Preparation method of butylene glycol fatty acid ester and application of butylene glycol fatty acid ester to gel factor
A fatty acid ester and butanediol technology, which is applied in the preparation of carboxylic acid esters, organic compounds, gel preparation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 This example illustrates the synthesis of 1,4-butanediol stearate and its application as a gelling factor
[0037] The synthetic reaction formula of this reaction is:
[0038]
[0039] Weigh 0.45g of 1,4-butanediol and 3.55g of stearic acid into a three-necked flask, and put it in a nitrogen atmosphere to preheat to 178 o In the oil bath of C, add 0.0192g p-toluenesulfonic acid after melting, and cool down to 80 after 3 hours of reaction o C. Pour it into chloroform while it is hot, add methanol after dissolving until no white precipitate appears in the upper layer, and repeat twice. The precipitate was dissolved in chloroform, and rotary evaporation gave a white product with a melting point of 77.2 o c.
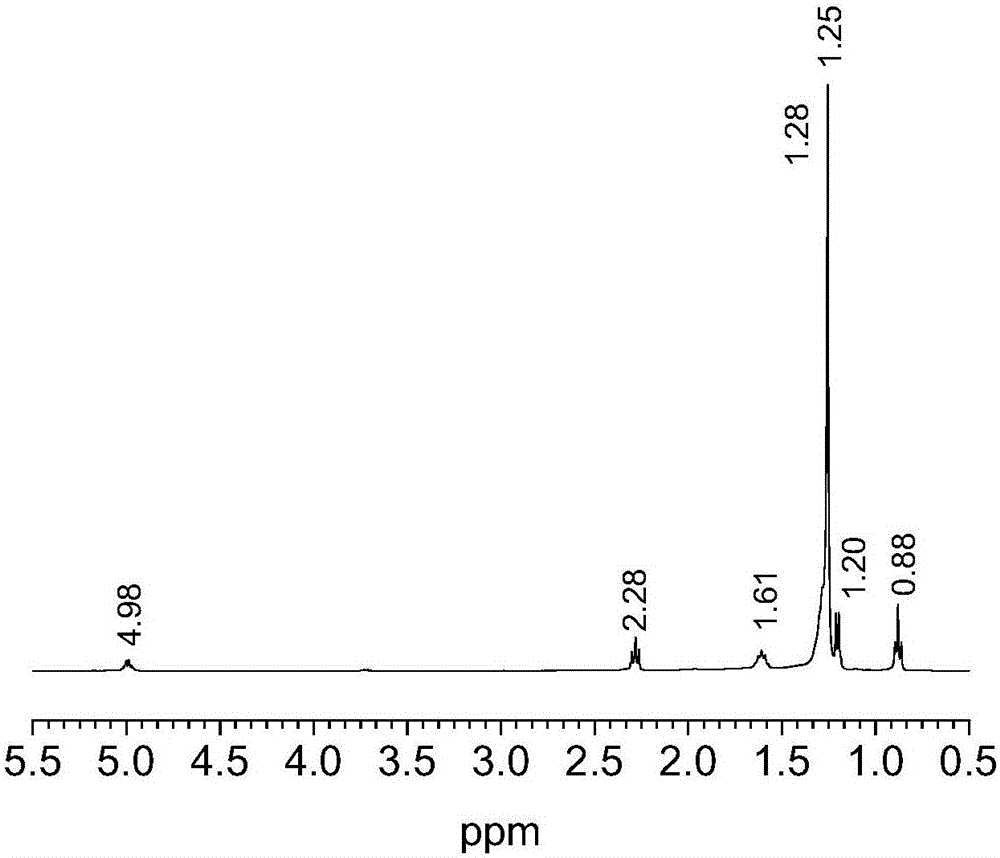
[0040] Its nuclear magnetic spectrum shows (nuclear magnetic picture as figure 1 shown), 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ4.09 (s, 4H) ,2.27 – 2.31 (t, 4H) , 1.70 (s,4H) , 1.60 – 1.63 (t, 4H) , 1.28 (s,4H) , 1.25(s, 52H) , 0.86 – 0.90 (t, 6H).
[0041] T...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 This example illustrates the synthesis of 2,3-butanediol stearate and its application as a gelling factor
[0043] The synthetic reaction formula of this reaction is:
[0044]
[0045] Weigh 0.45g of 2,3-butanediol and 3.55g of stearic acid into a three-necked flask, and put it in a nitrogen atmosphere to preheat to 178 o In the oil bath of C, add 0.0192g p-toluenesulfonic acid after melting, and cool down to 80°C after reacting for 3.5h o C. Pour it into chloroform while it is hot, add methanol after dissolving until no white precipitate appears in the upper layer, and repeat twice. The precipitate was dissolved in chloroform, and rotary evaporation gave a white product with a melting point of 79.5 o c.
[0046] Its nuclear magnetic spectrum shows (nuclear magnetic picture as figure 2 shown), 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ( 6H) , 0.86 – 0.90 (t, 6H).
[0047] The number of 2,3-butanediol stearate synthesized in this example is b.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3 This example illustrates the gelling effect comparison between the gelling factor of the present invention and the sucrose ester gelling factor
[0049] Compounds a and b and sucrose esters obtained in implementation 1 and implementation 2 were mixed with liquid paraffin, olive oil, n-butanol, and isobutanol respectively, heated and cooled to room temperature, and their gel properties were evaluated.
[0050] The specific gel properties are shown in Table 1.
[0051] The gel performance of table 1 gel factor
[0052]
[0053] Compound a (1,4-butanediol stearate), compound b (2,3-butanediol stearate); the gel-sol transition temperature in brackets, unit:o c.
[0054] The results show that compound a can form a gel in liquid paraffin, olive oil, n-butanol, and isobutanol, and has thermoreversible properties, that is, it can become a sol after heating, and can form a gel again after cooling, and its gel-sol The transition temperature is 51.5 o C. 48.0 o C,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com