A Mode Converter Based on Asymmetric Bragg Grating
A mode converter, asymmetric technology, applied in light guides, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of waveguide height mutation, unfavorable light input or output, small process tolerance, etc., to achieve high conversion efficiency, large tolerance, small size compact effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
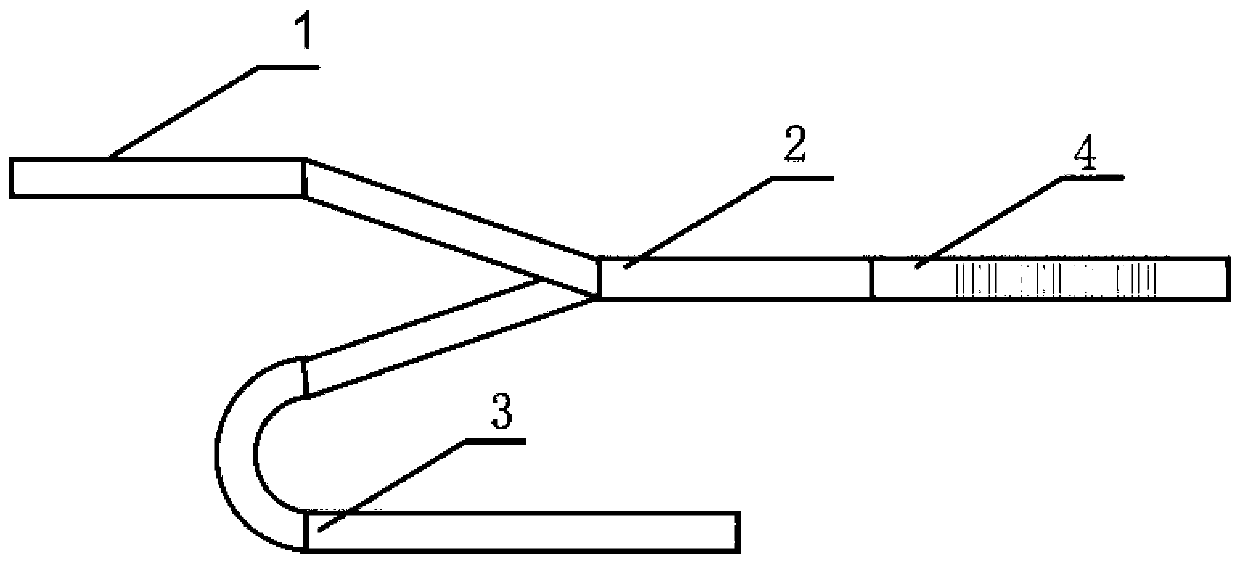
[0030] Such as figure 1 and Figure 4 As shown, using a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) material with a top silicon thickness of 340nm and a silicon dioxide buried layer of 2 μm, after cleaning the wafer surface, perform deep ultraviolet lithography or electron beam direct writing lithography to obtain silicon etching Mask, through silicon dry etching twice, to produce a silicon ridge waveguide with an inner ridge width of 450nm and an outer ridge width of 5μm, and an outer ridge height of 120nm. The grating teeth of the asymmetric Bragg waveguide grating are designed on one side of the waveguide, that is, the Bragg waveguide grating is etched on one side of the waveguide, the rectangular grating teeth are 150nm, the depth of the grating teeth is 220nm, and the period of the grating is 300nm.
[0031] The grating period parameters in the above embodiments are designed for ridge waveguides with a width of 450nm. The device is also suitable for ridge waveguides with other widths, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com