Two-dimensional material phase change memory cell
A two-dimensional material and memory cell technology, applied in the field of microelectronics, can solve the problems of large thermal stress and low electrical and thermal efficiency of phase-change memory cells, and achieve the effects of small high pressure resistance, reduced heat loss, and high elastic coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
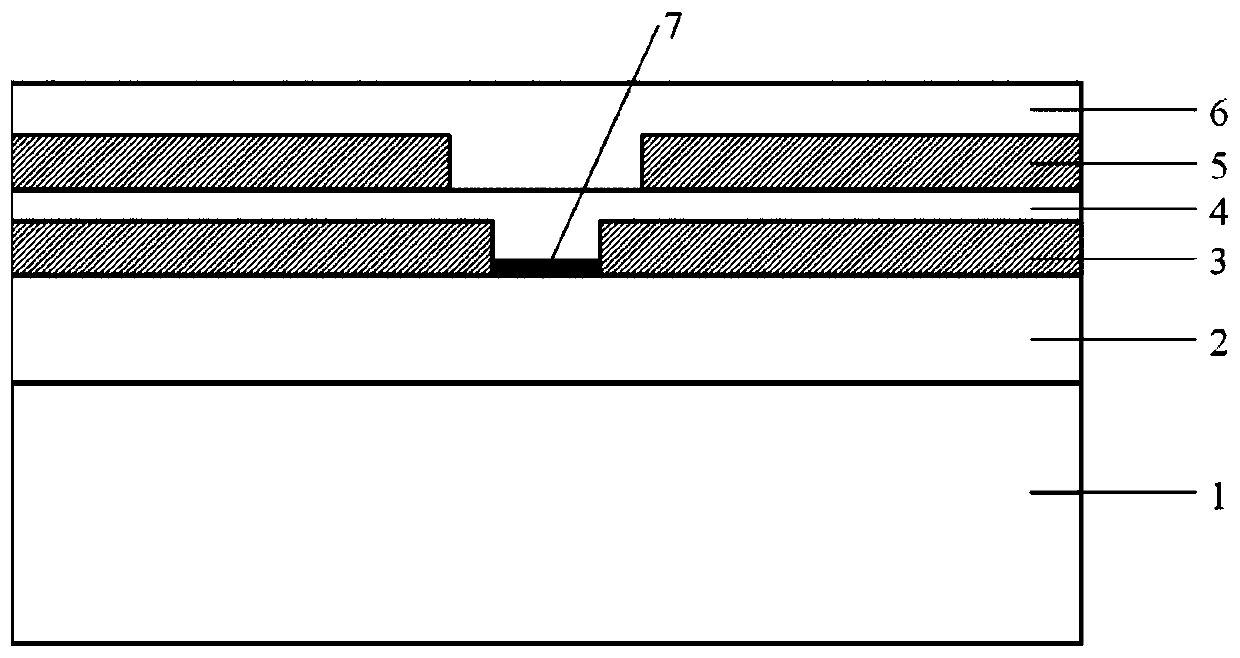
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a two-dimensional material phase-change memory unit, including a substrate 1, a lower electrode 2, a first insulating layer 3, a phase-change layer 4, a second An insulating layer 5 , an upper electrode 6 , and a two-dimensional material layer 7 , wherein the two-dimensional material layer 7 is disposed on the contact surface between the phase change layer 4 and the lower electrode 2 .
[0036] Specifically, the substrate 1 may be a silicon single wafer substrate or other semiconductor material substrates.
[0037] Specifically, the lower electrode 2 is a conductive material that requires low resistivity and stable properties, and materials such as TiW, TiN, HfN, Ag, Al, Cu, W, Ta, and Pt can be used. The lower electrode can be made of the same material as the lower electrode 2 .
[0038] Specifically, the first insulating layer 3 is an insulating material, which requires high resistivity, low thermal conductiv...
Embodiment 2
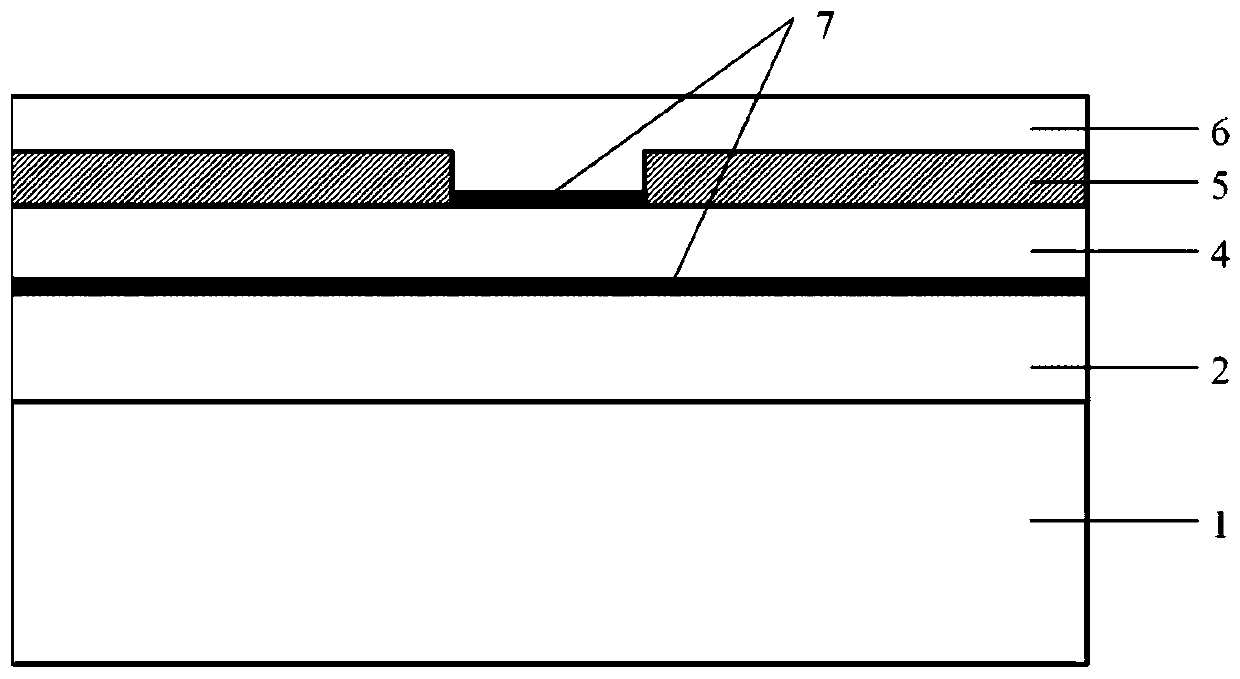
[0042] Different from the T-shaped structure of the embodiment, embodiment 2 provides a phase-change memory unit with a layered structure, such as figure 2 As shown, the difference lies in the structure of the phase change layer 4 and the two-dimensional material layer 7 is disposed between the upper electrode 6 and the lower electrode 2 and the phase change layer 4 at the same time.
Embodiment 3
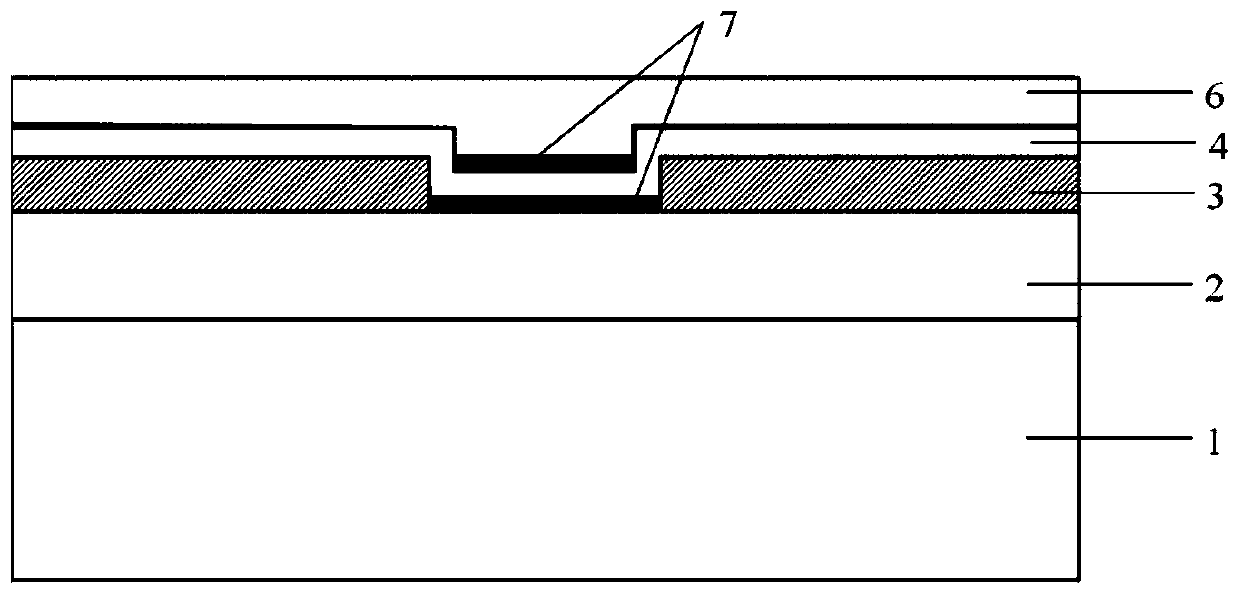
[0044] Such as image 3 As shown, a trench structure phase-change memory cell is provided, the difference lies in the structure of the phase-change layer 4 and the two-dimensional material layer 7 is disposed between the upper electrode 6 and the lower electrode 2 and the phase-change layer 4 at the same time.
[0045] Figure 4 to Figure 9 The specific preparation process of the two-dimensional material phase-change memory unit of Example 1 is shown:
[0046] Step 1: On the clean and dry silicon substrate 1, a TiW thin film for the lower electrode is prepared by magnetron sputtering. The thickness of the lower electrode 2 is 100 nm, and the width of the lower electrode 2 of TiW is controlled to 15 um by photolithography technology. The method for preparing the TiW lower electrode 2 can be selected from one of sputtering, evaporation, chemical vapor deposition, and plasma enhanced chemical vapor.
[0047] Step 2: A molybdenum disulfide thin film is grown on the surface of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com