A kind of diamond saw blade for dry cutting ceramics and preparation method thereof
A technology for diamond saw blades and ceramic products, applied in stone processing equipment, manufacturing tools, stone processing tools, etc., can solve the problems of late diamond saw blades, prone to chipping, high ceramic hardness, etc., to achieve high cutting efficiency, embedded Strong and compatible effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
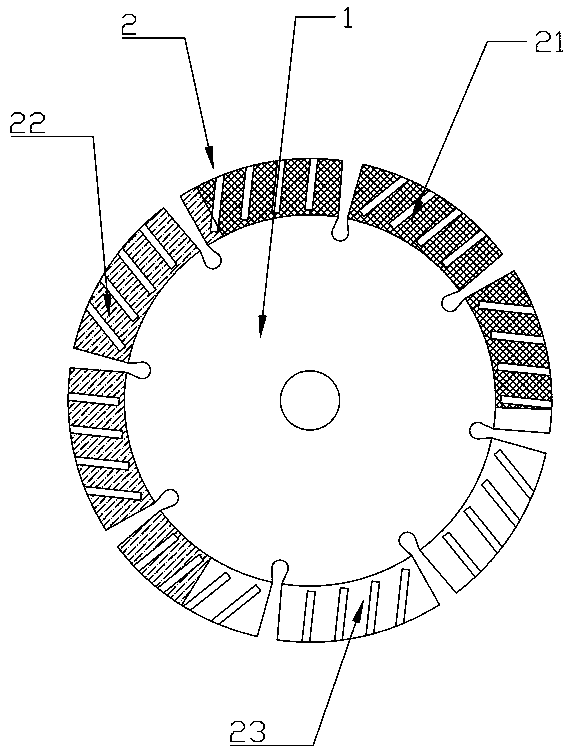
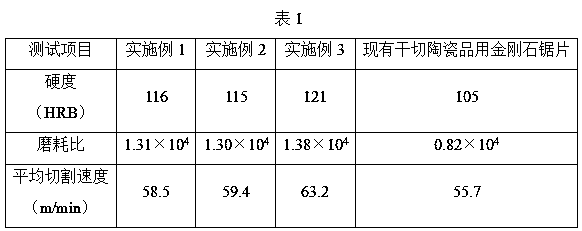
[0029] refer to figure 1 , a diamond saw blade for dry cutting ceramics, comprising a substrate 1 and a cutter head 2, the cutter head 2 including a first cutting zone 21, a second cutting zone 22 and a third cutting zone 23; the first cutting zone 21 includes the following raw materials in parts by weight: 8 parts of polycrystalline diamond particles, 45 parts of iron powder, 26 parts of copper powder, 3 parts of zinc powder, 2 parts of tin powder, 1.5 parts of nickel powder, 2 parts of manganese powder, and 1.5 parts of titanium carbide powder , 0.5 part of lanthanum-nickel five-powder; the second cutting zone 22 includes the following raw materials in parts by weight: 9 parts of polycrystalline diamond and boron carbide mixture particles, 42 parts of iron powder, 33 parts of copper powder, 3 parts of zinc powder, tin powder 2 parts, 1.5 parts of nickel powder, 2 parts of manganese powder, 1.5 parts of titanium carbide powder, 0.5 part of lanthanum nickel five powder; the th...
Embodiment 2
[0041] refer to figure 1 , a diamond saw blade for dry cutting ceramics, comprising a substrate 1 and a cutter head 2, the cutter head 2 including a first cutting zone 21, a second cutting zone 22 and a third cutting zone 23; the first cutting zone 21 includes the following raw materials in parts by weight: 14 parts of polycrystalline diamond particles, 55 parts of iron powder, 32 parts of copper powder, 5 parts of zinc powder, 3 parts of tin powder, 3 parts of nickel powder, 4 parts of manganese powder, 2.5 parts of titanium carbide powder , 0.9 part of lanthanum nickel five powder; the second cutting zone 22 includes the following raw materials in parts by weight: 16 parts of polycrystalline diamond and boron carbide mixture particles, 48 parts of iron powder, 37 parts of copper powder, 4.5 parts of zinc powder, tin powder 3 parts, 3 parts of nickel powder, 4 parts of manganese powder, 3 parts of titanium carbide powder, 0.9 part of lanthanum nickel five powder; the third ...
Embodiment 3
[0053] A diamond saw blade for dry cutting ceramics, including a base 1 and a cutter head 2, refer to figure 1 , the cutter head 2 includes a first cutting area 21, a second cutting area 22 and a third cutting area 23; the first cutting area 21 includes the following raw materials by weight: 11 parts of polycrystalline diamond particles, 50 parts of iron powder , 31 parts of copper powder, 3.5 parts of zinc powder, 2.5 parts of tin powder, 2.2 parts of nickel powder, 3 parts of manganese powder, 2.3 parts of titanium carbide powder, 0.75 part of lanthanum nickel five powder; the second cutting area 22 includes the following parts by weight Raw materials: 14 parts of polycrystalline diamond and boron carbide mixture particles, 44 parts of iron powder, 36 parts of copper powder, 4 parts of zinc powder, 2.6 parts of tin powder, 2.5 parts of nickel powder, 3 parts of manganese powder, 2.5 parts of titanium carbide powder, 0.7 part of lanthanum nickel five powder; the third cutting...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com