Method for removing hexavalent chromium in wastewater by magnetic cellulose/polyglutamic acid coupling material
A polyglutamic acid and cellulose technology, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of low selectivity, not very strong, enhancement, etc., and achieve a wide range of raw material sources , low price, and low processing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A kind of method utilizing magnetic cellulose / polyglutamic acid coupling material of the present invention to remove hexavalent chromium in waste water comprises the following steps:
[0035] 1. Preparation of magnetic cellulose / polyglutamic acid coupling materials
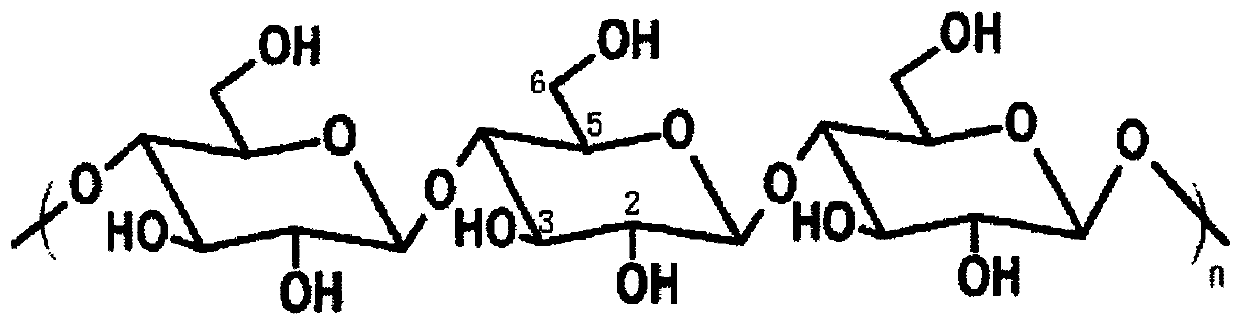
[0036] The peeled kenaf stems were dried at 80°C for 2 hours, pulverized by a pulverizer and then ground, passed through a 100-mesh sieve, and dried at 65°C for 2 hours. Take 10g of the above powder and disperse it into 60ml of n-hexane, 50°C for 3h to remove the vegetable wax, then add the dewaxed ramie fiber into 500ml of NaOH with a molar concentration of 4mol / L, shake at 25°C for 24h, then filter it, and then Wash with a large amount of ultrapure water, ethanol, and methanol, then dry at 65°C for 2 hours, and cool to room temperature to obtain alkalized kenaf cellulose;
[0037] Weigh 2.0g of cellulose and 4.0g of polyglutamic acid (monomer molar ratio about 1:2.5-3) and mix them fully under an infrare...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A kind of method utilizing magnetic cellulose / polyglutamic acid coupling material of the present invention to remove hexavalent chromium in waste water comprises the following steps:
[0043] 1. Preparation of magnetic cellulose / polyglutamic acid coupling materials
[0044] This step is the same as Step 1 of Example 1.
[0045] 2. Treatment of hexavalent chromium wastewater
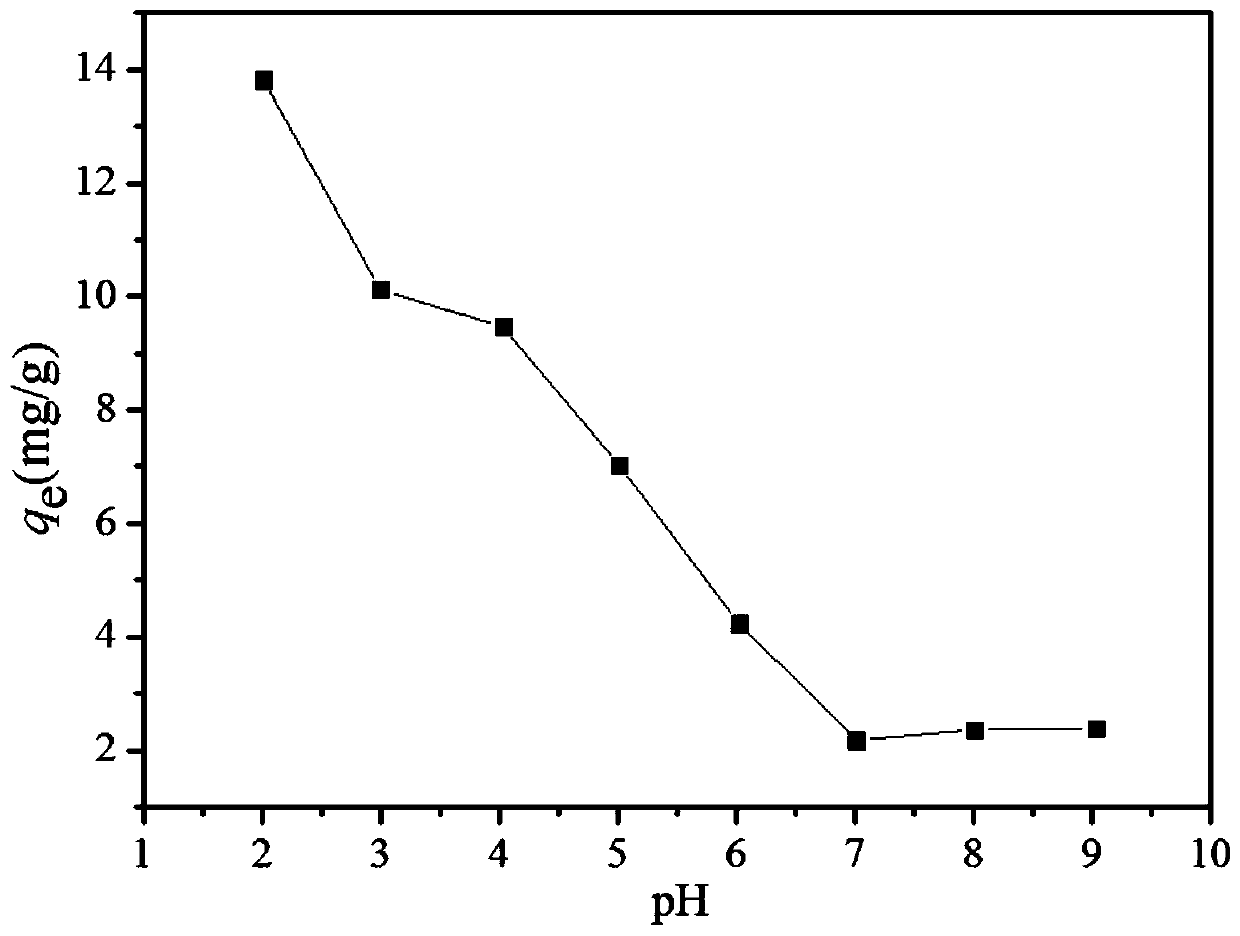
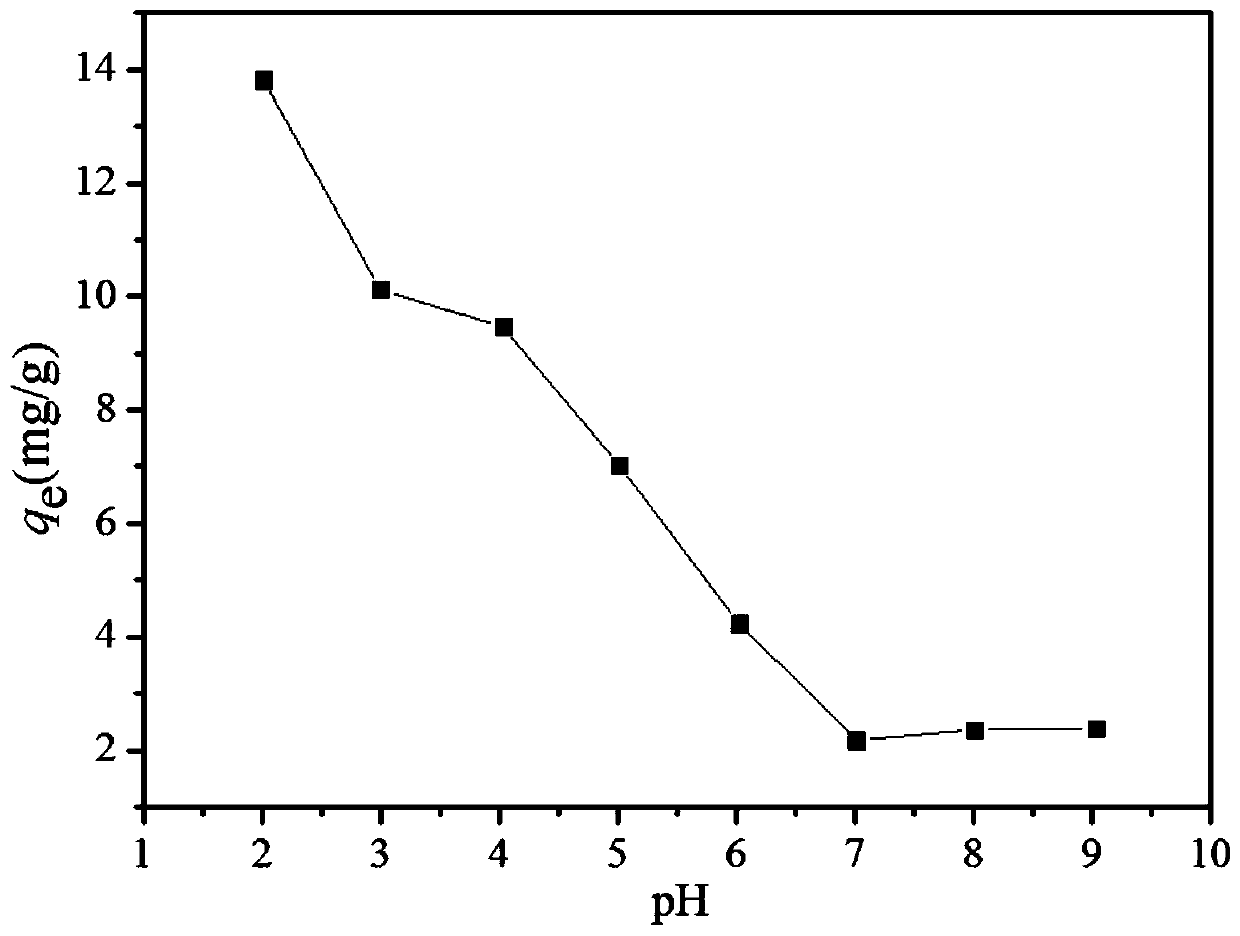
[0046] Add the magnetic cellulose / polyglutamic acid coupling material prepared by the above method to hexavalent chromium wastewater with an initial pH value of 2. The initial concentrations of hexavalent chromium ions are 10, 50, and 100 mg / L respectively, and each liter of wastewater The amount added in sodium humate / biochar magnetic composite material is 1.0g based on the dry weight of the sodium humate / biochar magnetic composite material. The reactor is placed in a shaking box with a rotation speed of 150rpm, and the temperature is kept at 30°C. After shaking for 24 hours, the magnetic cellulo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com