Formula of multiple oxidation-reduction alloy material with inactivated microorganisms
A technology of alloy materials and microorganisms, which is applied in the field of multiple redox alloy material formulations, to achieve in-situ reduction, solve the problem of environmental protection, and good mechanical and thermal processing performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The present embodiment 1 provides a water treatment alloy material formulation, which includes the following elements by weight ratio:
[0033] Zinc: 28%-35%;
[0034] Tin: 4%-7%;
[0035] Nickel: 19%-26%;
[0036] Rare earth: 1.5%-3.5%;
[0037] The balance is copper.
[0038] In the formula of the present invention:
[0039] The effects of its elements on microorganisms are:
[0040] Copper is the most critical element in sterilization materials, which can inhibit the growth of various bacteria, viruses, and microorganisms in water. Copper generates copper ions in the water environment, and copper ions can reach the interior of the cell through the cell membrane, denature some enzymes in the cell, thereby destroying its metabolism and killing microorganisms;
[0041] Zinc and copper elements have a large potential difference, and their alloys can form countless tiny primary batteries in solution. The electrode potential of zinc is low, and it is easy to lose el...
Embodiment 2
[0047] This embodiment is based on Embodiment 1, which is mainly used to inhibit microorganisms in water treatment.
[0048] This embodiment provides alloy sterilization experiment:
[0049] First, the alloy is processed into tubular structures of different diameters;
[0050] Assemble alloy pipes of different diameters in the form of large pipes and small pipes, and set stainless steel pipes on the outermost part of the combined pipe, and weld the inlet flange and outlet flange at the left and right ends of the combined pipe;
[0051] Install the combined pipeline in the water treatment system for treatment.
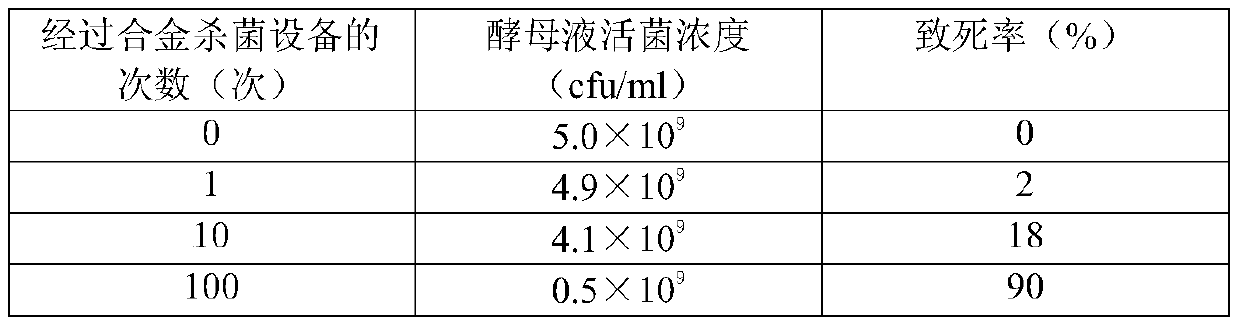
[0052] Then, the activated yeast liquid is passed through the alloy sterilization equipment at a certain flow rate for several times, and the yeast liquid that has been sterilized by the alloy sterilization equipment for different times is plate-plated and cultured and counted.
[0053] Finally, through the plate counting results, the concentration of viable bacteria ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] This embodiment is based on Embodiment 1, which is mainly used for inactivating microorganisms in water treatment.
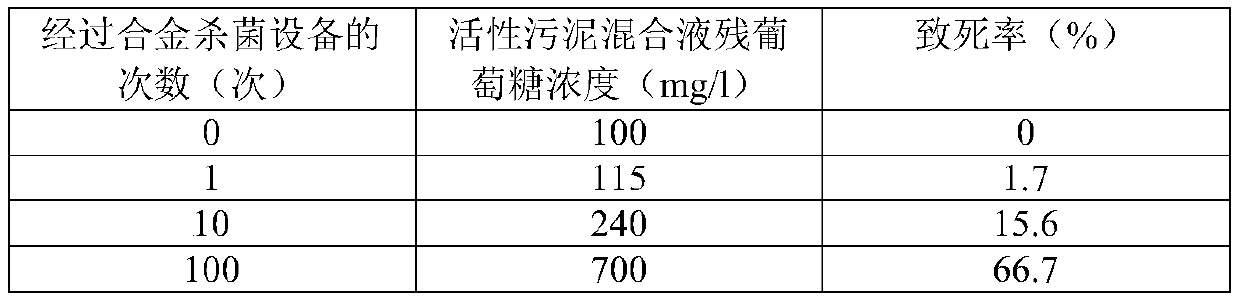
[0059] The alloy sterilization equipment is the same as in the above-mentioned single bacteria killing experiment, and the sterilization object is replaced by the activated sludge mixture composed of various microorganisms from yeast. The activated sludge mixture is sterilized for different times by alloy sterilizing equipment. Because there are many kinds of microorganisms in activated sludge, and there are a large number of non-culturable microorganisms, it is not suitable to use the plate counting method. This experiment uses the glucose metabolism rate to evaluate the sterilization effect. Shaking bed culture, before the culture, add a certain amount of glucose to the activated sludge mixture, so that the initial concentration of glucose is 1000mg / l, and then cultivate for 12 hours to detect the residual concentration of glucose in the mixture. The hi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com