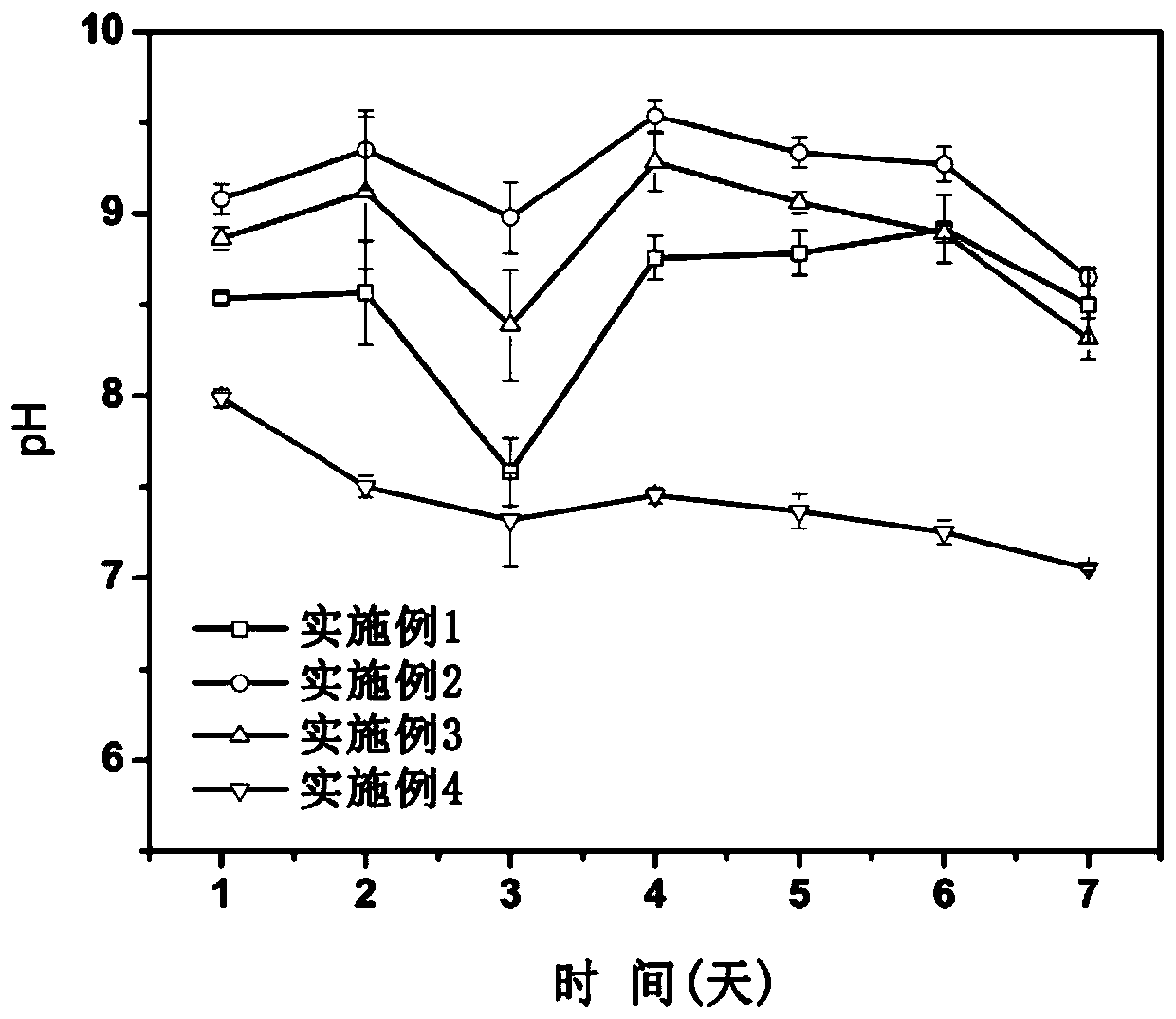
[0037] The pH change trend of the product after pyroly...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The stalks of agricultural waste were cleaned with deionized water, dried at 60°C for 24 hours, crushed with a pulverizer, and passed through a 20-mesh sieve. Place the red mud in a ventilated place to dry naturally for 72 hours and pass through a 100-mesh sieve. Then the treated straw and red mud were mixed and stirred evenly according to the mass ratio of 1:2, and put into the muffle furnace at 10°C·min. -1 After the heating rate was increased to 400 °C, it was pyrolyzed for 2 h. After the pyrolyzed product was cooled to room temperature, 10 g was dispersed in 50 ml of aqueous solution, and the pH value of the supernatant was measured.
[0040] The pH change trend of the product after pyrolysis in this example for 7 days is as follows figure 1 , the pH value of the product after pyrolysis was 9.08, which was lower than the pH value of 11.35 after only red mud was pyrolyzed. And the change trend of the pH value is small with the increase of time, indicating that the...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The stalks of agricultural waste were cleaned with deionized water, dried at 60°C for 24 hours, crushed with a pulverizer, and passed through a 20-mesh sieve. Place the red mud in a ventilated place to dry naturally for 72 hours and pass through a 100-mesh sieve. Then the treated straw and red mud were mixed and stirred evenly according to the mass ratio of 1:3, and put into the muffle furnace at 10°C·min. -1 After the heating rate was increased to 400 °C, it was pyrolyzed for 2 h. After the pyrolyzed product was cooled to room temperature, 10 g was dispersed in 50 ml of aqueous solution, and the pH value of the supernatant was measured.
[0043] The pH change trend of the product after pyrolysis in this example for 7 days is as follows figure 1 , the pH value of the product after pyrolysis was 8.86, which was lower than the pH value of red mud after only red mud pyrolysis was 11.35. And the change trend of the pH value is small with the increase of time, indicating ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com