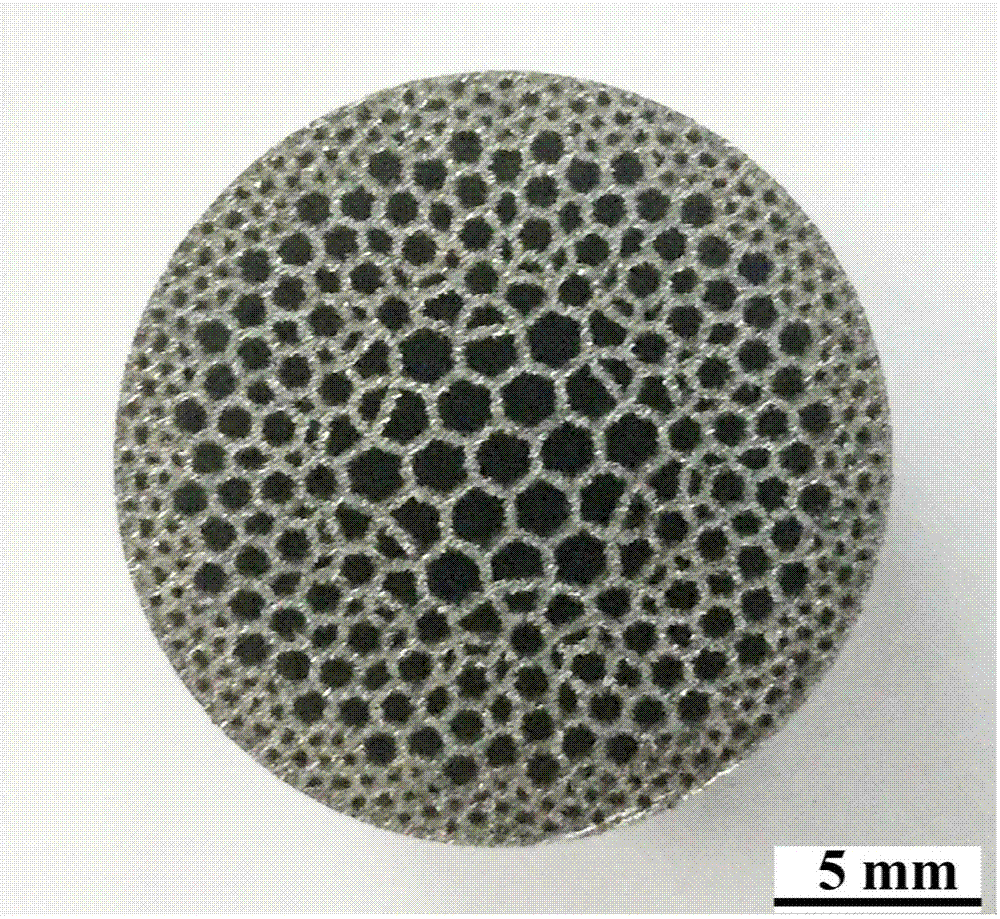
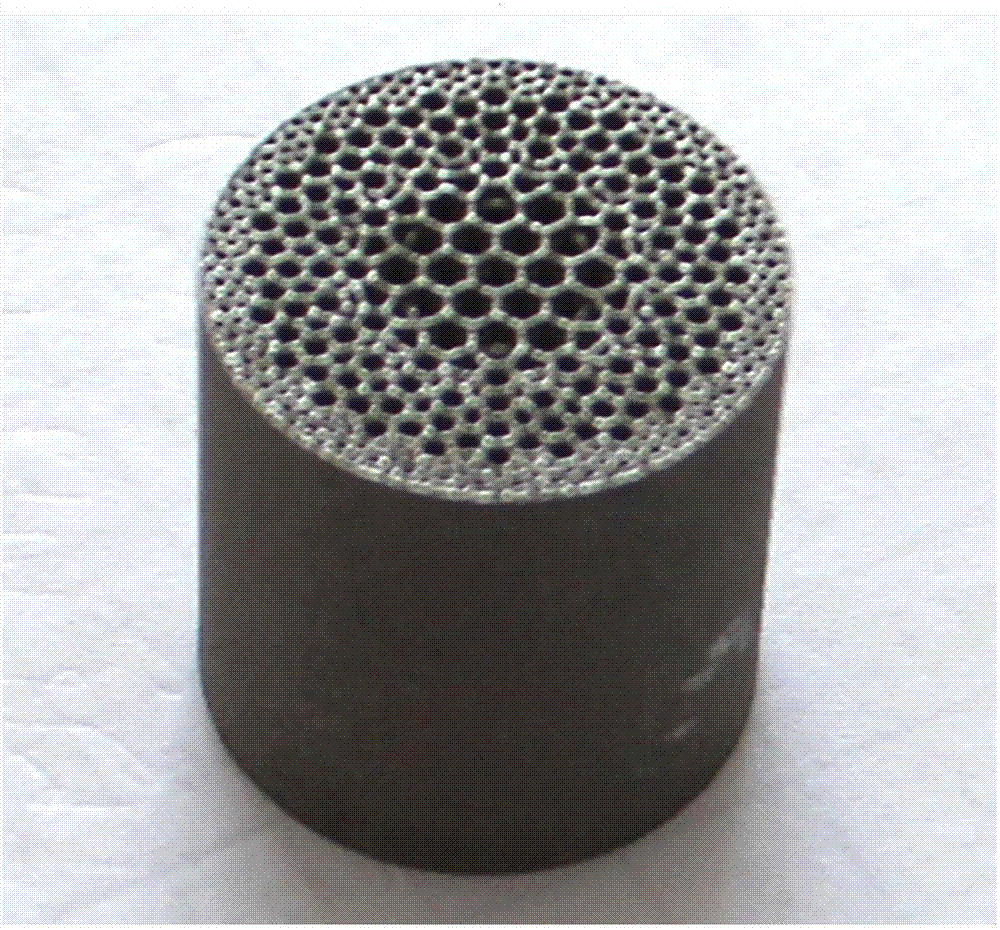
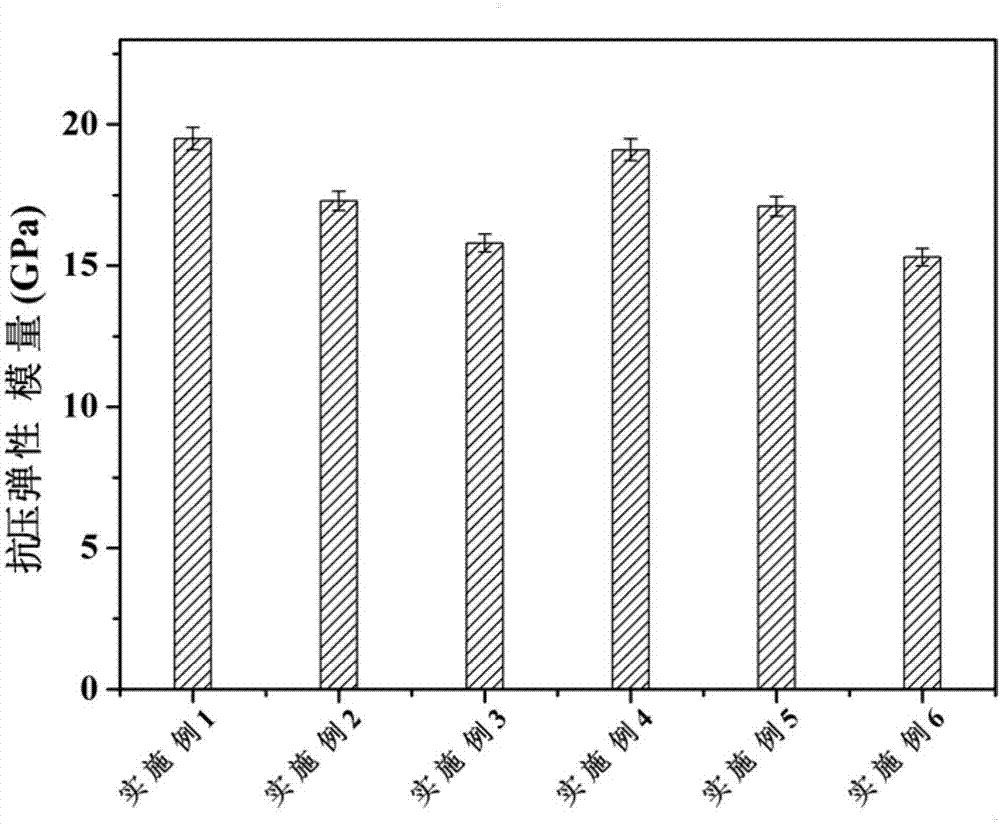
Function gradient bionic structure titanium alloy artificial implant and forming method thereof
A functional gradient, titanium alloy technology, applied in bone implants, metal processing equipment, prostheses, etc., can solve the problems of antibacterial coating cracks, limited bonding strength, broken, etc., to avoid stress shielding and reduce elastic modulus , Improve the effect of bonding strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Step 1: Use a CT scanner to scan the bones of different people to obtain 3D model data, and use the topology optimization TOSCA software to design the bones with a gradient design of a honeycomb structure with a gradient factor of 1.5:1 to obtain a 3D model of the gradient bionic structure implant;
[0034] Step 2: Perform curved surface repair on the gradient bionic structure implant model described in Step 1, and perform layered slice processing;
[0035] Step 3: Prepare the absolute ethanol solution of the surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide to obtain a solution with a concentration of 0.5 mol / L. Add nano silver particles with an average particle size of 15 nm to the solution, and after ultrasonic vibration dispersion Vacuum drying to obtain highly dispersed nano silver powder;
[0036] Step 4: After weighing the highly dispersible nano silver powder obtained in step 3 and the spherical medical pure titanium powder with a particle size of 15-60 μm and a purity of 99.5...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is that in step 3, the average particle size of nano silver particles is selected as 50 nm; in step 4, the titanium alloy is set to Ti-Zr alloy, and in step 5, the laser output line energy density is 300J / m, the concentration of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide is 2mol / L, and the others are the same as in Example 1.
[0043] The antibacterial performance test of the functionally graded bionic titanium alloy artificial implant formed in this example was carried out. Staphylococcus aureus was selected as the test object, and the artificial hip was tested according to QB / T2591-2003 "Antibacterial Plastics-Antibacterial Performance Test Method and Antibacterial Effect" The antibacterial properties of the joints, the results showed that after 24h of the test, the antibacterial rate of the titanium alloy hip joint against Staphylococcus aureus reached 96%, and the antibacterial rate still reached 95% after 72h of the test, and it...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The difference between this embodiment and Example 2 is that in step 4, the titanium alloy is set to Ti-Nb alloy, the mass ratio of nano silver particles to spherical titanium alloy powder is set to 1:95; the ball milling speed is set to 250 rpm; In step 5, the laser output line energy density is 100 J / m; in step 6, the annealing temperature is set to 250° C., the concentration of hexaalkyltrimethyl ammonium bromide is 1 mol / L, and the others are the same as in Example 2.
[0046] The antibacterial performance test of the functionally graded bionic titanium alloy artificial implant formed in this example was carried out. Staphylococcus aureus was selected as the test object, and the artificial hip was tested according to QB / T2591-2003 "Antibacterial Plastics-Antibacterial Performance Test Method and Antibacterial Effect" The antibacterial properties of the joints, the results show that after 24h of the test, the antibacterial rate of the titanium alloy hip joint against Sta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com