Acid resistant fungi alpha-amylase TaAMY, gene and applications thereof
An acid-resistant and amylase technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of large gap, lack of production and market competitiveness, and low production level of fungal α-amylase
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0094] Embodiment 1, the mutagenesis and cultivation of fungal alpha-amylase Aspergillus niger strain
[0095] Aspergillus niger strain AN0921 (strain preservation number ACCC30132), which is native to fungal α-amylase, was cultured on a PDA plate, and then used plasma (ARTP), ultraviolet light, and diethyl sulfate (DES) for individual and compound mutagenesis After treatment, a fungal α-amylase mutant strain TaAN0921 was screened.
[0096] The mutant strain is fermented and cultivated, and its fermentation medium composition is as follows:
[0097] Peptone 2%, yeast powder 0.5%, dextrin 10%, sodium glutamate 1.5%, potassium diammonium phosphate 0.15%, magnesium sulfate 0.10%
[0098] The above fermentation culture is based on sterilization at 121° C. and 0.1 MPa for 30 minutes, inoculation after cooling, and cultivation at 30° C. and 200 rpm for 4 to 5 days.
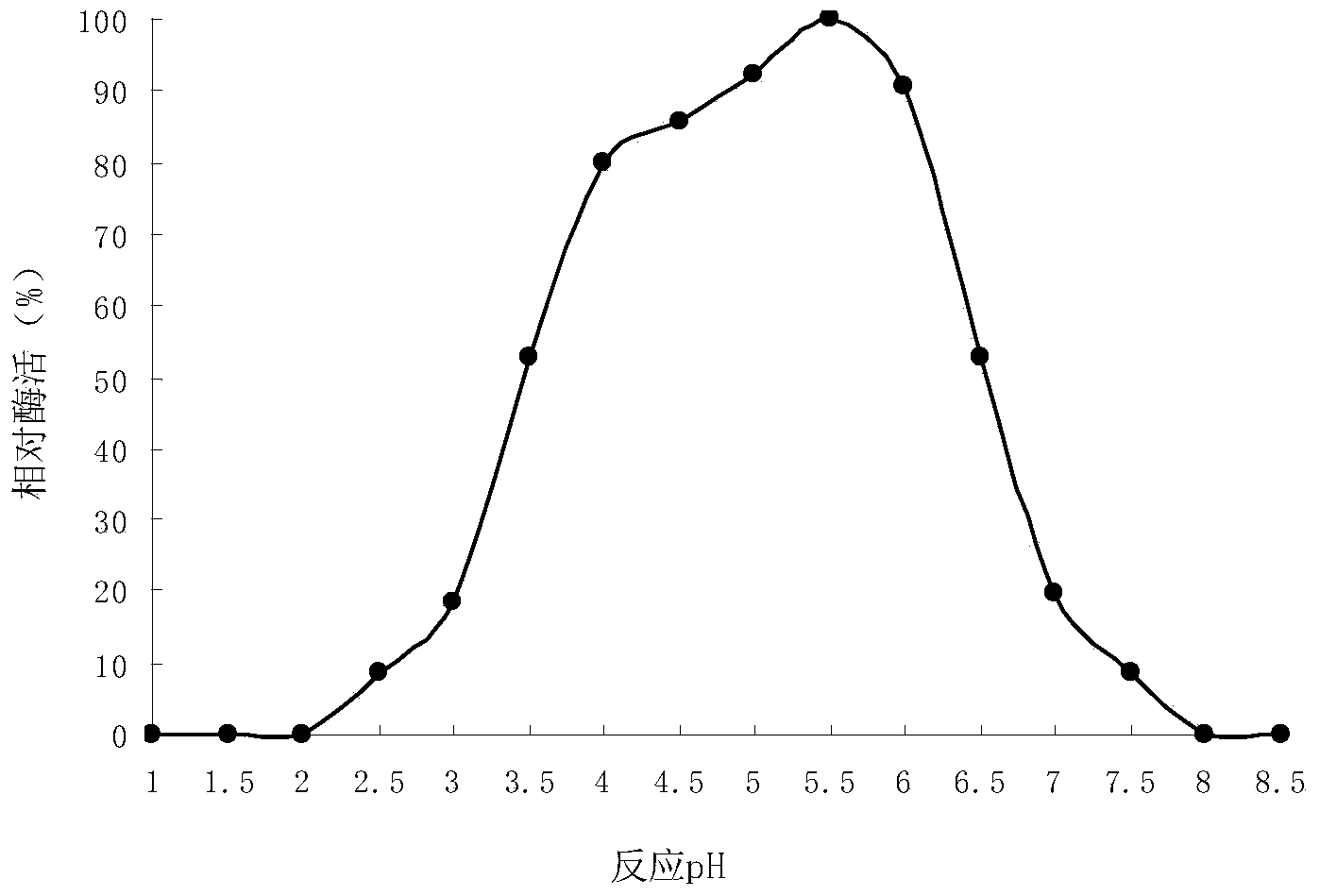
[0099] After the fermentation, take an appropriate amount of enzyme liquid for testing. The test results show that th...
Embodiment 2
[0101] Example 2, Cloning of Aspergillus niger (TaAN0921) α-amylase gene
[0102] According to reverse transcriptase SuperScript TM The operating instructions of III Reverse Transcriptase, use the RNA extraction kit to extract the total RNA of Aspergillus niger (TaAN0921) and synthesize the first-strand cDNA. Using cDNA as a template, primers were designed for PCR amplification, and the PCR product was digested with EcoRI and NotI, and then connected with the Pichia pastoris expression vector pPICzαA that had undergone the same digestion, and the ligated product was transformed into Escherichia coli Topl0 competent cells, After screening by the antibiotic Zeocin, positive clones were obtained. Plasmids of positive clones were extracted and sequenced. Sequencing results showed that the cloned DNA insert contained the complete open reading frame of the fungal α-amylase gene. The total length of the fungal α-amylase gene (NTaAMY) is 1704bp, encoding 567 amino acids, and the re...
Embodiment 3
[0108] Embodiment 3, Pichia pastoris engineered bacteria construction comprising novel acid-resistant fungal α-amylase gene NTaAMY
[0109] The above-mentioned recombinant expression vector (NTaAMY-pPICzαA) was linearized with SacI, and the linearized recombinant vector was electroporated to transform Pichia pastoris X33. After electroporation, it was spread on a YPD plate containing Zeocin for screening to obtain a recombinant strain of Pichia pastoris NTaAMY-pPICzαA-X33.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com