Magnetic molecular imprinting sensor for detecting Gram-negative bacterium signal molecule
A technology of magnetic molecular imprinting and Gram-negative bacteria, which is applied in the direction of material electrochemical variables, can solve the problems of high cost, inability to detect, and long detection time, and achieve strong electrode regeneration, hazard prevention, and high accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Preparation of Magnetic Molecular Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor
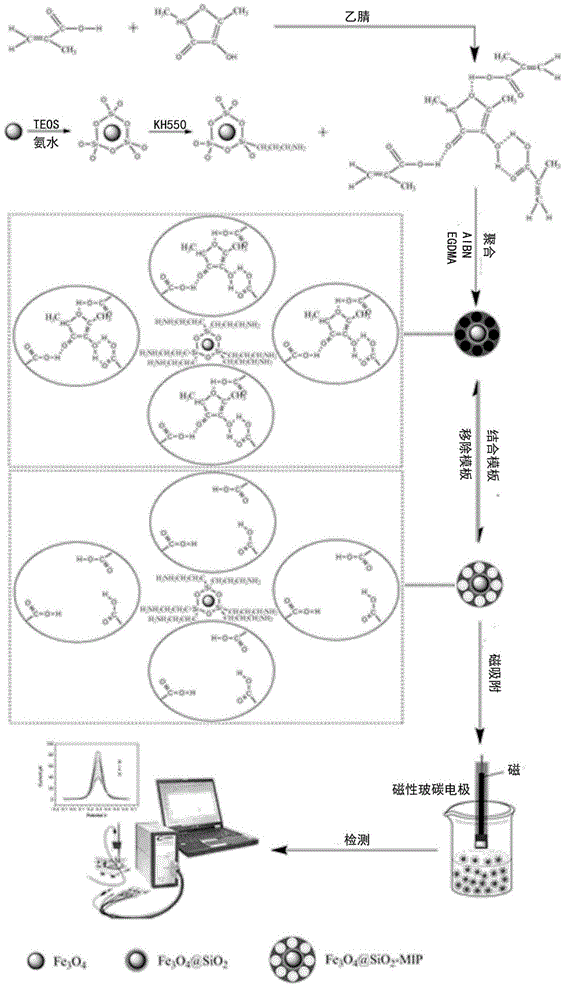
[0041] The schematic diagram of the preparation and use of magnetic molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors is shown in figure 1 shown.
[0042] Step 1, Preparation of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Preparation of Fe by Solvothermal Method 3 o 4 MNPs, Fe prepared by the Stober method 3 o 4 SiO 2 , Fe was obtained by grafting amino groups on the surface of "core-shell" magnetic spheres by silane reagent KH550 3 o 4 SiO 2 -NH 2 . Mix the template molecule furanone: functional monomer methacrylic acid: crosslinking agent ethylene glycol dimethacrylate according to the molar ratio of 1: (1-8): (10-30), add an appropriate amount of acetonitrile, and ultrasonically ; Add 100-300mg of Fe per millimole template molecule 3 o 4 SiO 2 -NH 2 Magnetic nanoparticles, 10-30 mg of initiator azobisisobutyronitrile, sonicated until uniform; 2 Under the atmosphere, react in an oil...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Study on the electrochemical performance of magnetic molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors
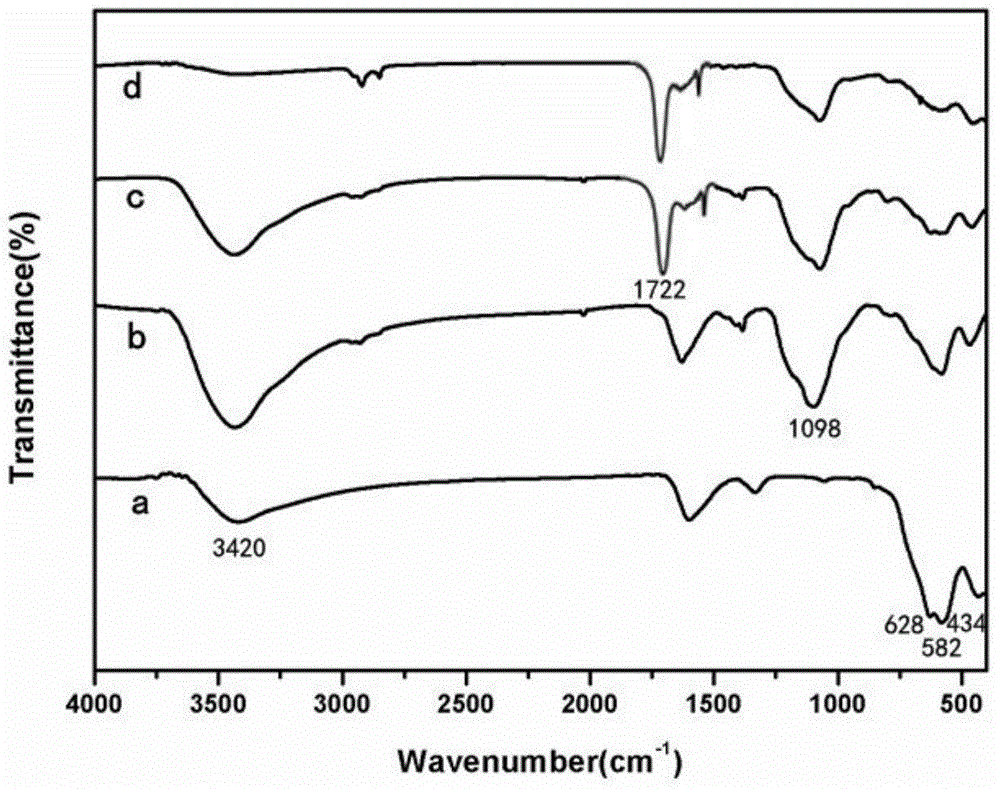
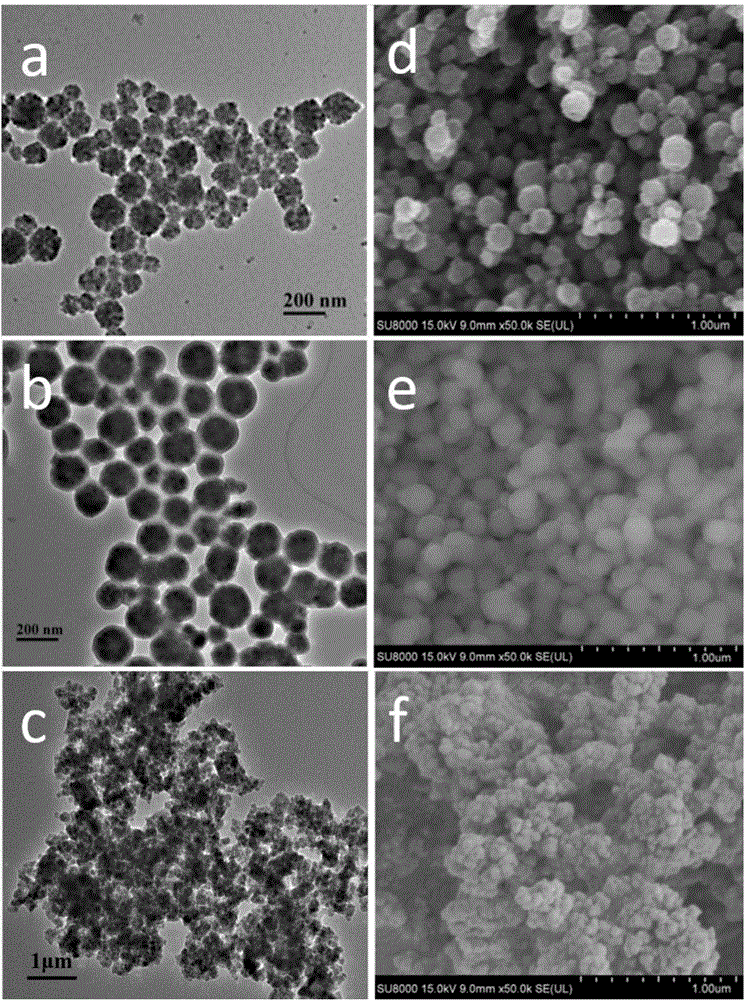
[0047] In this experiment, the performance of the magnetic molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor was studied in 2.5mM potassium ferricyanide buffer solution of 1.0M KCl, and the results are as follows: Figure 4 shown.
[0048] Step 1, due to the molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere Fe 3 o 4 SiO 2 -MIP (MMIP for short) is a non-conductive material, and furanone and AHL are non-electroactive substances, so potassium ferricyanide-potassium ferrocyanide is selected as the probe between the base solution and the electrode to characterize magnetic molecular imprinting Electrochemical performance of electrochemical sensors. After MMIP is eluted, the imprinted holes left behind can provide mass transfer channels for probe ions. When the electrode is placed in the C4-HSL solution for adsorption, due to the specific recognition of C4-HSL by the imprinted...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3 Detection of C4-HSL Standards by Magnetic Molecular Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor
[0052] Add appropriate amount of molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere Fe 3 o 4 SiO 2 -MIP, adsorption at room temperature for 5-10min; the pretreated magnetic glassy carbon electrode is inserted into the above solution, adsorbed for 1-10min, taken out from the solution, carefully washed with double distilled water for 20s to remove the physically adsorbed substances on the electrode surface ( including unbound samples). The magnetic molecular imprinted electrochemical sensor was placed in the electrolytic cell, and the DPV was measured in 2.5mM potassium ferricyanide buffer containing 1.0M KCl. DPV test conditions: the voltage sweep range is -0.1V to 0.65V, the pulse amplitude is 25mV, the pulse width is 50ms, the pulse period is 500ms, and the potential increment is 5mV. All tests are carried out at room temperature. There is a quantitative relationship between the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com