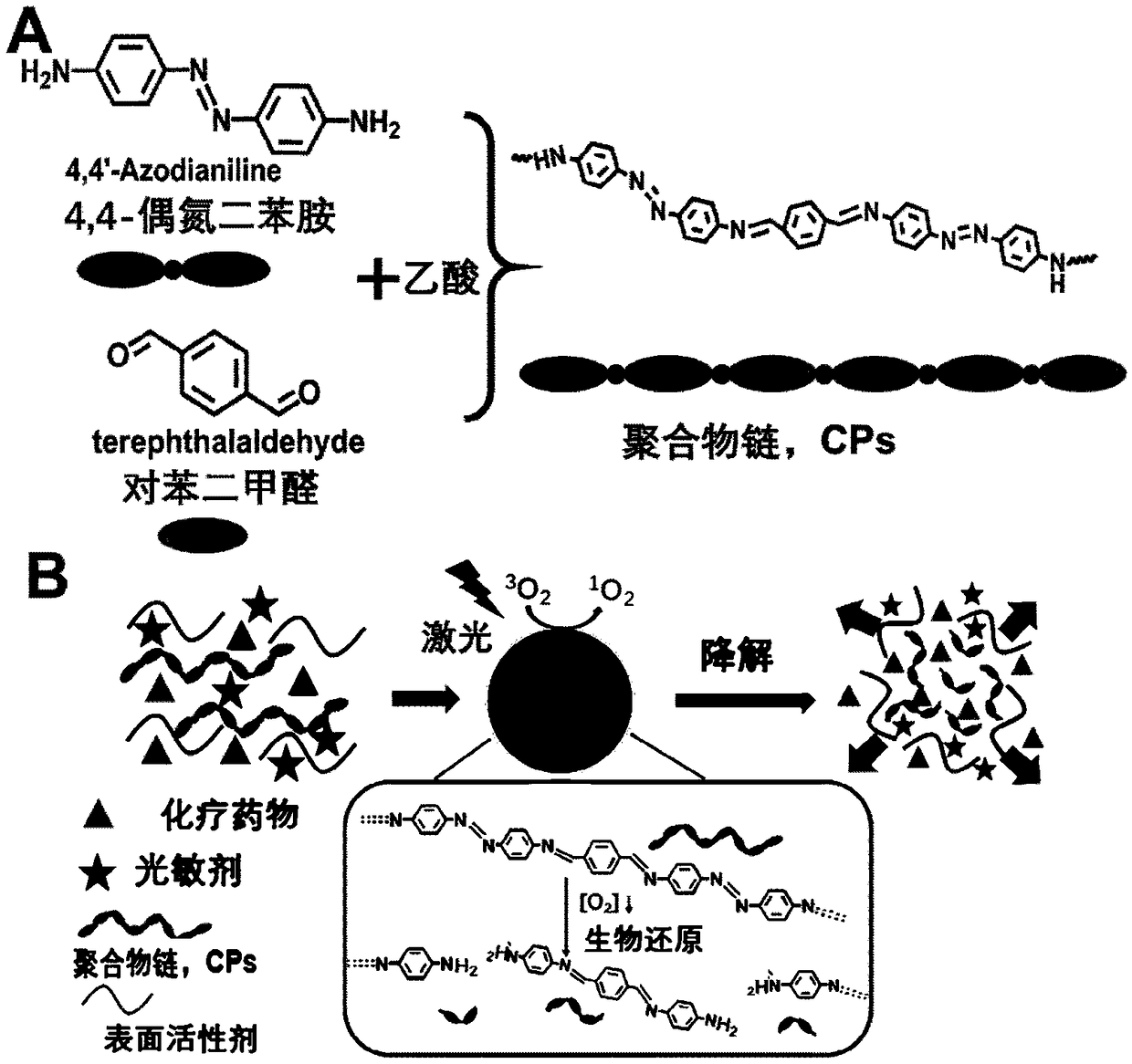
Hypoxia response polymer nanoparticle and application thereof
A nanoparticle and polymer technology, which is applied in the field of nanomaterial preparation and biomedicine, can solve the problems of reducing active oxygen species in local tumor tissues, limiting the clinical application of cancer treatment, and affecting the effect of photodynamic therapy, so as to enhance the joint killing ability, Achieving therapeutic effects and avoiding destructive effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Synthesis of polymer nanomedicine: Weigh 4.2mg 4,4-Azodianiline (4,4'-Azodianiline, 0.02mmol) and 2.7mg terephthalaldehyde (terephthalaldehyde, 0.02mmol) and dissolve in 4mL N,N- Add 0.2 mL of glacial acetic acid (98%) to the dimethylformamide (DMF) solution to initiate polymerization for 5 minutes. Add 400 μL of 2 mg / mL CPT (camptothecin, CPT, as the chemotherapeutic drug in this example) into the polymer solution, mix well, and continue to react for 5 minutes. Under the condition of stirring, add the above mixed solution dropwise to 20mL of 1mg / mL polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP, molecular weight 40K) aqueous solution, after the dropwise addition, after ultrasonic reaction for 5 minutes, continue to stir for 10 minutes, then add dropwise 400μL of 2mg / mL The DMF solution of chlorin e6 (Ce6, as the photosensitizer in this embodiment) was continued to react for 30 minutes. Centrifuge the reacted solution at 6000rpm for 5 minutes, remove the precipitate, centrifuge the upper l...
Embodiment 2
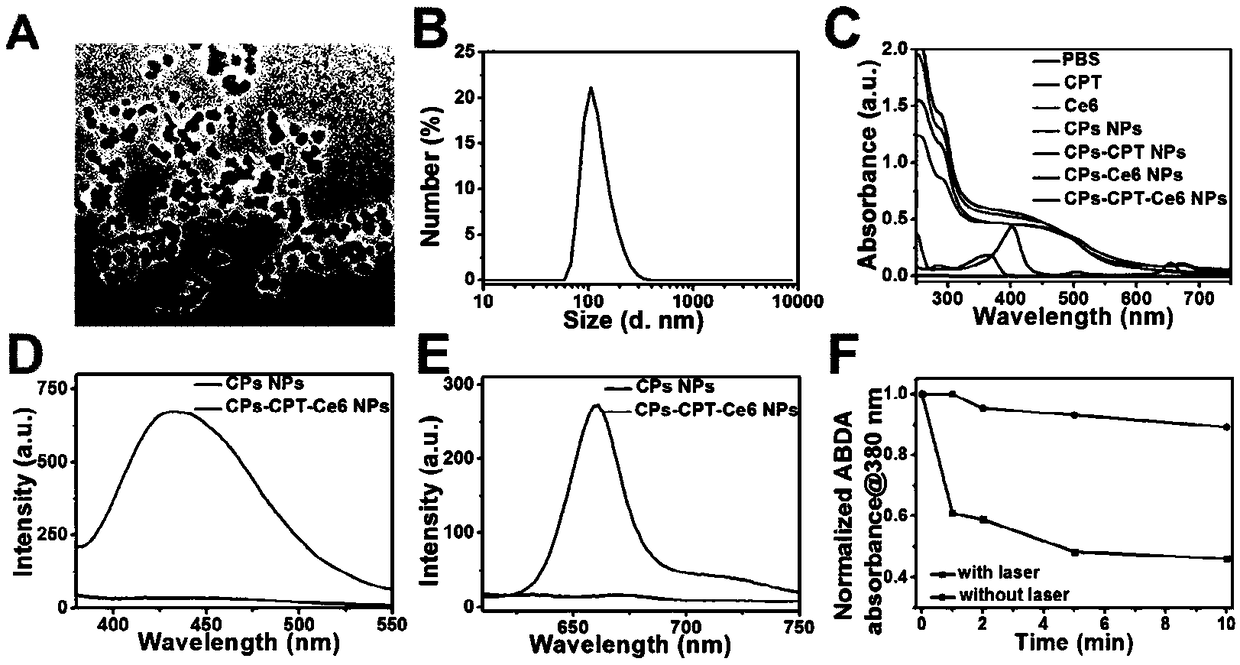
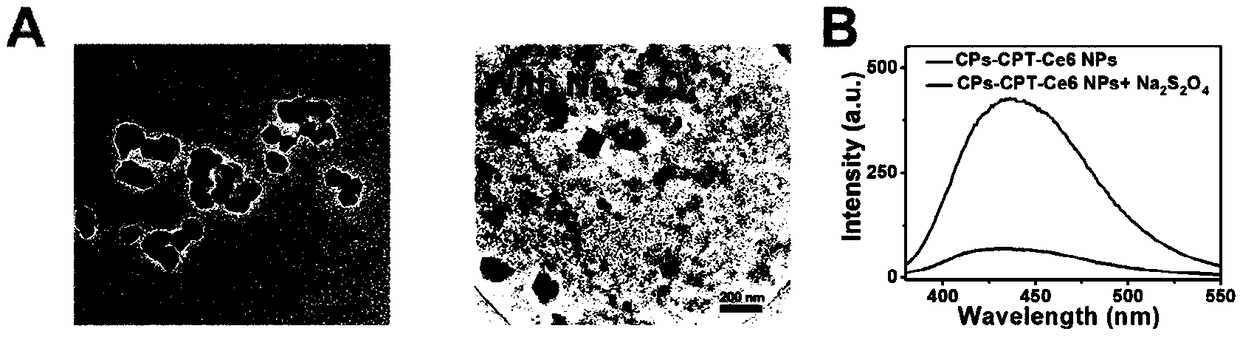
[0037]The relevant physicochemical properties of the polymer nanomedicine synthesized in Example 1 were characterized to prove the successful synthesis of the polymer nanomedicine. It is characterized by transmission electron microscope (TEM), particle size tester (DLS), ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer (UV-Vis), and fluorescence spectrometer. In addition, to verify the ability of polymer nanomedicine to generate active oxygen under 670nm laser irradiation, 9,10-anthracenyl-bis(methylene) dimalonic acid (ABDA) was used as active oxygen indicator, polymer nano After the drug was mixed with ABDA, the laser was irradiated for different times, and the absorption value change at 380nm was tested, normalized, and compared with the non-light-irradiated sample to prove the active oxygen generation ability of the polymer nano-medicine. To investigate the ability of nanopolymer drugs to respond to reductases, sodium dithionite (Na 2 S 2 o 4 ) is a reductase simulant, by testing ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Using cervical cancer cells (HeLa cells) as a model, using confocal fluorescence microscopy to test the ability of polymer nanomedicines to carry drugs and photosensitizers at the cell level; combined with reactive oxygen species fluorescent indicator 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) to investigate the ability of polymer nanomedicine to generate reactive oxygen species in cells; combined with live-dead double-stained fluorescent indicator (calcein-propidium iodide Calcein-AM-PI) to investigate the ability of polymer nanomedicine under light and without Therapeutic effect under light conditions. Using the Cell Viability Quantitative Detection Kit (CCK-8 kit), quantitatively test the therapeutic effect of the polymer nanomedicine under light and no light conditions.
[0044] The specific test results are as follows:
[0045] (1) After co-incubating the polymer nanomedicine with HeLa cells for 4 hours, the fluorescence of Ce6 and CPT were detected by confocal...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com