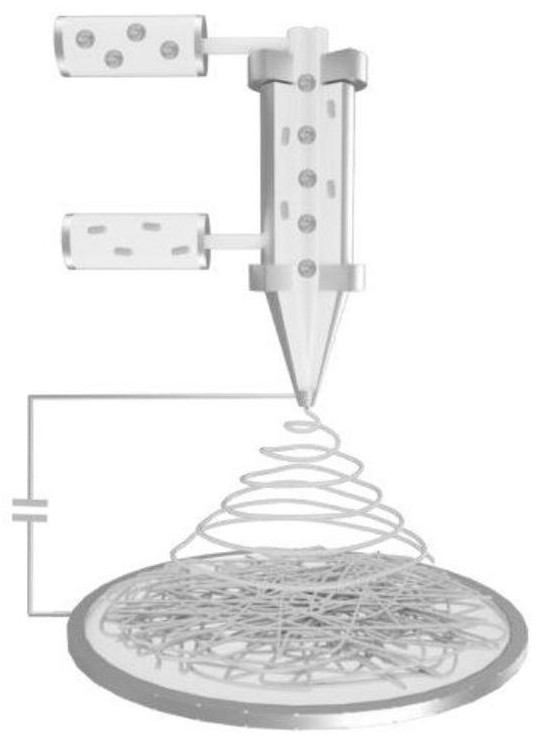
A kind of fiber material and its preparation method and application
A fiber material and fiber technology, which is applied in the field of fiber material and its preparation and application, can solve the problems of complicated loading and release process, limit practical application, etc., and achieve the effects of not easy to degrade and fail, simple loading method and high transfer efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] (1) The steps for synthesizing GNR are as follows: first, prepare its seed solution, mix hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) (0.1M, 9.75mL), chloroauric acid (HAuCl 4 ) (0.01M, 0.25mL), NaBH 4 (0.01M, 0.6mL) was mixed and stirred for 2min, and then used after standing for at least 2h. 4 (0.01M, 0.4mL), AgNO 3 (0.01M, 80μL), ascorbic acid (0.1M, 64μL), add HCl (1.0M, 160μL) and mix well; finally, add 17μL of prepared seed solution to 8.7mL growth solution, leave it overnight at 28°C, and The centrifuge was used after centrifuging at 8000 rpm to remove impurities, and the aspect ratio of the prepared GNR was 4.08.
[0048] (2) Prepare the outer layer spinning solution: dissolve PLLA (2.8g), gelatin (200mg), and GNR (15.6mg) in 20mL of polyhexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP), stir overnight into a colorless viscous shape , take out 5mL as the outer spinning solution.
[0049] (3) Configure the inner layer spinning solution: the bFGF plasmid encoding GFP green fluoresce...
Embodiment 2
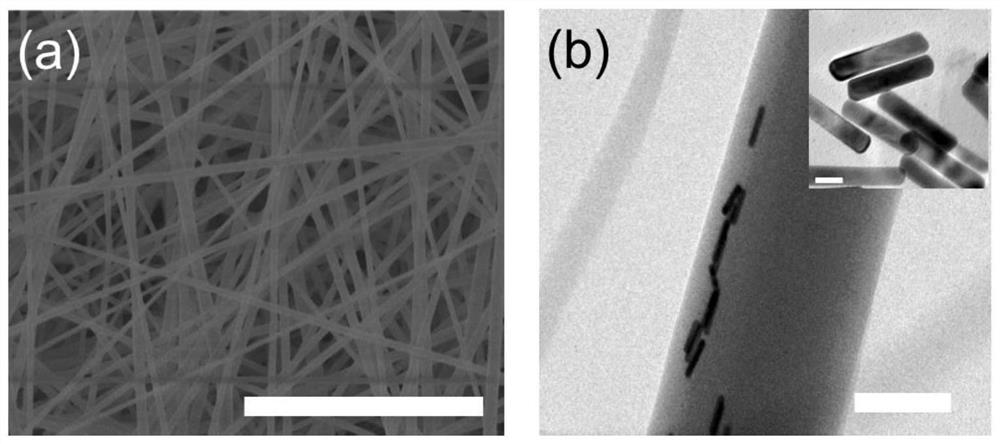
[0056] The preparation method of the electrospun fiber is the same as that of Example 1 when the N / P is 30. The SEM and TEM figures of the electrospun fiber (expressed in PG / GNR) obtained in this embodiment are shown in image 3 , wherein, (a) SEM characterization of PG / GNR core-shell structure spun fibers, scale bar: 5 μm. (b) TEM characterization of PG / GNR core-shell structure spun fibers and GNRs. GNRs are uniformly distributed in the shell of spun fibers. Scale bar: 20nm, 200nm.
[0057] The cell experiment method is basically the same as in Example 1, the difference is that: the laser light source with a wavelength of 808nm is used at a rate of 0.45W / cm 2 The power density in the hole was irradiated for different times to measure the photothermal effect of the electrospun fiber. The measurement results are shown in Figure 4 (Wet state), it can be seen from the results that the surface temperature of the spun fiber rises rapidly, and the temperature reaches about 45°C a...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The preparation method of the electrospun fiber is the same as in Example 2.
[0060] The electrospun fibers prepared in this example were subjected to cell culture according to the method of Example 1 (ie steps (5) to (7) of Example 1).
[0061] The sample processing of the cultured cells is divided into three parts, which are (1) flow cytometry to characterize the transfection, (2) cell proliferation experiment, and (3) cell migration experiment.
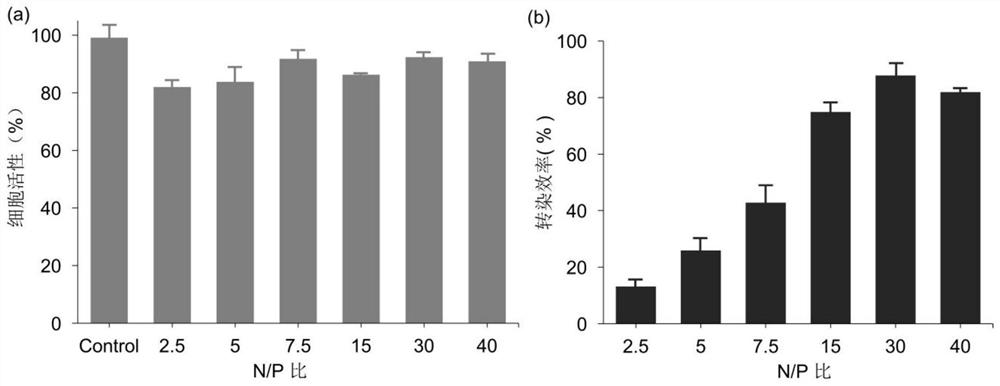
[0062] (1) Characterization of transfection by flow cytometry: After 48 hours of laser irradiation, the cells cultured on the fiber were digested with trypsin, centrifuged, resuspended in sterile PBS and placed in a flow tube, and placed in a flow tube without any Treated NIH-3T3 cells were used as a control group for flow cytometry testing, and the test results are shown in Figure 5 . The results of flow cytometry to characterize the transfection efficiency show that the electrospun fiber material described in the prese...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com