Method for large-scale continuous preparation of nanometer zero-valent metal materials
A nano-zero-valent, metal material technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, can solve the problems of being easily oxidized by air, the cost of raw materials, and the troublesome effective utilization rate, so as to improve the dispersion and reduction activity, optimize the reduction reaction conditions, and avoid The effect of reductive activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Weigh the garlic waste, crush and sieve through 40 mesh, throw it into water, stir and soak for 24 hours; collect the garlic waste particles floating on the water surface, add a mixed solution of magnesium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide to adjust its pH Value is at 13, after keeping stirring for 12 hours, the particles therein are collected;
[0036] Prepare 50 liters of ferric chloride ion solution of 0.01M concentration, initial pH is 2.5, drop into last step and prepare 2000 grams (dry basis measurement) of garlic waste granule (adsorbent), after stirring reaction 30 minutes, adsorbent is filtered, with After washing with distilled water for 3 times, add 100 liters of water to make a uniform slurry;
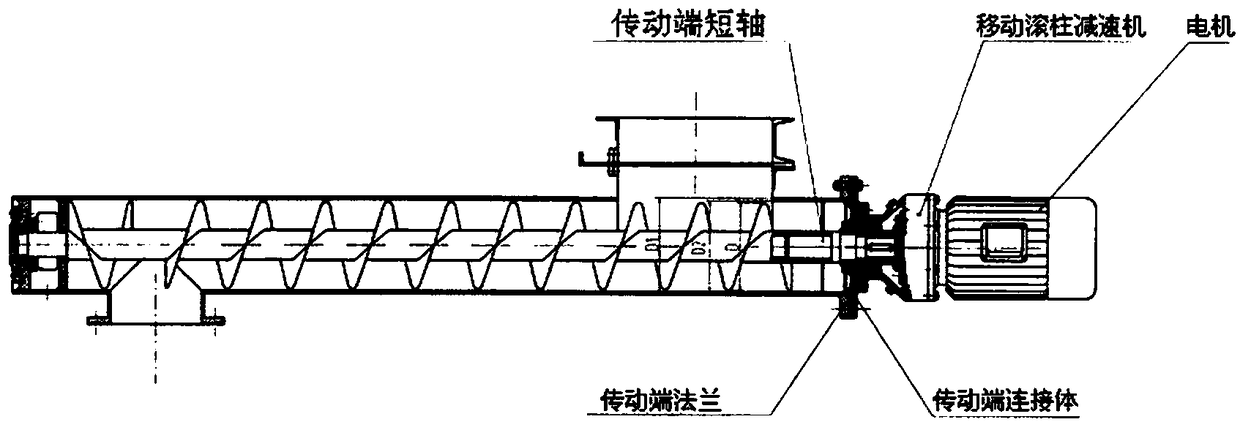
[0037] Prepare 100 liters of sodium borohydride solution with a concentration of 0.1M, and pump the above-mentioned garlic waste particle slurry loaded with iron ions into an auger reactor with a total reaction space of 500 liters with an infusion pump. The mixing, con...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Weigh the garlic waste, crush and sieve through 80 mesh, throw it into water, stir and soak for 12 hours; collect the garlic waste particles floating on the water surface, add a mixed solution of calcium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide to adjust its pH Value is at 11, after keeping stirring for 24 hours, the particles therein are collected;
[0040] Prepare 100 liters of ferric chloride ion solution of 0.02M concentration, initial pH is 2.5, drop into last step and prepare 10 kilograms (dry basis measurement) of garlic waste granule (adsorbent), after stirring reaction 30 minutes, adsorbent is filtered, with After washing with distilled water for 3 times, add 500 liters of water to make a uniform slurry;
[0041] Prepare 500 liters of sodium borohydride solution with a concentration of 0.2M, and pump it into the auger reactor with a total reaction space of 500 liters with the above-mentioned garlic waste particle slurry adsorbed and loaded with iron ions, respectively. ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Weigh the garlic waste, crush and sieve through 80 mesh, throw it into water, stir and soak for 12 hours; collect the garlic waste particles floating on the water surface, add a mixed solution of calcium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide to adjust its pH Value is at 11, after keeping stirring for 24 hours, the particles therein are collected;
[0044] Prepare 200 liters of nickel chloride ion solution of 0.05M concentration, initial pH is 6.5, drop into last step and prepare 10 kilograms (dry basis measurement) of garlic waste particle (adsorbent), after stirring reaction 30 minutes, adsorbent is filtered, with After washing with distilled water for 3 times, add 100 liters of water to make a uniform slurry;
[0045] Prepare 100 liters of sodium borohydride solution with a concentration of 0.05M, and pump the above-mentioned garlic waste particle slurry loaded with iron ions into an auger reactor with a total reaction space of 500 liters with an infusion pump. The mixing, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com