Heparinase high-yielding strain and breeding method thereof
A high-yielding strain, heparinase technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of wasting manpower and material resources, and achieve the effect of increasing yield and saving manpower
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
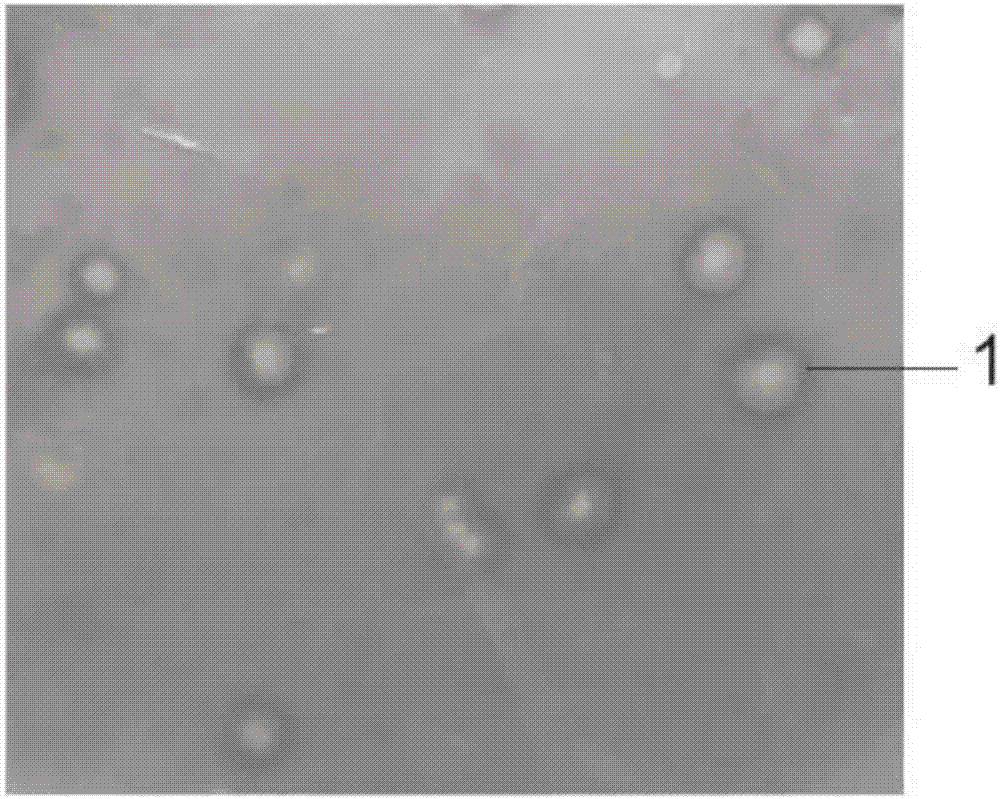
[0033] Example: Add 1.0 g of the collected soil sample into a test tube containing 10 mL of sterile saline and shake well, then take 5 mL of the suspension and add it to a conical flask containing 25 mL of enrichment medium, shake at 200 r / min at 37 °C The flasks were cultured for 2 days. Dilute the enriched cultured bacterial solution with sterile normal saline gradient to an appropriate dilution, and take an appropriate amount of bacterial solution and spread it on the primary screening plate. After the strains on the plate grow to a certain size, wash off the colonies with distilled water, add 2% protamine solution, and place at 37°C for 1 hour. Pour off the protamine solution, wash it with distilled water, and place it at room temperature for a period of time, and a transparent circle will appear at the place where the original colony grew. Select the strain with a larger ratio of transparent circle to colony diameter and transfer it to the seed medium. Pick the colony w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com