Phospholipase A2 mutant and preparation method thereof
A technology of mutant and phospholipase, applied in the field of genetic engineering of enzymes, can solve the problems of narrow enzyme source, complicated process, unfavorable mass production and utilization of phospholipase A, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing production cost and simplifying production links.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1: Wild-type phospholipase A 2 Acquisition of the mature peptide gene
[0053] 1. Wild-type phospholipase A 2 The mature peptide gene comes from Streptomyces coelicolor ATCC23899, and its genomic DNA is extracted.
[0054] Wherein the extraction steps of Streptomyces coelicolor genomic DNA are as follows:
[0055] (1) Pick a ring of bacteria from the culture plate and inoculate in 40mL of appropriate medium, culture at 26°C, 150r / min for 2-3d.
[0056] (2) Take 1 mL of the culture solution in a 1.5 mL EP tube, centrifuge at 12,000 r / min for 10 min, pour off the supernatant, and resuspend with 200 μL of Solution I.
[0057] (3) Add 50 μL of 50 mg / mL lysozyme and digest at 4°C for 1 hour.
[0058] (4) Add 1 / 2 volume of 2% SDS solution and react for 10 minutes until the bacterial suspension becomes viscous.
[0059] (5) Add an equal volume of saturated phenol: chloroform = 1:1, mix well, centrifuge for 10 min, transfer the supernatant to another clean EP tube,...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Embodiment 2: high activity phospholipase A 2 Gene acquisition.
[0070] 1. Wild-type phospholipase A 2 The gene is ligated into the T vector.
[0071] The purified target gene was connected to the pUC-T vector, and the recombinant plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α, which was verified by EcoRI and MluI double enzyme digestion, and the wild-type phospholipase A 2 The gene has been successfully cloned into the T vector.
[0072] 2. Site-directed mutation
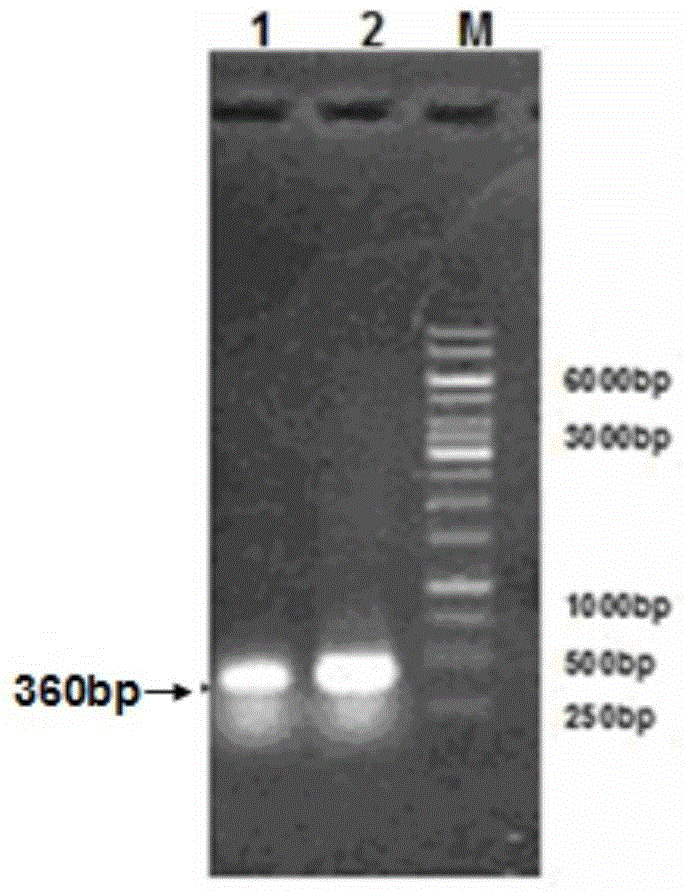
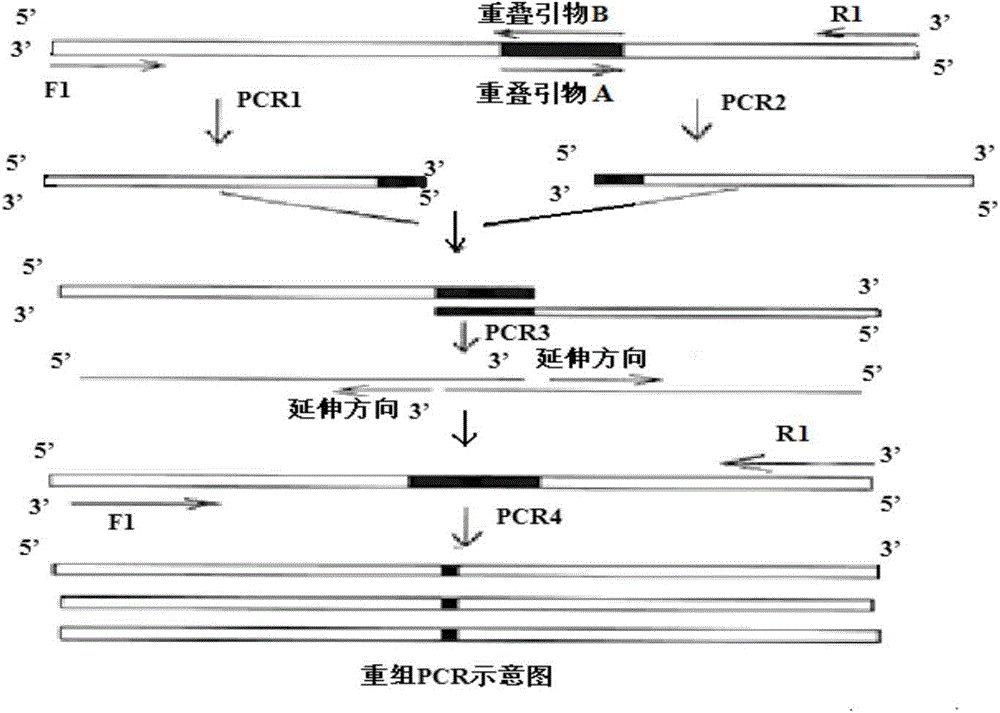
[0073] Based on overlapping PCR technology (see figure 2 ) for site-directed mutagenesis to construct a highly active phospholipase A 2 , design primers as follows:
[0074] Upstream P1 (SEQ ID NO.1): 5'-GCCCCCGCGGACAAGCCCCAGGT-3'
[0075] Downstream P2 (SEQ ID NO.2): 5'-TCAGCCGAAGATCTTGACGGC-3'
[0076] Overlapping primer P3 (SEQ ID NO.3): 5'-GGCCGCCTACGCGTTCGACTGGT-3'
[0077] Overlapping primer P4 (SEQ ID NO.4): 5'-ACCAGTCGAACGCGTAGGCGGCC-3'
[0078] Overlapping primer P5 (SEQ ID NO.5): 5'...
Embodiment 3
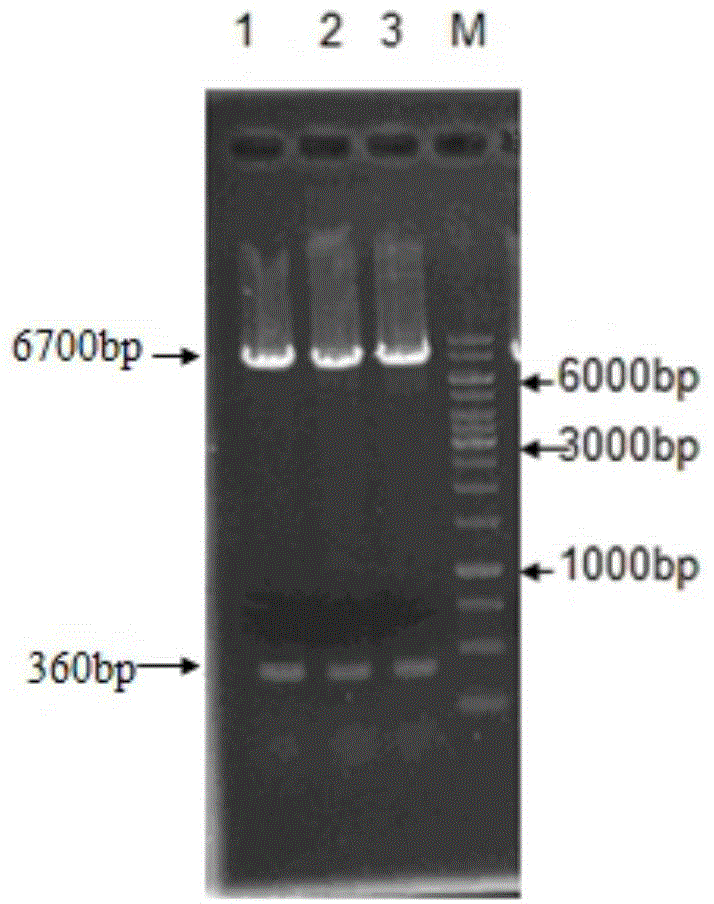
[0106] Embodiment 3: Bacillus subtilis high activity phospholipase A 2 Construction of recombinant bacteria
[0107] 1. Construction of expression vector pBSA43
[0108] pBSA43 is based on the Escherichia coli-Bacillus subtilis shuttle cloning vector pBE2 as the backbone, cloned into a strong Bacillus constitutive promoter P43, and the fructan sucrase signal sequence sacB that can directly secrete the recombinant protein into the medium. get. it comes with amp r Gene that can use ampicillin resistance as a selectable marker in E. coli. At the same time with Km r , Kanamycin resistance can be used as a selection marker in Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis.
[0109] 2. High activity phospholipase A 2 Expression vector pBSA43-plA 2 construction of m
[0110] The high-activity phospholipase A obtained through overlapping PCR construction 2 After the gene was digested with BamHI and HindIII, it was ligated with the same double digested Bacillus subtilis expressi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com