Nontarnishing multi-element nickel, tin and brass alloy and preparation method thereof
A brass alloy, anti-tarnish technology, applied in the field of non-ferrous metal processing, can solve the problem that it is difficult to achieve semi-continuous + hot billet uniform fine structure, tin-brass alloy is difficult to promote and industrial production, and the anti-tarnish property is difficult to meet the market development To meet the needs and other issues, achieve good golden luster, good cold and hot processing characteristics, and improve the effect of anti-tarnish ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0027] The preparation method of the copper alloy described in the present invention is: a. batching, feeding, smelting and casting according to the weight percentage; b. hot rolling; c. milling; d. intermediate rolling; e. edge trimming; f. intermediate annealing ; g. pickling; h. finish rolling; i. low temperature annealing; j. pickling;
[0028] The alloy of the present invention is smelted using the following raw materials: electrolytic copper, industrial pure nickel, pure aluminum, pure tin, copper-manganese alloy, pure tin, pure silicon, copper-boron alloy, copper-chromium alloy, phosphorus copper alloy, and rare earth alloy.
Embodiment 1
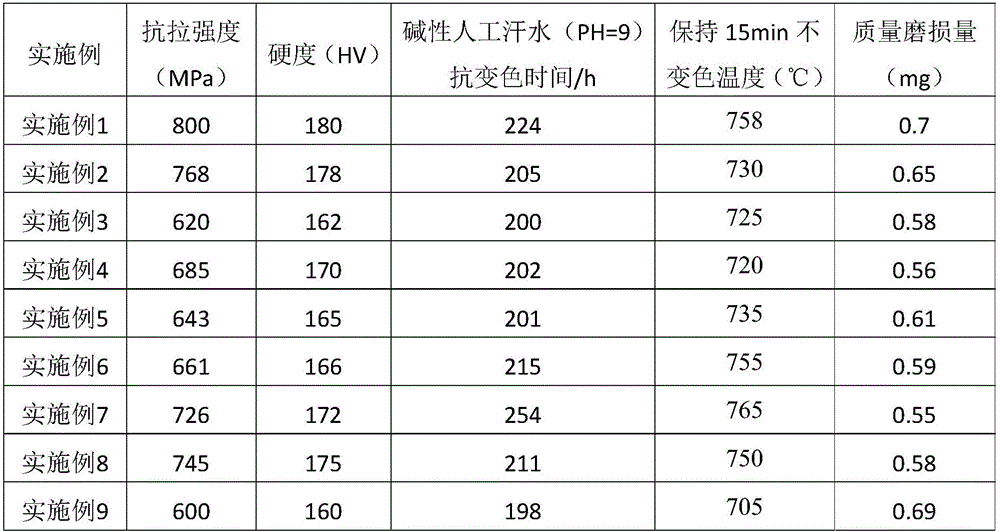
[0030] The composition of the alloy is shown in Example 1 of Table 1.
[0031] 1. Melting: use non-vacuum induction furnace for smelting, the order of adding alloys is: first add copper (Cu), after melting, then add pure aluminum (Al), nickel (Ni), silicon (Si), copper-manganese alloy ( Cu‐Mn), and then add zinc (Zn) at a low temperature of 1120 °C, and add copper boron (Cu‐B) alloy, copper chromium alloy (Cu‐Cr), pure tin (Sn) after it is completely melted. Add 0.5‰ phosphorus copper alloy (Cu-P) deoxidation and rare earth purification solution, and cover with calcined charcoal; the melting temperature is 1150°C, and the casting temperature is controlled at 1100°C.
[0032] 2. Hot rolling of cast slab, first heat the cast ingot to 550°C, keep it warm for a period of time, then raise the temperature to 820°C for soaking, and the furnace temperature is 820°C, 11 passes of rolling, the total deformation of hot rolling is 90%.
[0033] 3. Face milling: face milling of the alloy ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The composition of the alloy is shown in Example 2 of Table 1.
[0041] 1. Melting: use non-vacuum induction furnace for smelting, the order of adding alloys is: first add copper (Cu), after melting, then add pure aluminum (Al), nickel (Ni), silicon (Si), copper-manganese alloy ( Cu‐Mn), and then add zinc (Zn) at a low temperature of 1130 °C, and add copper boron (Cu‐B) alloy, copper chromium alloy (Cu‐Cr), pure tin (Sn) after it is completely melted. Add 0.5‰ phosphorus copper alloy (Cu-P) deoxidation and rare earth purification solution, and cover with calcined charcoal; the melting temperature is 1140°C, and the casting temperature is controlled at 1120°C.
[0042] 2. Hot rolling of cast slab, first heat the cast ingot to 590°C, keep it warm for a period of time, then raise the temperature to 840°C for soaking, and the furnace temperature is 840°C, 11 passes of rolling, the total deformation of hot rolling is 86%
[0043] 3. Face milling: face milling of the alloy (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com