Low-modulus high-corrosion-resistance ternary Ni-Ti-Cu alloy and preparation method thereof
A ni-ti-cu, low-modulus technology, applied in the field of biomaterials, can solve the problems of size limitation, high equipment cost, and difficulty in meeting the requirements of material fracture toughness, so as to reduce material waste and improve mechanical properties, size and size. The effect of reducing the number of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0020] The low modulus and high corrosion resistance alloy of the present invention is composed of Ni, Ti and Cu, wherein the atomic ratio of Ti element is 49%, the atomic ratio of Ni element is 26%, and the atomic ratio of Cu element is 25%.
[0021] 1. Convert the samples of three kinds of Ni, Ti, Cu pure metals into weight percentage according to atomic percentage, cut and weigh the required amount. Then place it in an acetone solution for ultrasonic cleaning for 30 minutes to remove pollutants on the surface of raw materials;
[0022] 2. Wipe the inside and bottom crucible of the electric arc furnace clean with acetone, and place the weighed metal raw materials in the crucible;
[0023] 3. Use the mechanical pump to pump the cavity of the arc melting equipment to a vacuum higher than 6 Pa, then turn on the molecular pump and continue vacuuming until the vacuum reaches 5 × 10 -5 Above Pa.
[0024] 4. Introduce argon gas to control the pressure of the vacuum chamber at ab...
Embodiment approach 2 3
[0027] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the diameters of the cylindrical samples in step 5 are 5 mm and 2 mm respectively, and the rest of the steps are the same as those of the first embodiment.
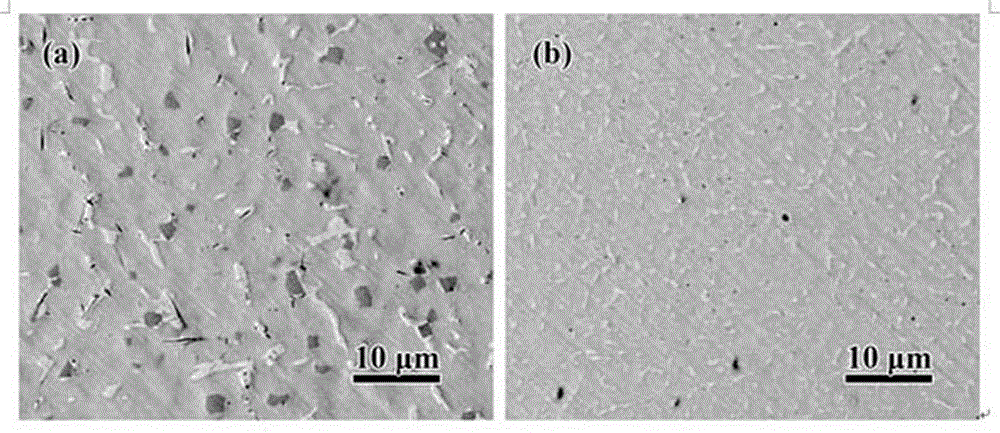
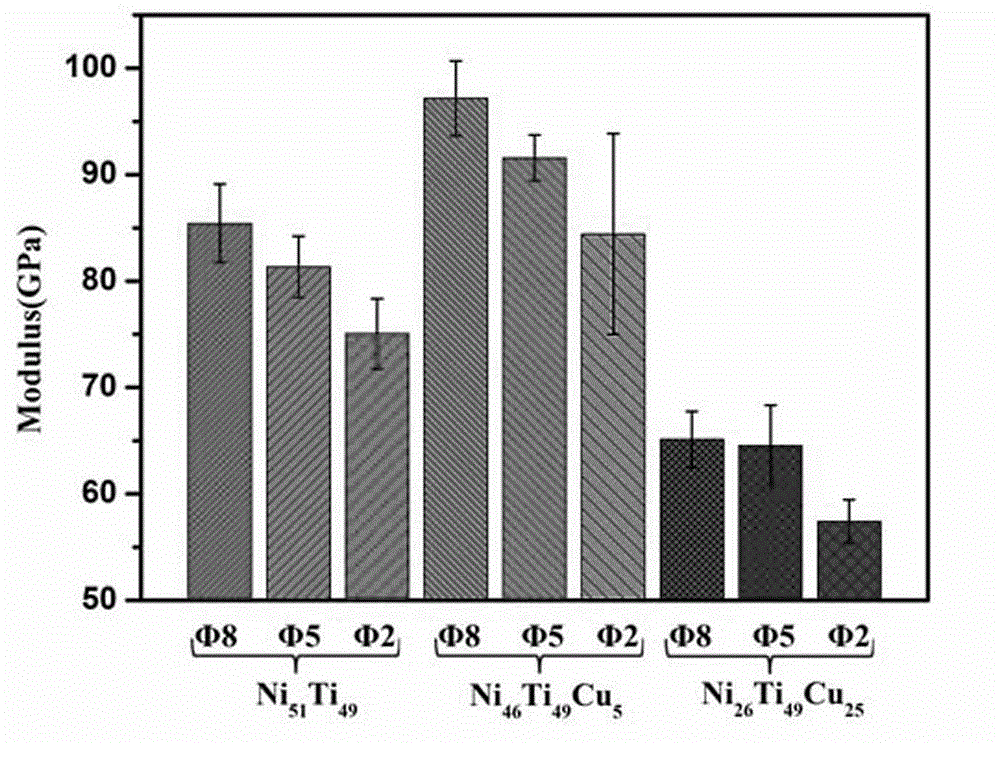
[0028] attached by figure 1 It can be seen that the precipitated phase size of the cylindrical sample with a diameter of 2 mm is smaller. This is due to the higher cooling rate during solidification of cylindrical specimens with smaller diameters, resulting in microstructure refinement. In this way, samples with finer microstructures have better mechanical properties in comparison.
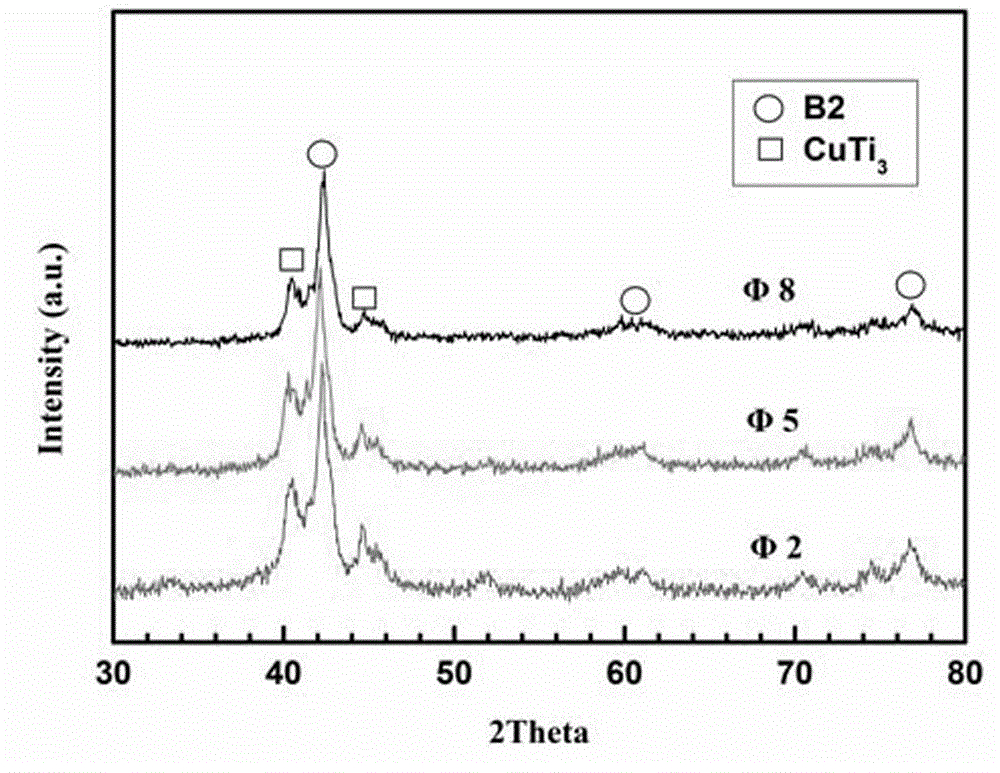
[0029] The XRD pattern of the alloy shows that, see attached figure 2 , the main phase composition of all samples is austenite phase at room temperature, and the half width of the diffraction peaks increases with the decrease of the sample size, which proves that the alloy microstructure can be improved at a higher cooling rate The refinement phenomenon below. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com