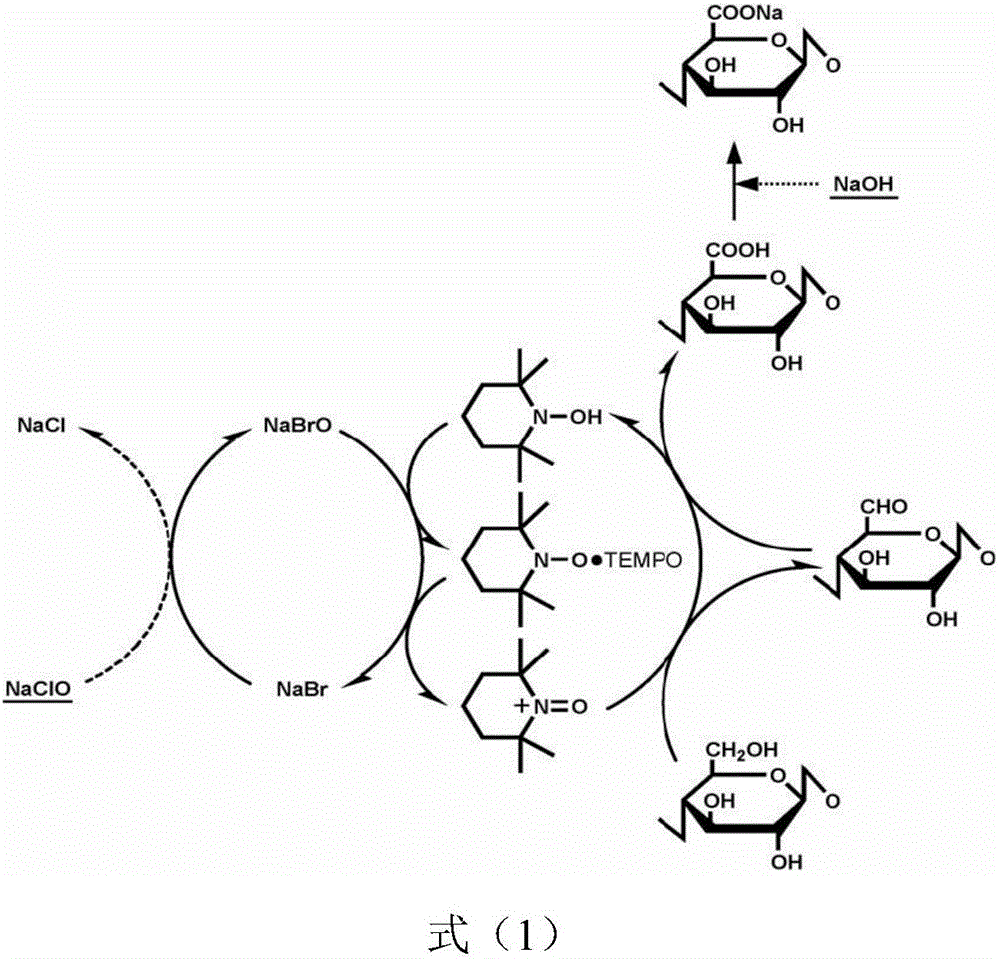
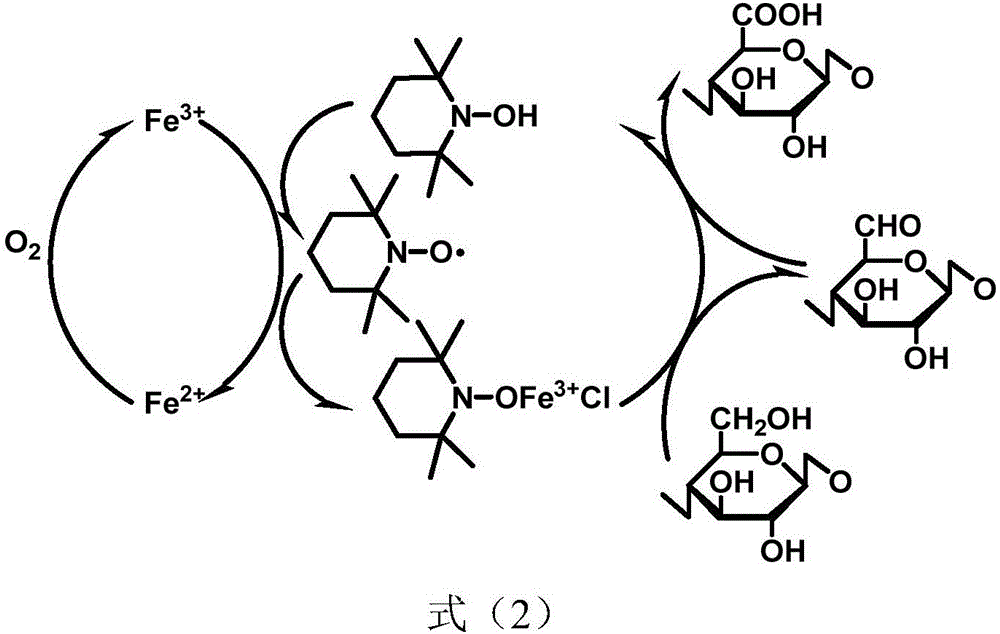
Method for preparing C6-site selective carboxylation cellulose by using air as oxidizing agent
A cellulose and selective technology, applied in the field of preparation of oxidized cellulose, can solve the problems of reduced equipment corrosion, high production risk, explosiveness, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] (1) Soak 5 g of absolute-dry bleached softwood kraft pulp in a 0.5M sodium hydroxide solution, perform an alkaline pretreatment for 20 minutes, and then wash the cellulose to reduce the pH to 9.5;
[0047] (2) Prepare Na with a total concentration of 0.1M at a molar ratio of 6:4 2 CO 3 / NaHCO 3 200 mL of buffer solution. Dissolve 0.1g TEMPO, 0.25g iron nitrate nonahydrate, and 0.07g potassium chloride in the prepared buffer solution. Then add the above-mentioned alkaline pretreated cellulose into the buffer solution to form a suspension. At room temperature, air is blown into the reaction solution as an oxidant, and the reaction is stirred for 12 hours. The oxygen / primary hydroxyl molar ratio is 3;
[0048] (3) Filter the above reaction stock solution, filter and wash the insoluble oxidized cellulose product with deionized water until neutral, collect and dry to constant weight, and grind into powder. The yield of carboxylated cellulose was 95%, the content of carbo...
Embodiment 2
[0050] (1) Soak 5 g of absolute-dry bleached softwood kraft pulp in a 0.5M sodium hydroxide solution, perform an alkaline pretreatment for 20 minutes, and then wash the cellulose to reduce the pH to 9.5;
[0051] (2) Prepare Na with a total concentration of 0.1M at a molar ratio of 6:4 2 CO 3 / NaHCO 3 200 mL of buffer solution. Dissolve 0.1 g of 4-acetylamino-TEMPO, 0.25 g of iron nitrate nonahydrate, and 0.07 g of potassium chloride in the prepared buffer solution. Then add the above-mentioned alkaline pretreated cellulose into the buffer solution to form a suspension. At room temperature, air is blown into the reaction solution as an oxidant, and the reaction is stirred for 8 hours. The oxygen / primary hydroxyl molar ratio is 2;
[0052] (3) Filter the above reaction stock solution, filter and wash the insoluble oxidized cellulose product with deionized water until neutral, collect and dry to constant weight, and grind into powder. The yield of carboxylated cellulose was ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] (1) Soak 5 g of absolute dry bleached cotton pulp in a 0.5M sodium hydroxide solution, perform an alkaline pretreatment for 30 minutes, and then wash the cellulose to reduce the pH to 9.5;
[0055] (2) Prepare Na with a total concentration of 0.1M at a molar ratio of 6:4 2 CO 3 / NaHCO 3 200 mL of buffer solution. Dissolve 0.1 g of 4-acetylamino-TEMPO, 0.25 g of iron nitrate nonahydrate, and 0.07 g of potassium chloride in the prepared buffer solution. Then add the above-mentioned alkaline pretreated cellulose into the buffer solution to form a suspension. At room temperature, air is blown into the reaction solution as an oxidant, and the reaction is stirred for 12 hours. The oxygen / primary hydroxyl molar ratio is 3;
[0056] (3) Filter the above reaction stock solution, filter and wash the insoluble oxidized cellulose product with deionized water until neutral, collect and dry to constant weight, and grind into powder. The yield of carboxylated cellulose was 96%, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com