Biodegradable preservative film and preparation method thereof
A biodegradable and fresh-keeping film technology, which is applied in the field of biodegradable fresh-keeping film and its preparation, can solve the problems of reduced material degradability, limited application, short antibacterial period, etc., to improve dispersion and interface bonding, and increase strength and ductility, the effect of improving surface compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
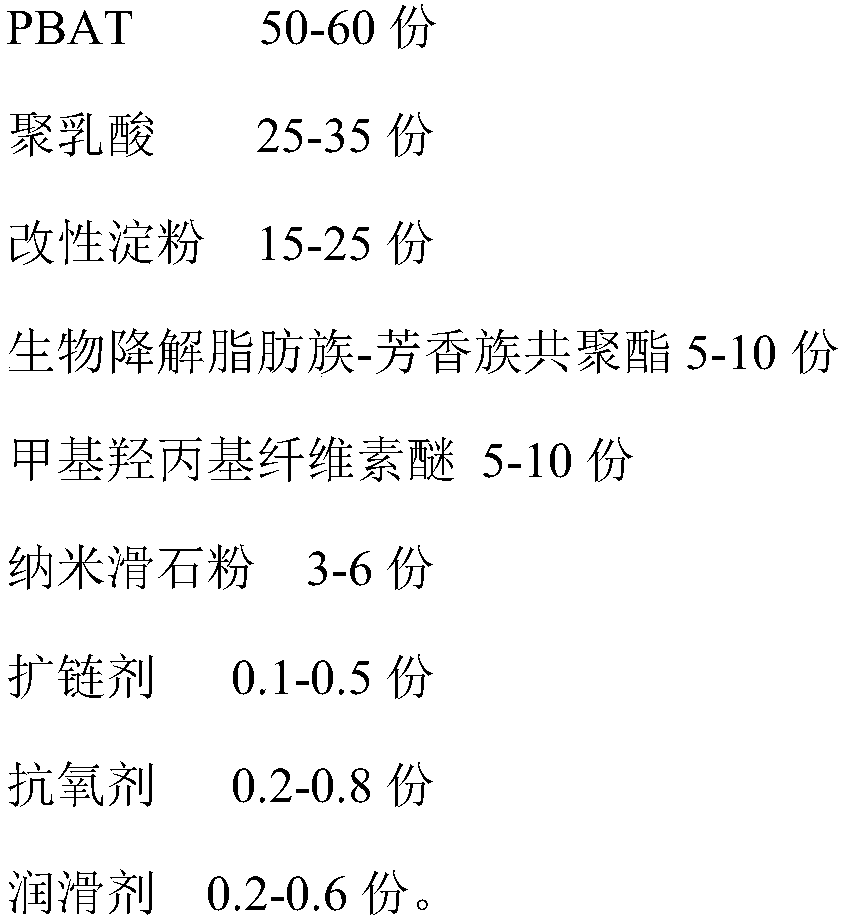
[0034] A kind of preservative film of the present embodiment, the preparation method is as follows (the following components are all in parts by weight):
[0035] Step a. At 20°C, mix 50 parts of tapioca starch with 50 parts of distilled water and stir evenly, then add 4 parts of glycerin and 0.6 parts of maleic anhydride, and keep stirring to form a colloidal mixture; then place it in a water bath or Heat gelatinization in an oil bath at a heating temperature of 95°C for 25 minutes to obtain a viscous colloid; place the viscous colloid in an oven at a drying temperature of 100°C for 15 minutes, then dry The solid was crushed to 200 mesh to obtain modified starch.
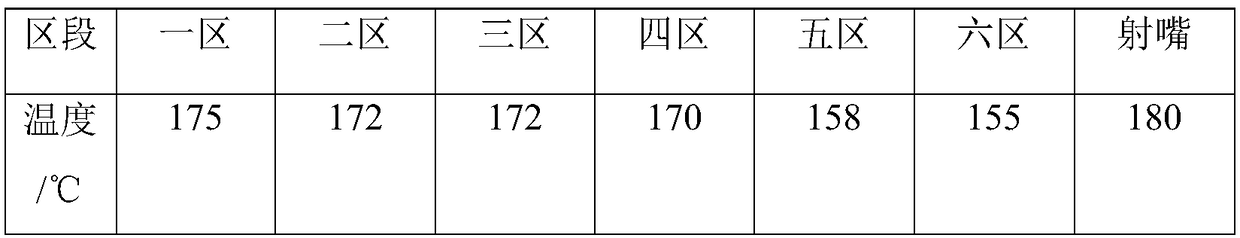
[0036] Step b, weighing 20 parts of modified starch, 50 parts of PBAT, 25 parts of polylactic acid, 3 parts of biodegradable aliphatic-aromatic copolyester, 5 parts of methyl hydroxypropyl cellulose ether and 5 parts of nano talcum powder (the average particle size is 50nm), dry at 75°C for 4 hours, so that the mo...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A kind of preservative film of the present embodiment, the preparation method is as follows (the following components are all in parts by weight):
[0043] Step a. At 22°C, mix 45 parts of tapioca starch with 55 parts of distilled water and stir evenly, then add 2 parts of glycerin and 0.4 parts of maleic anhydride, and keep stirring to form a colloidal mixture; then place it in a water bath or Heat gelatinization in an oil bath at a heating temperature of 85°C for 30 minutes to obtain a viscous colloid; place the viscous colloid in an oven at a drying temperature of 110°C for 20 minutes, then dry The solid was crushed to 100 mesh to obtain modified starch.
[0044] Step b, weigh 15 parts of modified starch, 60 parts of PBAT, 35 parts of polylactic acid, 5 parts of polyethylene terephthalate-co-adipate, 3 parts of methyl hydroxypropyl cellulose ether and 6 parts of nano talcum powder (average particle diameter is 70nm), dry at 78 ℃ for 5h, make the water content of eac...
Embodiment 3
[0050] A kind of preservative film of the present embodiment, the preparation method is as follows (the following components are all in parts by weight):
[0051] Step a. At 25°C, mix 60 parts of tapioca starch with 45 parts of distilled water and stir evenly, then add 8 parts of glycerin and 1 part of maleic anhydride, and keep stirring to form a colloidal mixture; then place it in a water bath or Heat gelatinization in an oil bath at a heating temperature of 100°C for 10 minutes to obtain viscous colloids; place the viscous colloids in an oven at a drying temperature of 120°C for 10 minutes, then dry The solid was crushed to 230 mesh to obtain modified starch.
[0052] Step b, weighing 25 parts of modified starch, 56 parts of PBAT, 30 parts of polylactic acid, 10 parts of biodegradable aliphatic-aromatic copolyester, 10 parts of methyl hydroxypropyl cellulose ether and 8 parts of nano talcum powder (the average particle size is 60nm), dry at 80°C for 4.5h, make the moisture...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com