Method for producing mineral wool fiber by using high-temperature liquid waste slags of metallurgical furnace as raw material
A technology of mineral wool fiber and waste residue, which is applied in the field of resource regeneration and utilization, can solve problems such as melting waste, and achieve the effects of reducing energy consumption and production cost, superior acid resistance and good waterproof performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Follow the process flow. The chemical composition of copper, lead, zinc, nickel, tin, iron and other high-temperature liquid waste slag and conditioner in a factory is shown in Table 1.
[0037] Step 1: Release high-temperature liquid waste slag from metallurgical furnaces such as copper, lead, zinc, nickel, tin, and iron in Table 1, and flow it into an electric heat preservation furnace for heat preservation. The temperature is controlled at 1400-1500 °C. After heat preservation in the electric furnace, the temperature can be controlled and the hot slag can be released evenly.
[0038] Step 2: Adjust the acidity coefficient with alkaline conditioner. In the electric furnace, the conditioner 1 is added into the electric furnace according to a certain proportion and melted. Adjust its chemical composition, temperature, and viscosity to the range required by the slag wool fiber melt, that is, the melt acidity coefficient Mk Reach 1.1~1.8 (acidity coefficient=(SiO 2 +A...
Embodiment 2
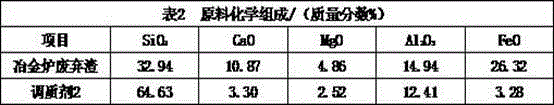
[0051] Follow the process flow. The chemical composition of waste slag and conditioning agent of a factory is shown in Table 2.
[0052]
[0053] Step 1: Release high-temperature liquid waste slag from metallurgical furnaces such as copper, lead, zinc, nickel, tin, and iron in Table 1, and flow it into an electric heat preservation furnace for heat preservation. The temperature is controlled at 1400-1500 °C. After heat preservation in the electric furnace, the temperature can be controlled and the hot slag can be released evenly.
[0054] Step 2: Adjust the acidity coefficient with alkaline conditioner. In the electric furnace, the conditioner 1 is added into the electric furnace according to a certain proportion and melted. Adjust its chemical composition, temperature, and viscosity to the range required by the slag wool fiber melt, that is, the melt acidity coefficient M k Reach 1.1~1.8 (acidity coefficient=(SiO 2 +Al 2 o 3 ) / (CaO+MgO). Control the temperature a...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Follow the process flow. The chemical composition of waste slag from a fuming furnace in a factory is shown in Table 3.
[0068]
[0069] Step 1: Release high-temperature liquid waste slag from metallurgical furnaces such as copper, lead, zinc, nickel, tin, and iron in Table 1, and flow it into an electric heat preservation furnace for heat preservation. The temperature is controlled at 1400-1500 °C. After heat preservation in the electric furnace, the temperature can be controlled and the hot slag can be released evenly.
[0070] Step 2: Adjust the acidity coefficient with alkaline conditioner. In the electric furnace, the conditioner 1 is added into the electric furnace according to a certain proportion and melted. Adjust its chemical composition, temperature, and viscosity to the range required by the slag wool fiber melt, that is, the melt acidity coefficient M k Reach 1.1~1.8 (acidity coefficient=(SiO 2 +Al 2 o 3 ) / (CaO+MgO). Control the temperature at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com