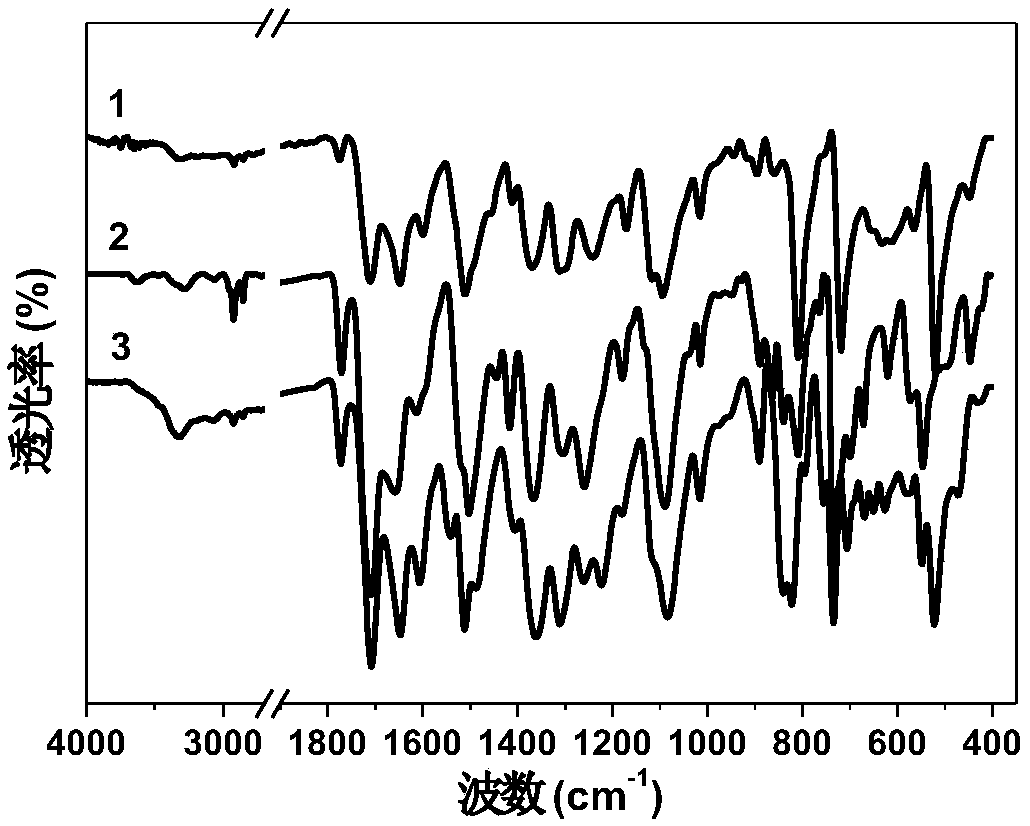
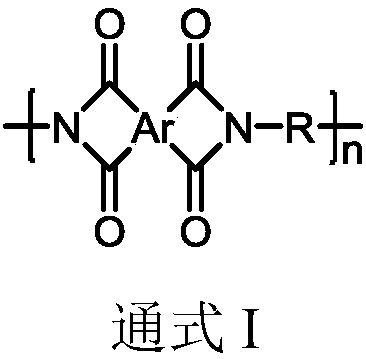
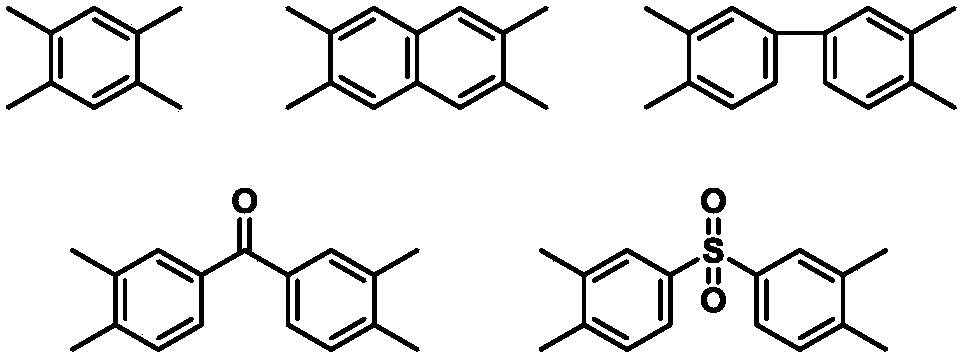
Highly heat-resistant ultralow-expansion polyimide film and preparation method and application thereof
A polyimide film and polyimide technology, which is applied in the field of polyimide, can solve the problems of low thermal expansion coefficient and heat resistance of polyimide film, so as to improve the packing density and achieve good super performance. Low coefficient of expansion, the effect of reducing the coefficient of thermal expansion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] (1) Under the protection of an inert gas, add 17.30 grams (0.05 moles) of N,N'-bis(4-aminophenyl)-terephthalamide to a three-necked flask equipped with mechanical stirring, nitrogen inlet and outlet, and a thermometer and 110 grams of N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP), stirring at room temperature until completely dissolved; lowering the system to a low temperature of -10°C, adding 10.91 grams (0.05 moles) of 1,2,4,5-pyromellitic dianhydride, After complete dissolution, stir at low temperature for 24 hours to obtain a homogeneous polyamic acid homogeneous solution with a viscosity of 20,000 cP and a solid content of about 20 wt.%.
[0054] (2) The polyamic acid homogeneous solution obtained in step (1) is filtered, vacuum defoamed, and then coated on a dry glass plate with a flat and smooth surface, placed in an oven and heated and solidified under a nitrogen atmosphere, specifically 60°C / 2 hours, 180°C / 1 hour, and 350°C / 1 hour. After cooling down to room temperature, the subs...
Embodiment 2
[0058] (1) Under the protection of an inert gas, add 17.79 grams (0.0475 moles) of N,N'-bis(4-amino-2-methylphenyl)- Terephthalamide and 290 grams of N,N'-dimethylacetamide (DMAc), stirred at room temperature until completely dissolved; the system was lowered to -5°C, and 14.71 grams (0.05 moles) of 3,3', 4,4'-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride was completely dissolved and then stirred at low temperature for 15 hours to obtain a homogeneous polyamic acid homogeneous solution with a viscosity of 13000 cP and a solid content of about 10 wt.%.
[0059] (2) The polyamic acid homogeneous solution obtained in step (1) is filtered, vacuum defoamed, and then coated on a dry glass plate with a flat and smooth surface, placed in an oven and heated and solidified under a nitrogen atmosphere, specifically 80°C / 1.5 hours, 200°C / 2 hours, and 350°C / 1 hour. After cooling down to room temperature, the substrate is soaked in deionized water, the film is automatically peeled off and placed in ...
Embodiment 3
[0063] (1) Under the protection of an inert gas, add 18.17 g (0.0525 moles) of N,N'-(1,4-phenylene)-bis(4- aminobenzamide) and 150 grams of N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP), stirred at room temperature until completely dissolved; the system was lowered to a low temperature of 0°C, and 14.71 grams (0.05 moles) of 3,3',4,4'-bis Benzophenone tetra-acid dianhydride is completely dissolved and stirred at low temperature for 12 hours to obtain a homogeneous polyamic acid homogeneous solution with a viscosity of 16500 cP and a solid content of about 18 wt.%.
[0064] (2) The polyamic acid homogeneous solution obtained in step (1) is filtered, vacuum defoamed, and then coated on a dry stainless steel plate with a flat and smooth surface, placed in an oven and heated and solidified under a nitrogen atmosphere, specifically 100°C / 1 hour, 250°C / 1 hour, and 350°C / 0.5 hour. After cooling down to room temperature, the substrate is soaked in deionized water, the film is automatically peeled off an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thermal resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com