Diesel hydrogenation process
A technology for hydroprocessing and diesel oil, which is applied in the fields of hydroprocessing technology, petroleum industry, and hydrocarbon oil treatment. It can solve the problems of complex process and high energy consumption, and achieve the effects of simplifying the process, reducing energy consumption and difficulty of operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
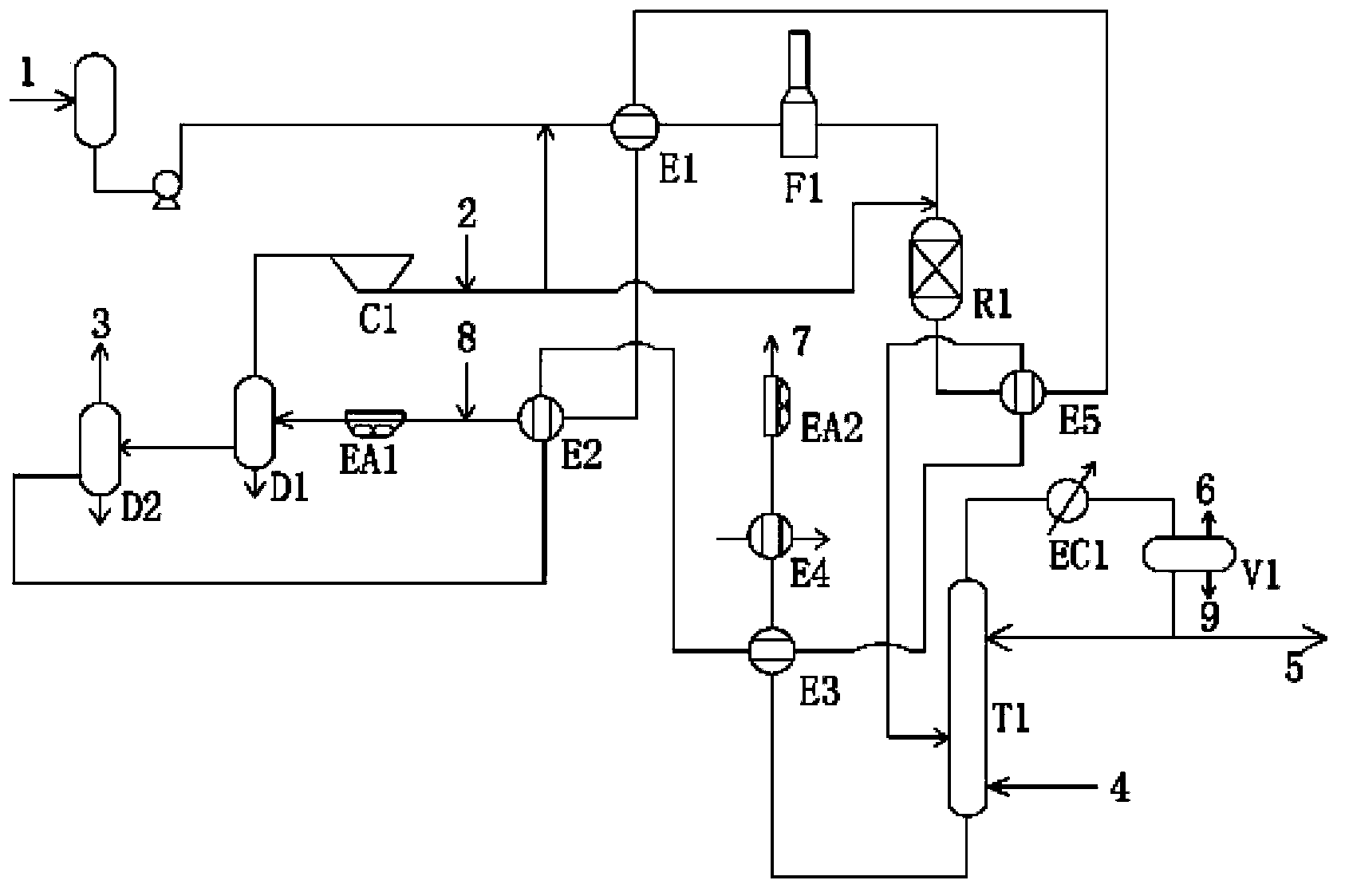
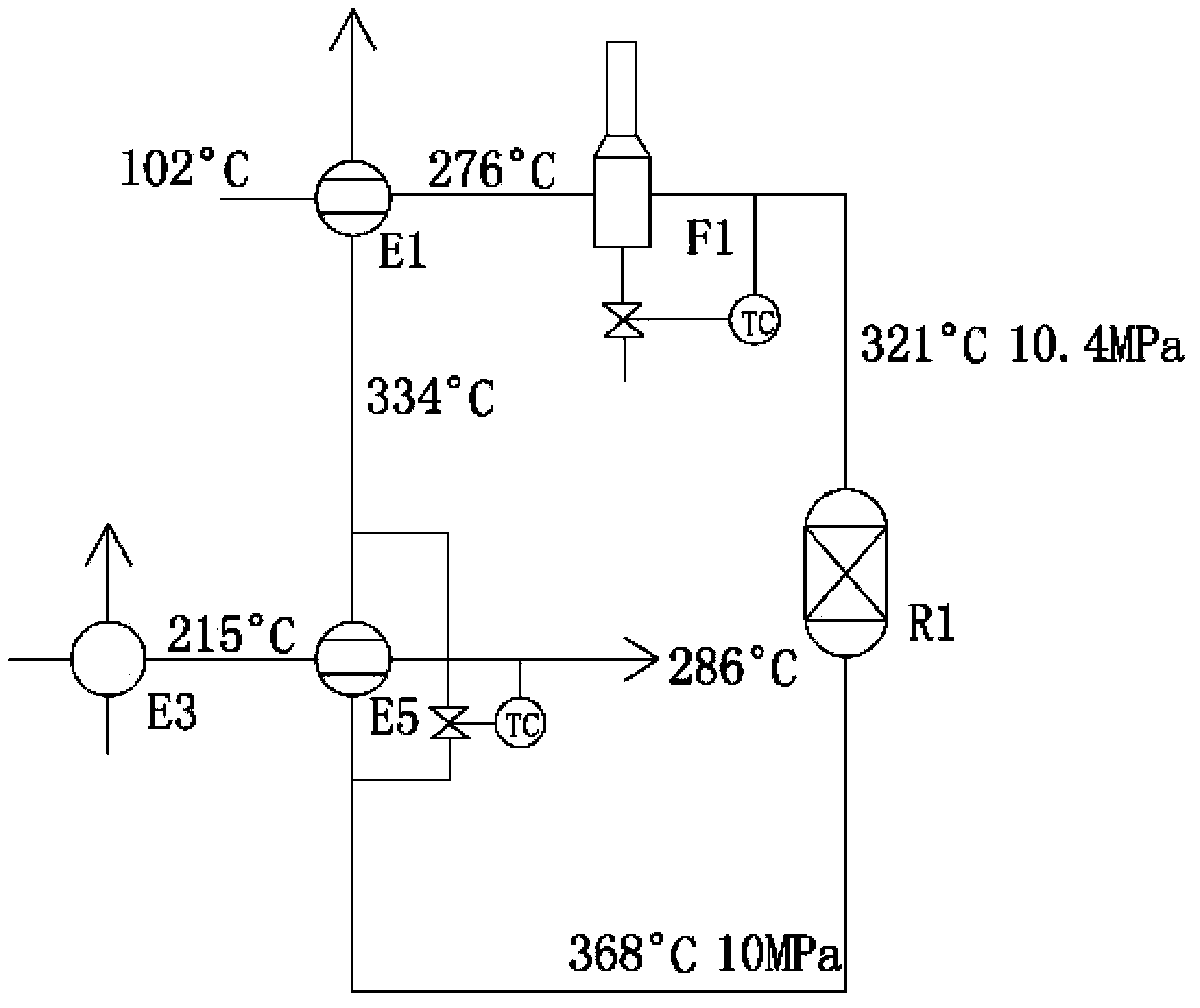
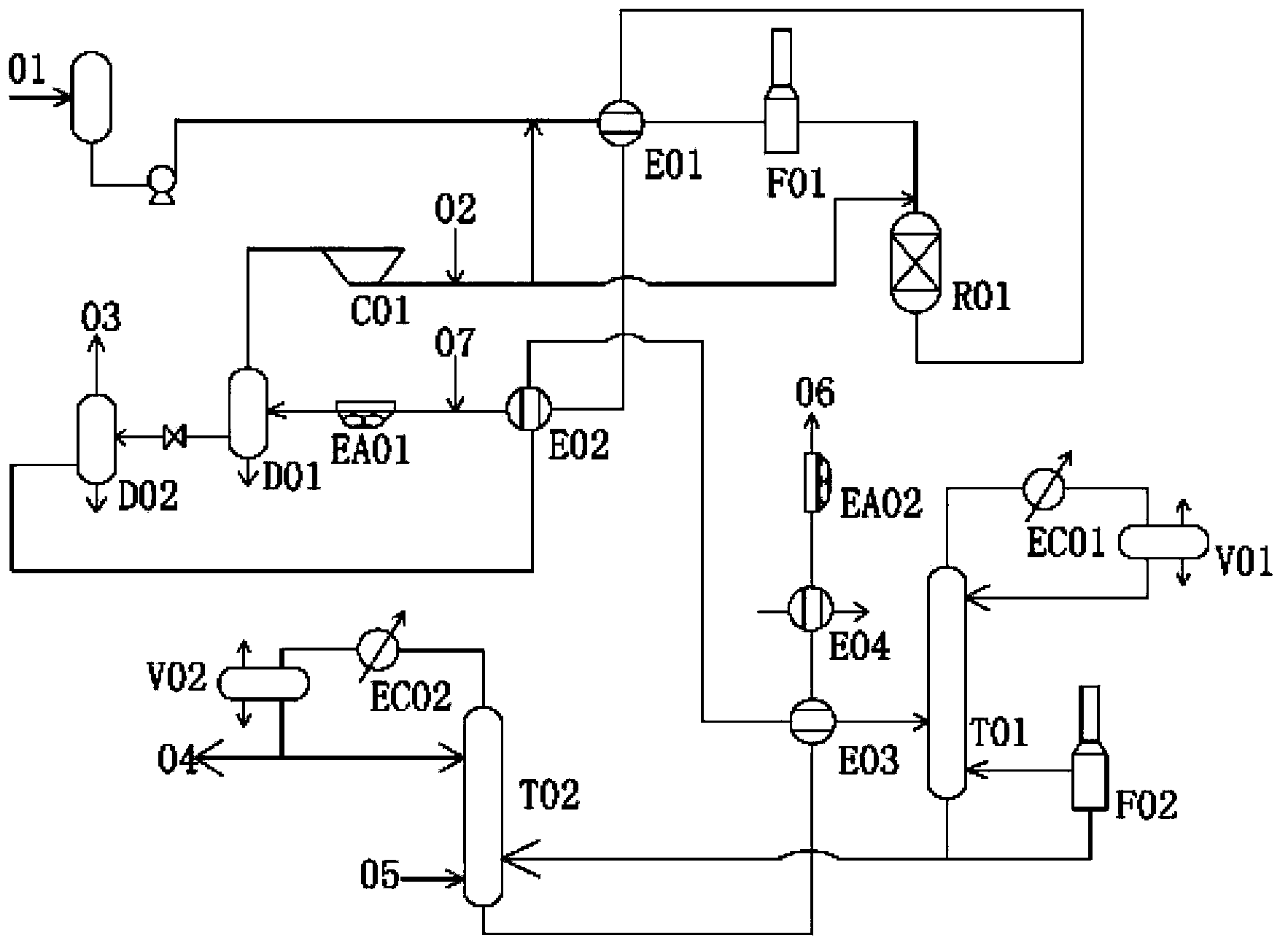
[0029] see figure 1 As shown, the diesel hydrotreating process described in this example is as follows: raw diesel oil 1 (120°C, 10.8MPag, 119048kg / h) from the upstream device and hydrogen (75°C, 10.8MPag, 130000Nm 3 / h, 24972kg / h) after mixing, enter the first heat exchanger E1 at 102°C to exchange heat with the hydrogenation reaction product for the second time (334°C, 10MPag, 153625kg / h), and then heat up to 276°C and enter the raw material heating furnace F1. After further raising the temperature to 321°C, it enters the hydrogenation reactor R1 (the effective heat load corresponding to the raw material heating furnace F1 is 7520.1kW). The temperature of the reaction product coming out of the hydrogenation reactor R1 is 368°C, and then the reaction product passes through the fifth heat exchanger E5 to exchange heat with the cold low fraction oil three times (215°C, 1.4MPag, 121816kg / h) and then cools down to 334°C ℃, and then mixed with hydrogen and cooled to 205℃ through...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The difference from Example 1 is the diesel hydrotreating process described in this example. The specific conditions are as follows: Raw diesel oil 1 (120°C, 10.8MPag, 119048kg / h) from the upstream device and hydrogen (75°C, 10.8MPag, 130000Nm 3 / h, 24972kg / h) after mixing, enter the first heat exchanger E1 at 102°C to exchange heat with the hydrogenation reaction product for the second time (334°C, 10MPag, 153625kg / h), and then heat up to 270°C and enter the raw material heating furnace F1. After further raising the temperature to 321°C, it enters the hydrogenation reactor R1 (the effective heat load corresponding to the raw material heating furnace F1 is 8513.6kW). The temperature of the reaction product coming out of the hydrogenation reactor R1 is 368°C, and then the reaction product passes through the fifth heat exchanger E5 to exchange heat with the cold low fraction oil three times (215°C, 1.4MPag, 121816kg / h) and then cools down to 334°C ℃, and then mixed with ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] The difference from Example 1 is the diesel hydrotreating process described in this example. The specific conditions are as follows: Raw diesel oil 1 (120°C, 10.8MPag, 119048kg / h) from the upstream device and hydrogen (75°C, 10.8MPag, 130000Nm 3 / h, 24972kg / h) after mixing, enter the first heat exchanger E1 at 102°C to exchange heat with the hydrogenation reaction product for the second time (334°C, 10MPag, 153625kg / h), and then heat up to 280°C and enter the raw material heating furnace F1. After further raising the temperature to 321°C, it enters the hydrogenation reactor R1 (the effective heat load corresponding to the raw material heating furnace F1 is 6910.7kW). The temperature of the reaction product coming out of the hydrogenation reactor R1 is 368°C, and then the reaction product passes through the fifth heat exchanger E5 to exchange heat with the cold low fraction oil three times (215°C, 1.4MPag, 121816kg / h) and then cools down to 334°C ℃, and then mixed with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com