Aspergillus flavus strain incapable of producing aflatoxin and application of aspergillus flavus strain in biological prevention and control of aflatoxin pollution of peanuts
A technology of aflatoxin and Aspergillus flavus strains, applied in the field of environmental biology, can solve problems such as limited production and application, and achieve the effects of reducing aflatoxin pollution, inhibiting infection, and good colonization ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
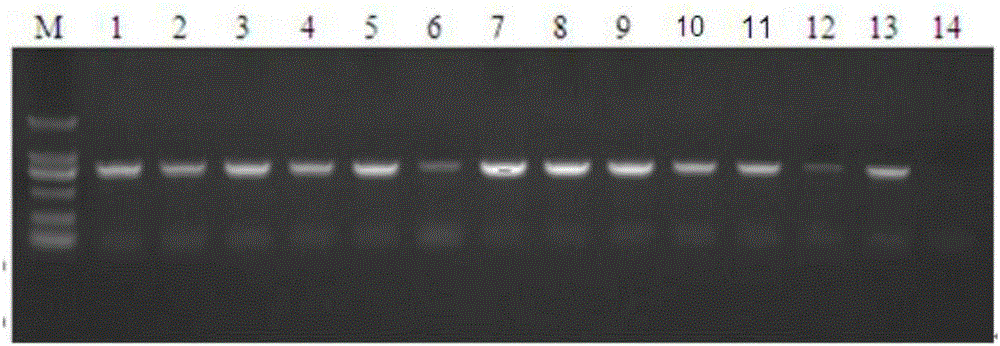
[0022] Example 1: Isolation, screening and identification of strains
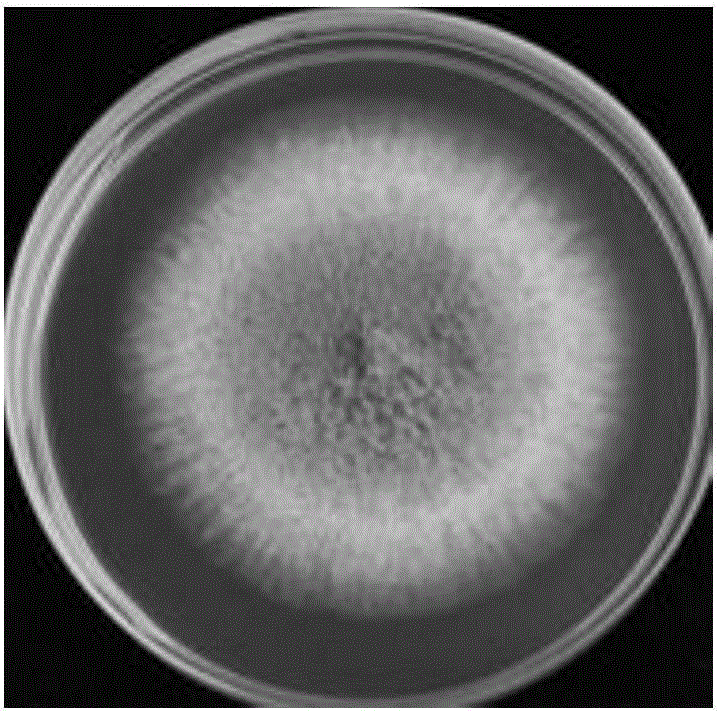
[0023] (1) Surface sterilization of peanut kernels with 70% ethanol for 30s, followed by soaking the kernels with 1wt% NaClO for 2 min, washing with sterile water 3 times, drying the peanut kernels, and evenly arranging the peanut kernels in a sterile plastic petri dish Medium, 10 grains / dish, keep the space between the kernels, not close to each other; after wrapping the petri dish containing the seeds with parafilm, carefully place it in the bottom layer of the finishing box with added moisture, cover the box, 30 ℃ culture for 7d;
[0024] (2) Use sterilized tweezers to pick up a small amount of yellow-green conidia produced on the kernels, fully suspend and serially dilute them in Tween-20 containing 0.1 wt%, and take 10 -4 Diluted conidia suspension was coated on PDA plate, cultured at 30 °C for 2 days, and a small amount of the growing single colony was transferred to the center of fresh CYA and AFPA ...
Embodiment 2
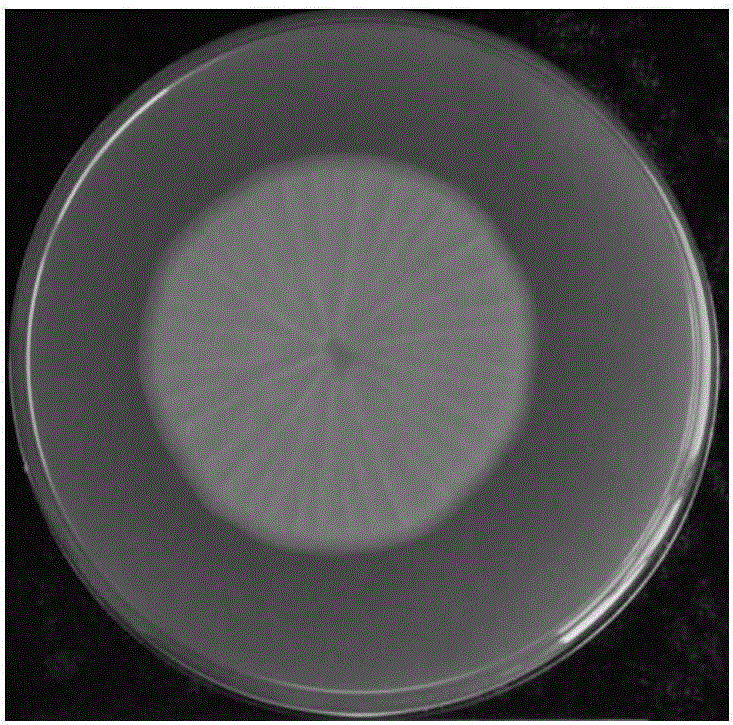
[0032] Example 2: Application of Aspergillus flavus NAFFHN396 in biological control of peanut aflatoxin contamination
[0033] The non-toxic Aspergillus flavus NAFFHN396 and the toxigenic Aspergillus flavus AF2202 were cultured on PDA solid medium for 7 days at 30°C, 0.1wt% Tween-20 water was used to suspend conidia, and the number of conidia was counted on a hemocytometer. , adjust the concentration of non-toxin-producing bacteria and toxin-producing bacteria to 1*10 4 , the ratio is 1:1, mixed in equal amounts and inoculated in the center of the CYA solid medium, or inoculated on the surface of the surface sterilized peanut kernels, shake the kernels sufficiently to make the conidia evenly adhere to the surface of the kernels, and at the same time CYA solid medium inoculated with AF2202 alone or peanut kernels was set up as a control, and cultured at 30°C for 7 days. The method described in step (4) of Example 1 was used to extract aflatoxin on the CYA solid medium; the ext...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com