Method for detecting carotenoid content of tea leaves by confocal micro-Raman
A confocal microscopy and carotene technology, applied in Raman scattering, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of unstable carotenoid properties, destructive properties, cumbersome detection steps, and inability to achieve online detection, etc. Economic benefits, shortened detection time, and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] The sample stage structure provided by the present invention is as Figure 4 As shown, it includes: slide glass 2, cover glass 1 and stage 3. Both the slide glass 2 and the cover glass 1 are made of quartz.
[0064] The surface of slide glass 2 is used to place tea sample, and slide glass 2 is rectangular, and two long sides of slide glass 2 are respectively fixed with a slide block 7, and spring pin is fixed on each slide block 7, and two slide blocks 7 corresponding to the location of the spring pin on the A silicon chip 5 is embedded on the slide glass 2 .
[0065] The cover glass 1 is rectangular, and the long side of the cover glass 1 is hinged with one of the sliders 7, and the cover glass 1 is overturned to compress the tea sample. The cover glass 1 is used to keep the surface of the tea leaves flat, to minimize the variation of the object distance when detecting different points on the tea samples, and to ensure that the Raman detection lens can be accurately...
Embodiment 2
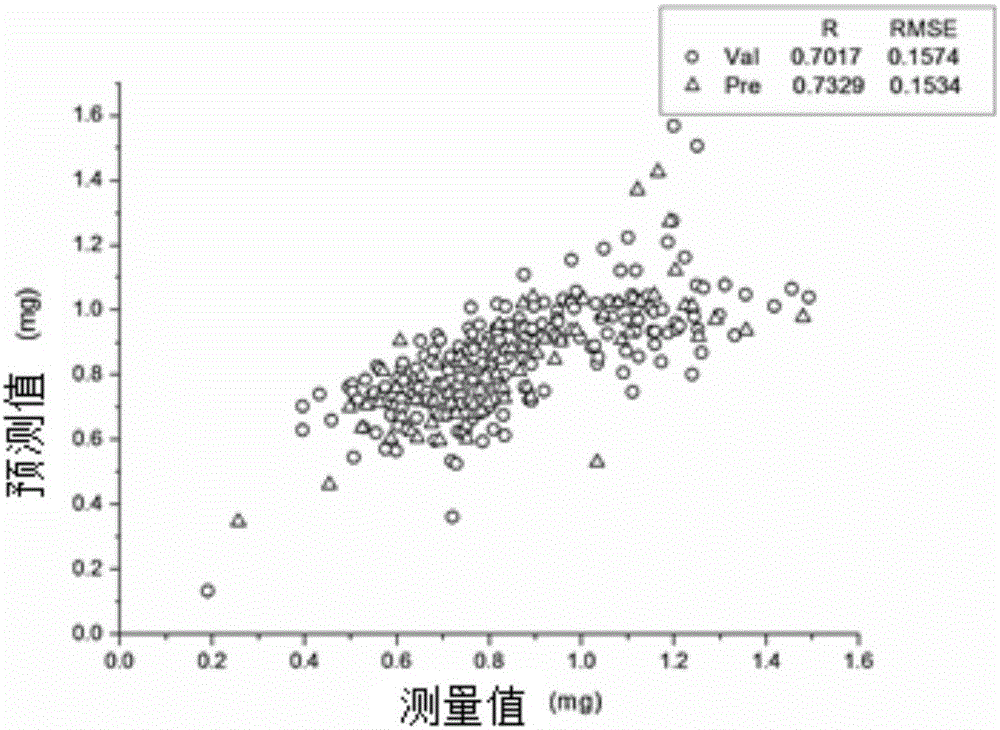
[0068] Take 315 pieces of Longjing 43 leaves. For each Longjing 43 leaf, randomly cut the leaves on both sides of the veins to obtain two tea samples. The mass of each tea sample is about 0.1g. After cutting, the actual measurement and record Ww. One of them is directly placed in the bag and labeled as Raman spectroscopic material A, the other is cut into pieces and placed in a centrifuge tube and labeled, added with 10mL of alcohol solution with a mass fraction of 95%, and stored in a dark room for about 24 hours , as UV spectrophotometric material B. For the same tea leaves, Raman spectroscopic material A and UV spectrophotometric material B have the same label.
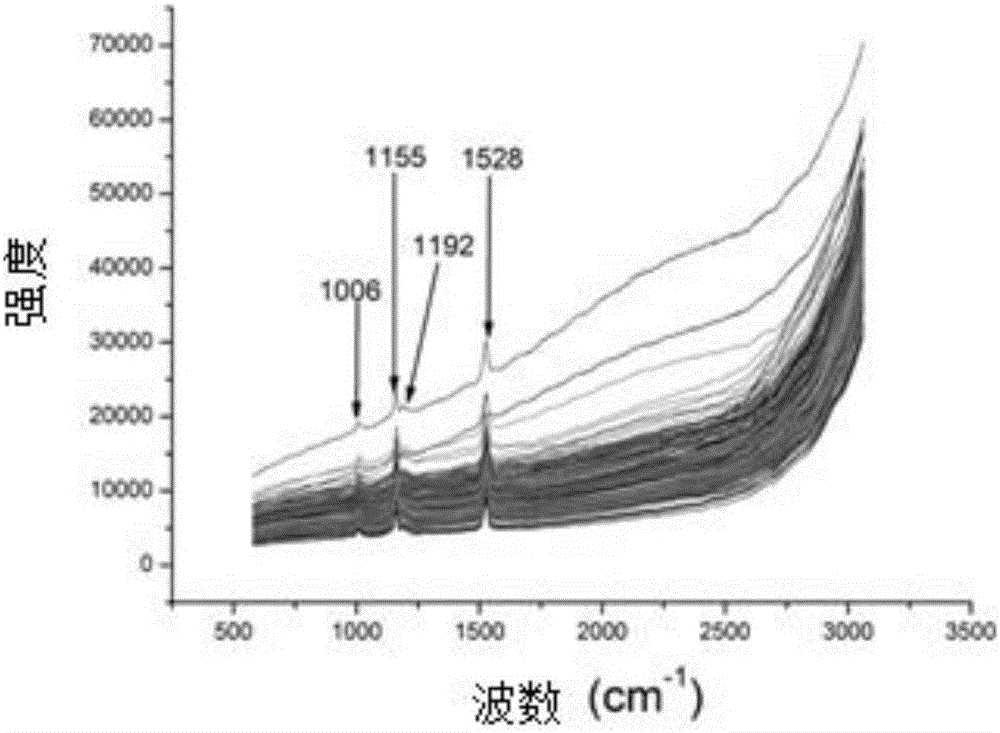
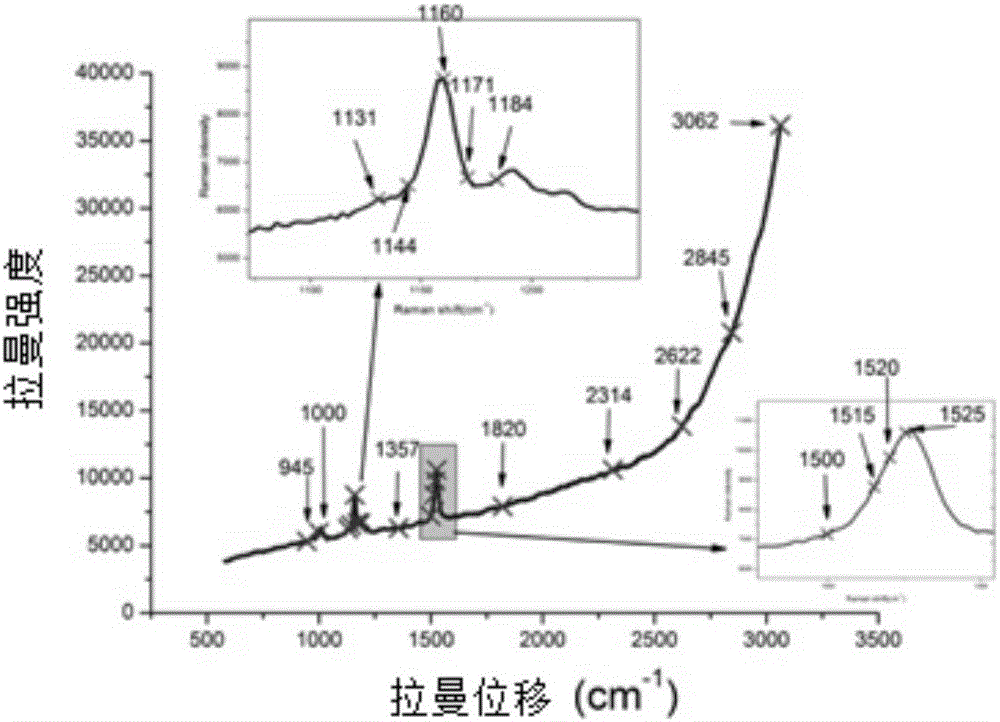
[0069] The Raman spectroscopic material A is fixed on the Raman stage described in Example 1, using a Renishaw confocal laser microscope Raman instrument (Renishaw in Via-Reflex 532 / XYZ), the excitation wavelength is 532nm; the laser intensity 50mW; integration time 1s; Raman spectrum detection wavelength range i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com