Chlorin e6 effective for treatment, prevention or improvement of acne
A technology of chlorin and acne, applied in the direction of medical preparations containing active ingredients, organic chemistry, organic active ingredients, etc., can solve the problem that the antibacterial activity of Propionibacterium acnes has not been reported yet
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0022] 1. Preparation of pharmaceutical composition
[0023] In addition to chlorin e6 as the active ingredient, the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can be made into a preparation for external use by further comprising a suitable carrier, excipient or diluent commonly used in the pharmaceutical field, such as liquid, Suspensions, ointments, patches, sprays, etc. Carriers, excipients or diluents that may be included in the compositions of the present invention may be, for example, lactose, glucose, sucrose, sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol, erythritol, maltitol, starch, gum arabic , Alginate, Gelatin, Calcium Phosphate, Calcium Silicate, Cellulose, Methylcellulose, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Polyvinylpyrrolidone, Water, Methylparaben, Propylparaben, Talc, Magnesium Stearate and Mineral Oil. Pharmaceutical compositions can be prepared by using commonly used diluents or excipients such as fillers, extenders, binders, wetting agents, disintegrants, surfactants an...
Embodiment 1
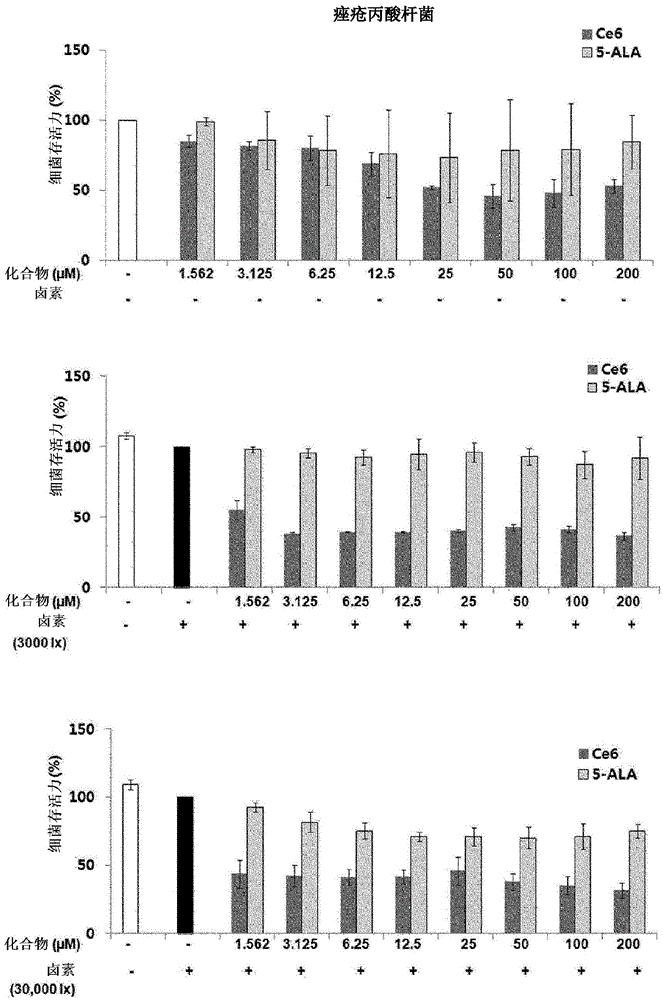
[0031] Example 1. Antibacterial effect against Propionibacterium acnes (Propionibacteriumacnes, KCTC3314)
[0032]P. acnes is a bacterium that lives mainly around the pores or in the infundibulum of the hair follicle. It feeds primarily on sebum, degrading the major components of sebum (ie, triglycerides) into fatty acids and glycerol. The free fatty acids produced severely irritate the skin, causing inflammation of the follicle wall or cells surrounding the pore. When treated at a concentration of 200 μΜ under dark conditions, chlorin e6 inhibited the growth of P. acnes by about 50% compared to the untreated control. As a result, only about 50% of the bacteria can proliferate. In contrast, 5-ALA inhibited the growth of bacteria by about 25% under the same conditions, and about 85% of bacteria could proliferate. When a halogen lamp was used to irradiate P. acnes with light of 3,000 Lux for 1 hour, chlorin e6 inhibited about 45% of the bacterial growth at a concentration of ...
Embodiment 2
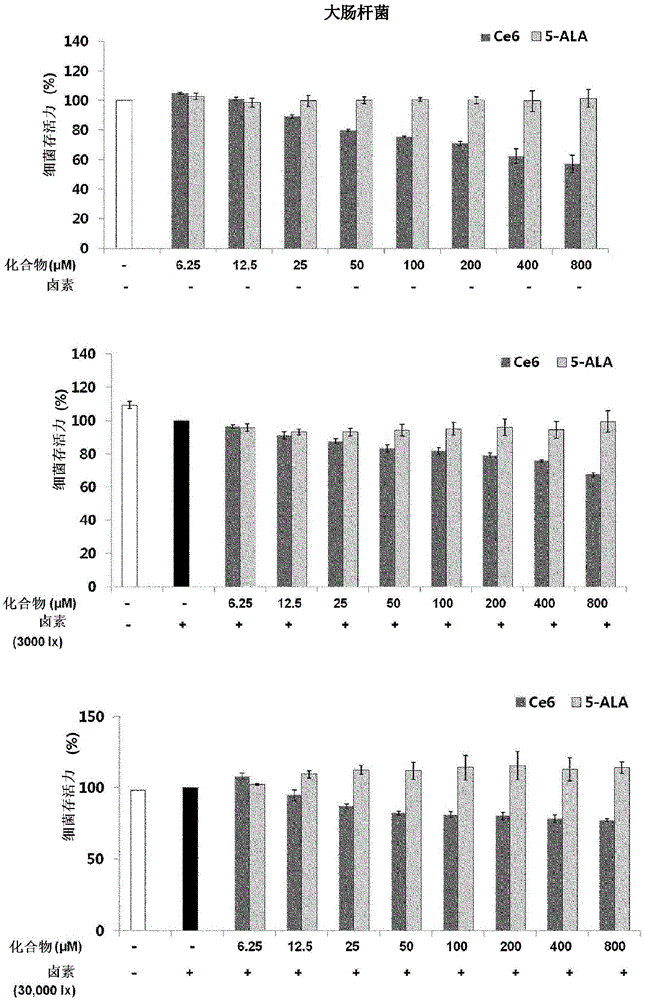
[0034] Example 2. Antibacterial effect against Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcusaureus)
[0035] Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium associated with sepsis, intestinal infections, skin infections, and joint infections. It can spread through contaminated hands, eyes or skin and can cause inflammation or food poisoning. Recently, antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus has been found. figure 2 Shown are the results of assaying the antibacterial effects of chlorin e6 and 5-ALA against Staphylococcus aureus. Under dark conditions, chlorin e6 inhibited the growth of Staphylococcus aureus by about 35% at a concentration of 100 μM compared to the control group. Under the same conditions, 5-ALA inhibited the growth of bacteria by about 10%. When irradiated with 3000 Lux of light for 1 hour, chlorin e6 at a concentration of 12.5 μM inhibited about 45% of the bacterial growth, and only about 55% of the bacteria could proliferate. In contrast, 5-ALA inhibited about 20% of ba...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com