Oryza sativa MIT1 gene as well as encoded protein and application thereof
A rice and protein technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of plant tillering or branch number increase, plant height reduction, etc., and achieve the effects of inhibiting tillering, increasing productivity, and huge economic value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
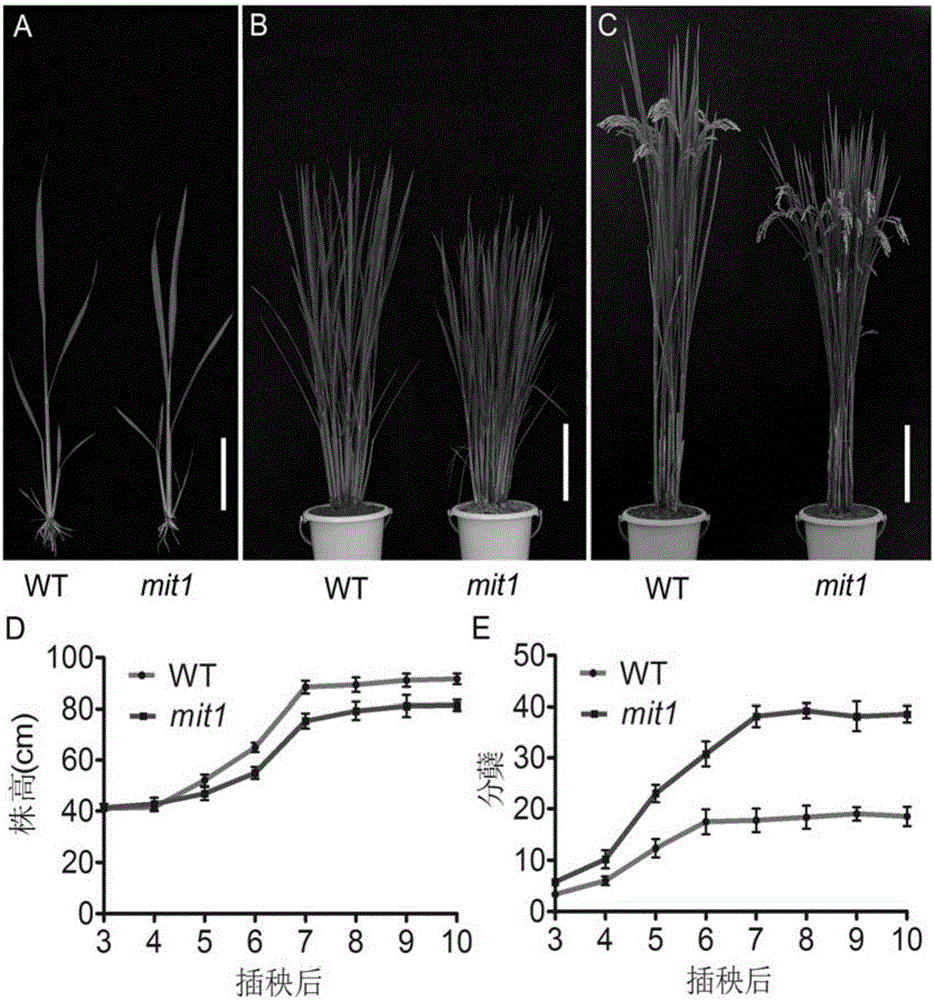
[0037] The acquisition and phenotype analysis of embodiment 1 mutant
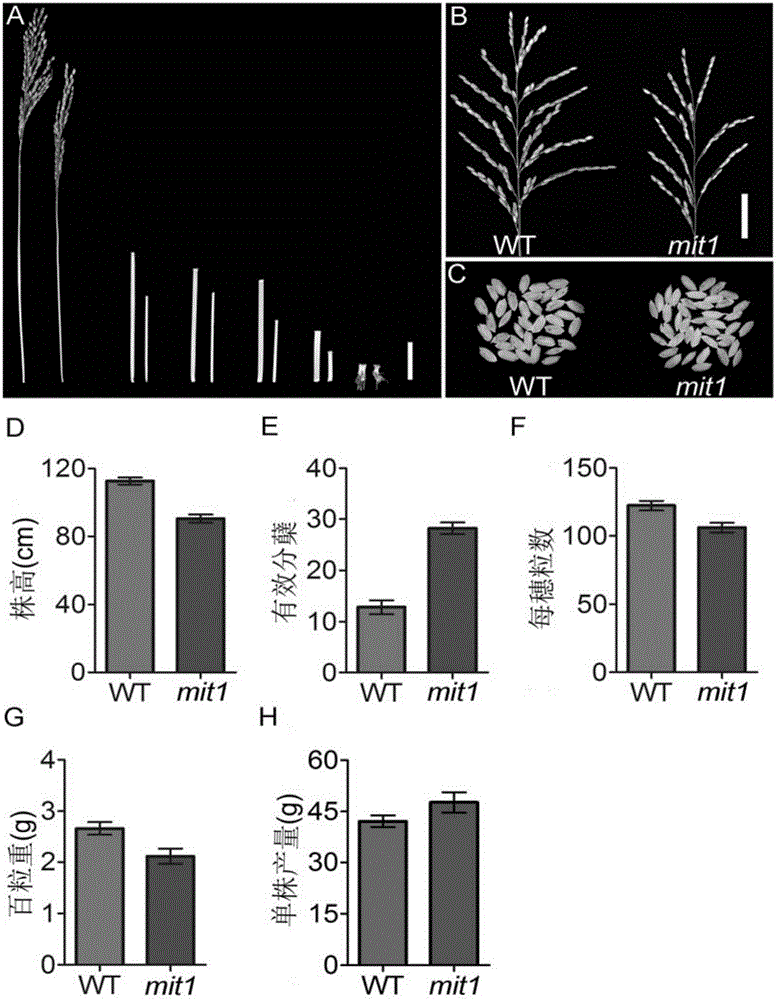
[0038] mutant mit1 is 60 Co-γ radiation mutagenesis japonica rice variety Chunjiang 06 (irradiation dose 200Gy, dose rate 10Gy·h -1 ), phenotypically it has many changes compared with the wild type. The mutant mit1 exhibited a phenotype of moderately increased tillers and semi-dwarf plant height. The plant height at maturity was slightly shorter, about 80% of the wild type, and the internodes were shortened to a certain extent; the number of tillers increased, about 80% of the wild type. type 2 times (see figure 1 ); the plant type is compact, and the tiller angle and leaf angle are small; at different development stages after transplanting, the plant height of mit1 is lower than that of wild type, and the tiller is more than that of wild type (see figure 2 ). The fertility of the mutant mit1 is normal, and the number of grains per panicle is about 70% of the wild type, but the total number of grains p...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 Acquisition of Rice MIT1 Gene and Verification of Functional Complementation
[0040] 1. Acquisition of rice MIT1 gene
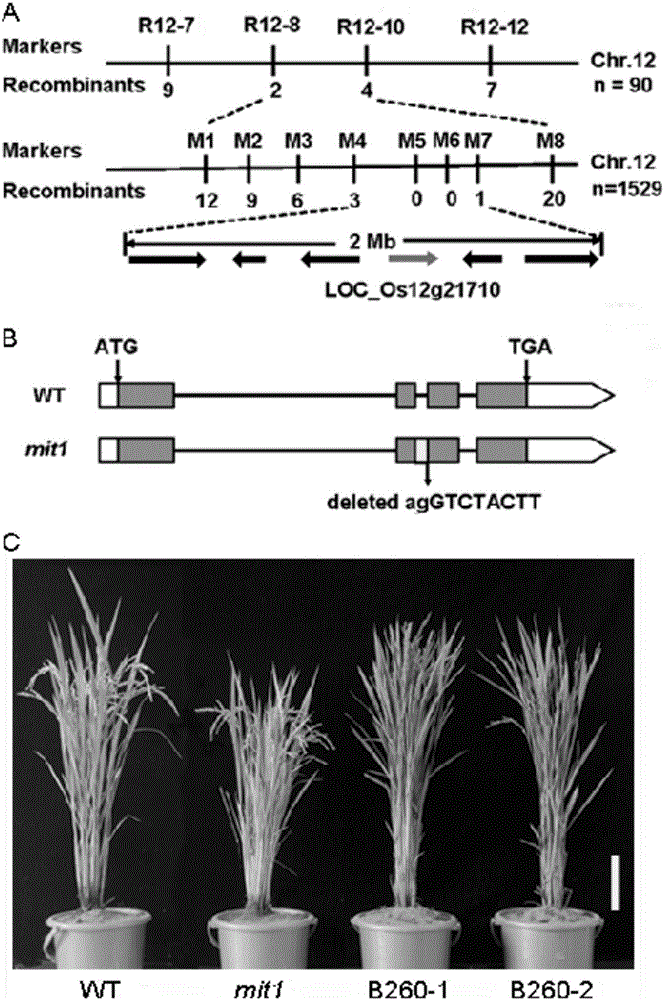
[0041] The MIT1 gene of the present invention is obtained by cloning the mutant mit1 by adopting a map position cloning method.
[0042] through 60 Mutant mit1 induced by Co-γ radiation has been confirmed to have stable inheritance characteristics after multiple generations of self-planting. Homozygous mutant mit1 was crossed with normal phenotype indica Dular, all crosses F 1 Medium individuals were dwarf and moderately increased tiller phenotype. in F 2 There was obvious segregation in the planting population. Through investigation and analysis, it was found that the segregation ratio of the wild type and the mutant was in line with the 3:1 genetic segregation ratio. Therefore, it can be inferred that the mutant traits of the rice mutant with moderately increased dwarf tillering are controlled by a pair of recessive genes.
[0043] I...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3 Homologous protein sequence alignment and evolution analysis of MIT1
[0052] Sequence alignment of rice Z-ISO (MIT1), maize Z-ISO (ZmZ-ISO) and Arabidopsis Z-ISO (AtZ-ISO) showed relatively high homology. According to the prediction of the rice genome annotation website (http: / / rice.plantbiology.msu.edu / ), MTI1 contains 368 amino acids, ChloroP 1.1Prediction Server predicts that the protein has a chloroplast transit peptide (box part) at the N-terminus, and the whole protein Contains 5 transmembrane regions (underlined), and an NnrU domain (see Figure 4 Figure A).
[0053] Z-ISO is 15-cis-ζ-carotene isomerase, which is one of the key enzymes involved in the biosynthetic pathway of carotenoids. Phylogenetic tree analysis shows that MTI1 has homologous genes in higher plants and diatoms, and they all have a common origin—the NnrU gene, which is found in denitrifying bacteria, such as Agrobacterium fabrumstr.C58 and Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 (see Figure ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com