Method for inducing differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts and application thereof
An osteoblast differentiation and stem cell technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of restricting clinical application, side effects of bone tissue, complex induction system, etc., and achieve the effect of promoting osteoblast differentiation and avoiding osteoblast difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Isolation, culture and identification of human mesenchymal stem cells
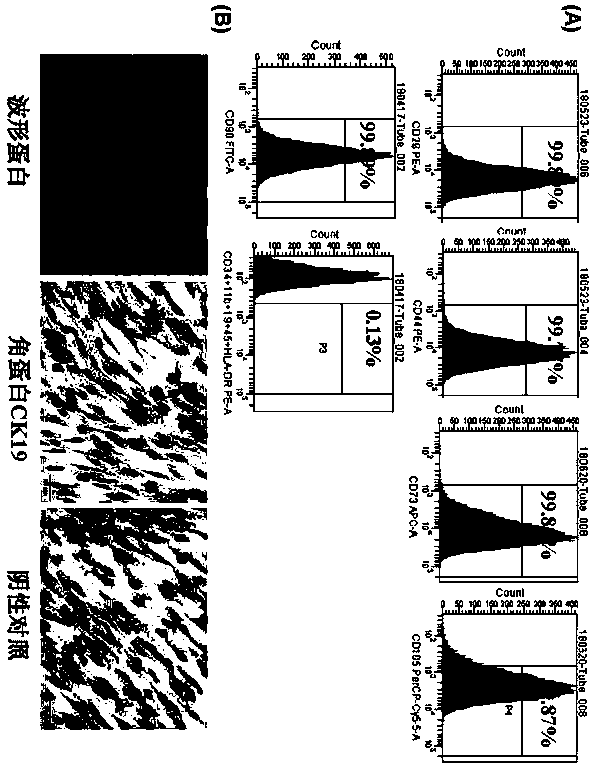
[0033] Mesenchymal stem cells were isolated from amniotic membrane using fresh placenta of healthy pregnant women who were delivered by full-term cesarean section by mechanical method combined with two enzymes (trypsin and type II collagenase) digestion. Resuspend the cells in low-sugar DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, plant them in T25 cell culture flasks, and culture at 37°C, containing 5% CO2 and air saturation humidity above 95%, until the cell fusion degree reaches 80% or more. Subcultured, the 2nd-5th passage cells were used for subsequent experiments. When the second generation cells were cultured to a confluence of 80%, the cells were collected to identify cell surface molecules by flow cytometry. The cells highly expressed CD90, CD105, CD73, CD44 and CD29 and other mesenchymal cell surface molecules, but did not express CD34 , CD11b, CD19, CD45 and HLA-DR and other...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: Isolation and identification of GD-A natural compound
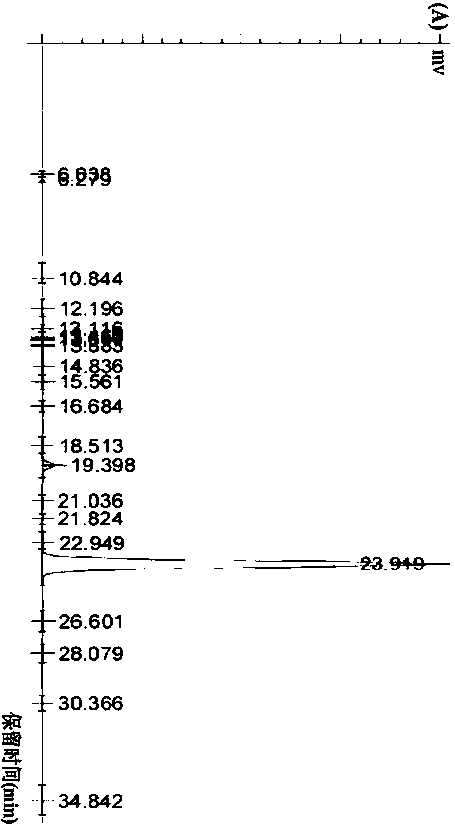
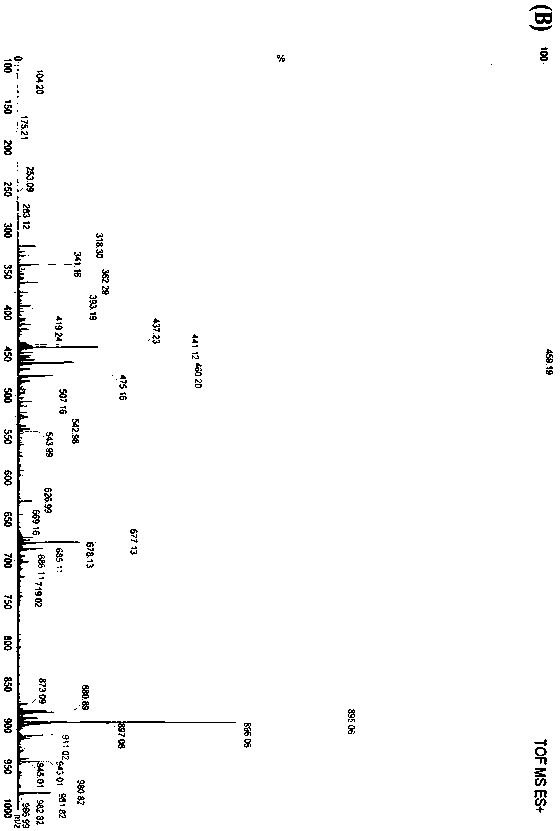
[0035] The dried Ganoderma lucidum fruiting bodies were crushed by micro-breaking the wall, extracted three times with 10 times the volume of 90-95% methanol under reflux, each time for 2 hours, and the extract was concentrated and dried under reduced pressure to obtain the extract. After being suspended in warm water, it was extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate extraction part was chromatographed on a silica gel column and eluted with a gradient of dichloromethane-methanol (1:0→0:1). Compound GD-A was obtained by gradient elution with petroleum ether-ethyl acetate (1:0→0:1), and the eluted fraction was separated by medium-pressure liquid chromatography and reversed-phase semi-preparative chromatography. The compound is 95% pure through HPLC analysis, as figure 2 As shown, its mass spectrometry results are shown in image 3 As shown, its molecular weight is 436, and its molecular formula...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Cytotoxicity analysis of GD-A on human mesenchymal stem cells
[0038] In order to illustrate the safety problem of using the compound of the present invention, that is, whether it is safe for human mesenchymal stem cells, a corresponding test is carried out:
[0039] Using the MTT method, different doses (0.001 μM, 0.01 μM, 0.1 μM, 1.0 μM, 10 μM and 100 μM) of GD-A were measured, and the human mesenchymal stem cells were continuously affected for 24 hours, 48 hours and 72 hours respectively. The result is as Figure 6 As shown, compared with the control group, after GD-A was treated for 24h, 48h and 72h, in the dose range of 0.001μM-10μM, GD-A had no cytotoxicity to human mesenchymal stem cells, and even promoted cell proliferation, especially After 24 hours, it showed obvious effect of promoting cell proliferation. However, when the dose of GD-A was 100μM, the three time points all inhibited cell proliferation and had obvious cytotoxicity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com