Protein-polymer composite nano-carrier and preparation method thereof
A nano-carrier and polymer technology, which is applied in the field of nano-preparation of anti-tumor drugs, can solve the problems of poor targeting effect and achieve the effects of easy storage, improved stability, and increased tumor targeting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1: Preparation of bufotoxin-loaded ursodeoxycholic acid modified protein-polymer composite nanoparticles.
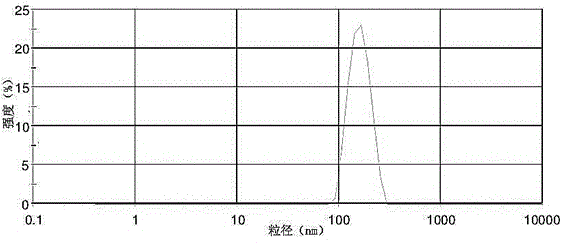
[0048] Weigh 3.5 mg bufalin, 5 mg stearylamine and 30 mg pluronic F127 and dissolve them in dichloromethane. Slowly add 60 mg of n-butyl cyanoacrylate (BCA) dropwise into 5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid (0.1 M) containing 25 mg each of dextran 70 and Pluronic F68, and slowly add the mixed solution of dichloromethane into the system, Add dropwise while stirring. After stirring for 4 h, adjust the pH to neutral with sodium hydroxide, add 5 mg ursodeoxycholic acid-modified bovine serum albumin, and continue stirring for 1 h. Remove residual methylene chloride by rotary evaporation, centrifuge at 5000 rpm for 3 min, and pass through a microporous membrane to obtain a composite nanocarrier suspension containing bufotoxin-ursodeoxycholic acid-modified protein-polymer.
[0049] Add 30mg of mannitol and 30mg of trehalose to the bufafolin-ursodeoxycholic acid mo...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: Preparation of bufotoxin-loaded hyaluronic acid modified protein-polymer composite nanoparticles.
[0051] Weigh 10 mg bufalin and 10 mg stearylamine, respectively, and dissolve them in dichloromethane. Slowly add 100 mg of ethyl cyanoacrylate (ECA) dropwise to 10 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid (0.1M) containing 50 mg of dextran 70 and 50 mg of Pluronic F68, and slowly add the mixed solution of dichloromethane into the system, Add dropwise while stirring. After stirring for 4 h, adjust the pH to neutral with sodium hydroxide, add 20 mg of hyaluronic acid-modified bovine serum albumin, and continue stirring for 1 h. Remove residual dichloromethane by rotary evaporation, centrifuge at 5000 rpm for 3 min, and pass through a microporous membrane to obtain a suspension of bufotoxin-hyaluronic acid modified protein-polymer composite nanocarrier.
[0052] Add 50 mg of sucrose to the bufafolin-hyaluronic acid modified protein-polymer composite nanocarrier suspensio...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: Preparation of etoposide-glycyrrhetinic acid modified protein-polymer composite nanoparticles.
[0054] Weigh 30 mg etoposide, 3 mg stearylamine and 50 mg pluronic F127 and dissolve them in dichloromethane. Slowly add 210 mg of methyl cyanoacrylate (MCA) dropwise into 5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid (0.1 M) containing 10 mg of dextran 70 and 10 mg of Pluronic F68, and slowly add the dichloromethane mixed solution into the system dropwise. Add and stir. After stirring for 4 h, adjust the pH to neutral with sodium hydroxide, add 5 mg glycyrrhetinic acid-modified bovine serum albumin, and continue stirring for 1 h. Remove residual dichloromethane by rotary evaporation, centrifuge at 5000 rpm for 3 min, and pass through a microporous membrane to obtain etoposide-glycyrrhetinic acid modified protein-polymer composite nanocarrier suspension.
[0055] Add 20 mg PEG 400 and 10 mg glycine to the etoposide-glycyrrhetinic acid-modified protein-polymer composite nanoc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com