Method for preparing boron carbide
A technology of boron carbide and boric acid, which is applied in the field of ceramic materials, can solve problems such as difficulty in achieving densification, high overall cost, and long preparation cycle, and achieve energy utilization, environmental friendliness, high energy utilization, and excellent mechanical properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] A method for preparing boron carbide, comprising the steps of:
[0039] (1) Crushing natural coal, ball milling at 150r / min for 4 hours, and then passing through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain active coal powder;
[0040] (2) Weigh a certain amount of boric acid and dissolve it in distilled water at 80°C to obtain a saturated boric acid solution, then weigh the active coal powder and sodium carbonate prepared in step (1), dissolve them in the saturated solution of boric acid, and Vibration and dispersion are uniform on the ultrasonic vibrator, and the active coal powder weight is 30% of the boric acid weight, and the sodium carbonate weight is 5wt% of the boric acid weight;
[0041] (3) Put the shaken mixed powder into a constant temperature drying oven, dry and grind at 100°C;
[0042] (4) Attach the carbon paper to the inner wall of the graphite abrasive tool. The carbon paper on the inner wall of the mold and the carbon paper at the upper and lower pressure heads need t...
Embodiment 2
[0050] This example provides a boron carbide preparation method. Compared with Example 1, the difference is that in step (6), the pulse current ratio is 8-2, the load is 1MPa, the temperature is 1100°C, and the room temperature to 600°C The heating rate before and after 600°C is 60°C / min and 160°C / min respectively, keep warm for 2 minutes, then cool with the furnace, and keep the vacuum at 1Pa.
[0051] After testing, the density of the boron carbide material is 2.615g / cm 3 , the density is 100%, the Vickers hardness is 33.06±0.31GPa, the fracture toughness is 5.89±0.35MPa.m 1 / 2 .
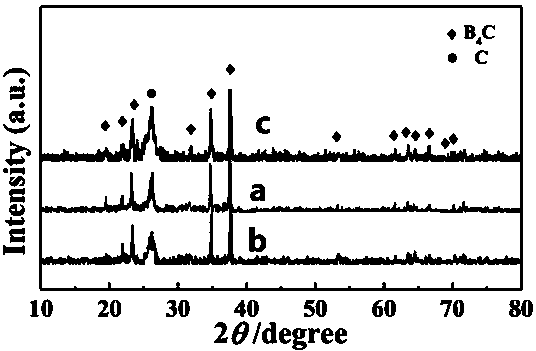
[0052] The obtained boron carbide material is subjected to XRD test, such as figure 1 As shown in (b), there is also some incompletely graphitized amorphous C in the sample, at 2 θ = 43°, there is also a small amount of steamed bun peak of amorphous C, indicating that boron carbide is not completely reacted at low temperature |.
[0053] Obtained boron carbide material is carried out microstru...
Embodiment 3
[0055] This example provides a boron carbide preparation method. Compared with Example 1, the difference is that in step (6), the pulse current ratio is 8-2, the load is 5MPa, the temperature is 1600°C, and room temperature to 600°C The heating rate before and after 600°C was 60°C / min and 160°C / min respectively, and the temperature was kept for 10 minutes, then cooled with the furnace, and the vacuum degree was kept at 1Pa.
[0056] After testing, the density of the boron carbide material is 2.623g / cm 3 , the density is 100%, the Vickers hardness is 32.56±0.38GPa, the fracture toughness is 5.95±0.36MPa.m 1 / 2 .
[0057] The obtained boron carbide material is subjected to XRD test, such as figure 1 As shown in (c), the diffraction peak of boron carbide is getting sharper and sharper, indicating that boron carbide crystals are in a good crystallization state at high temperature, and the position of the diffraction peak of C is relatively shifted, and the intensity of the diffra...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Vickers hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com