Cement-based composite material used for 3D printing as well as preparation method and application thereof
A composite material and 3D printing technology, which is applied in the field of building materials, can solve problems such as slow condensation, low toughness, and difficult molding, and achieve the effects of low long-term strength, long service life, and guaranteed safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
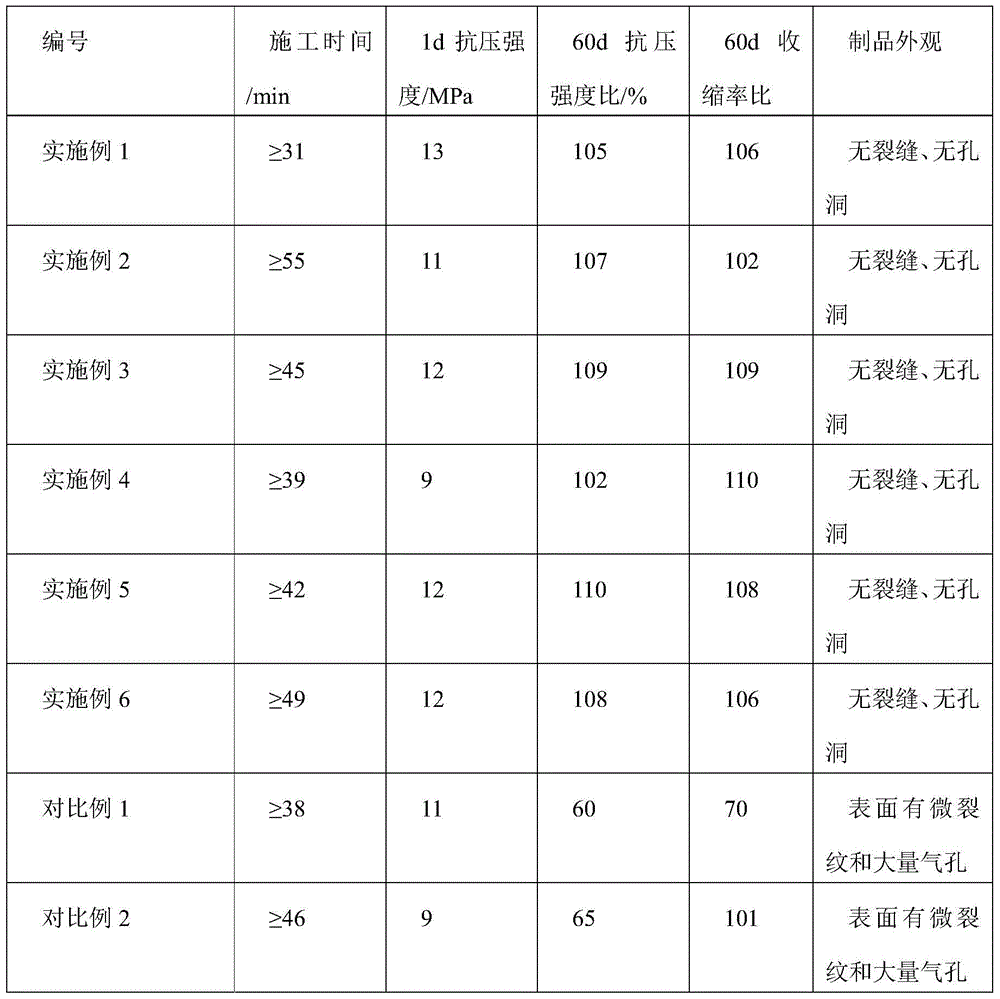
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] A preparation method for a cement-based composite material for 3D printing, comprising the steps of:
[0072] Step 1: Prepare composite cementitious material: Mix 10kg P.I. type Portland cement, 30kg steel slag powder and 60kg sulphoaluminate cement evenly, wherein the steel slag powder is obtained by mixing 20kg slag and 10kg steel slag; The prepared composite gel material is ready for use.
[0073] Step 2: Preparation of anti-carbonation agent: Use a paint disperser to fully mix 0.75kg of chlorine partial emulsion and 6.75kg of styrene-acrylic emulsion for use.
[0074] Step 3: Prepare 3D printing fiber cement composite material, weigh 1.5kg shrinkage inhibitor (alkyl polyoxyethylene ether), 330kg aggregate (ceramsite), 5kg fiber reinforced material (basalt fiber), 7.5kg liquid alkali-free speed Coagulant, 6kg retarder (sucrose), 1kg thickener (polyethylene oxide), 1kg plasticizer (melamine formaldehyde sulfonate), 0.25kg defoamer (corn oil), 0.25kg water reducer (po...
Embodiment 2
[0092] The preparation method of this example is the same as that of Example 1, except that the types and contents of specific raw materials are different. The cement-based composite material for 3D printing prepared in this example consists of the following components:
[0093] P.I. type Portland cement 48kg; silica fume 28.8kg; slag powder 43.2kg; sulphoaluminate cement 120kg; alkyl polyoxyethylene ether: 6kg; Expanded perlite (particle size≤5mm): 290kg; carbon fiber: 2kg; polyvinyl alcohol fiber: 1kg; polypropylene alcohol fiber: 3kg; liquid alkali-free accelerator: 10kg; sucrose: 5kg; sorbitol: 3kg; maltitol : 5kg; salicylic acid: 1kg; methylcellulose: 1kg; montmorillonite 1kg; glycerin: 2kg; polyoxyethylene oxypropylene glycerin: 0.5kg; Naphthalene-based water-reducer: 0.5kg; polycarboxylate-based water-reducer: 0.4kg; water: 110kg.
[0094] The liquid alkali-free quick-setting agent is composed of the following components in terms of weight percentage: polyaluminum sulfat...
Embodiment 3
[0106] The preparation method of this example is the same as that of Example 1, except that the types and contents of specific raw materials are different. The cement-based composite material for 3D printing prepared in this example consists of the following components:
[0107] P.I. Portland cement 11kg; fly ash 5.5kg; metakaolin 5.5kg; sulphoaluminate cement 198kg; alkyl polyoxyethylene ether: 4kg; chlorine partial emulsion 5.5kg; diameter≤5mm): 320kg; natural sand: 320kg; glass fiber: 5kg; liquid alkali-free accelerator: 13kg; sucrose: 12kg; methyl cellulose: 0.3kg; glycerin: 3kg; Naphthalene-based water reducer: 1kg; water: 90kg.
[0108] The liquid alkali-free quick-setting agent is composed of the following components in terms of weight percentage: polyaluminum sulfate: 40%; magnesium sulfate: 10%; alcohol amine: 15% of the weight of the polyaluminum sulfate; inorganic acid: 2%; Agent: 3%; the balance is water.
[0109] The follow-up test of this embodiment is carried ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com