Sintered porous material and filter element using same
A technology of porous materials and filter elements, applied in the field of sintered porous materials and filter elements using the porous materials, to achieve the effects of improving pore structure, reducing passage resistance, and excellent corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
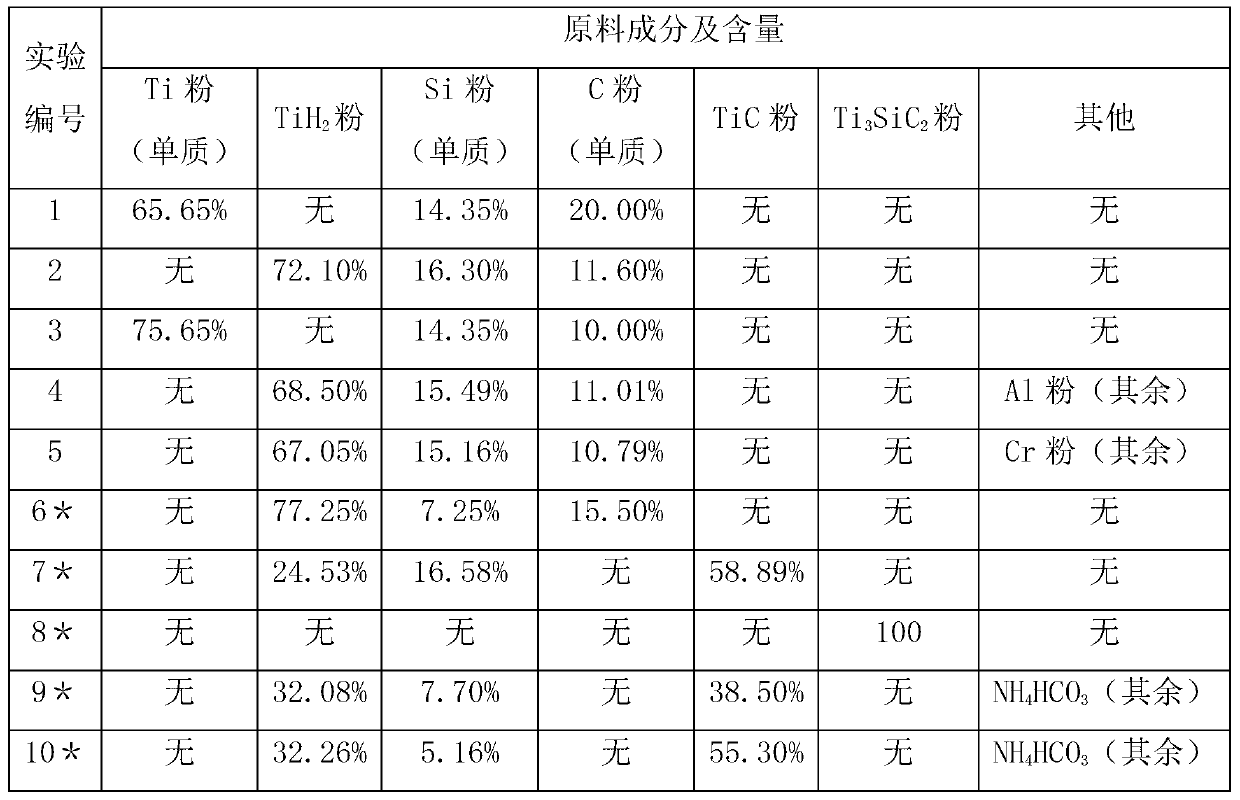
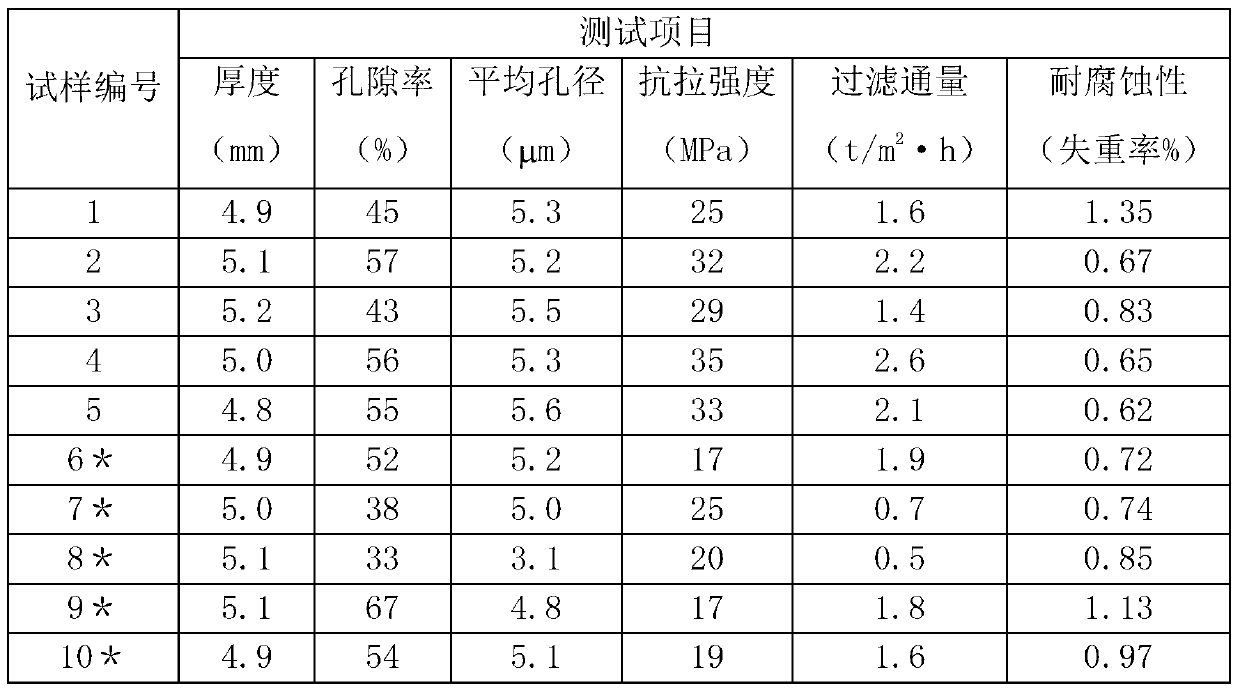
[0015] The preparation method of the sintered porous material and the sintered porous material obtained by these methods will be described in detail through experiments below. Through these descriptions, those skilled in the art can clearly understand the outstanding features of the sintered porous material of the present application. The numbers of the experimental examples mentioned below correspond to the numbers corresponding to "green compact" and "sample".
[0016] In order to illustrate the sintered porous material of the present application and its preparation, the following 10 sets of experimental examples have been prepared. Among them, samples 1 to 5 respectively prepared through experimental examples 1 to 5 all belong to the scope of the sintered porous material to be protected in claim 1 of the present application. Experimental examples 6 to 10 are comparative experiments embodying the substantive characteristics and technical effects of experimental examples 1 t...
experiment example 8
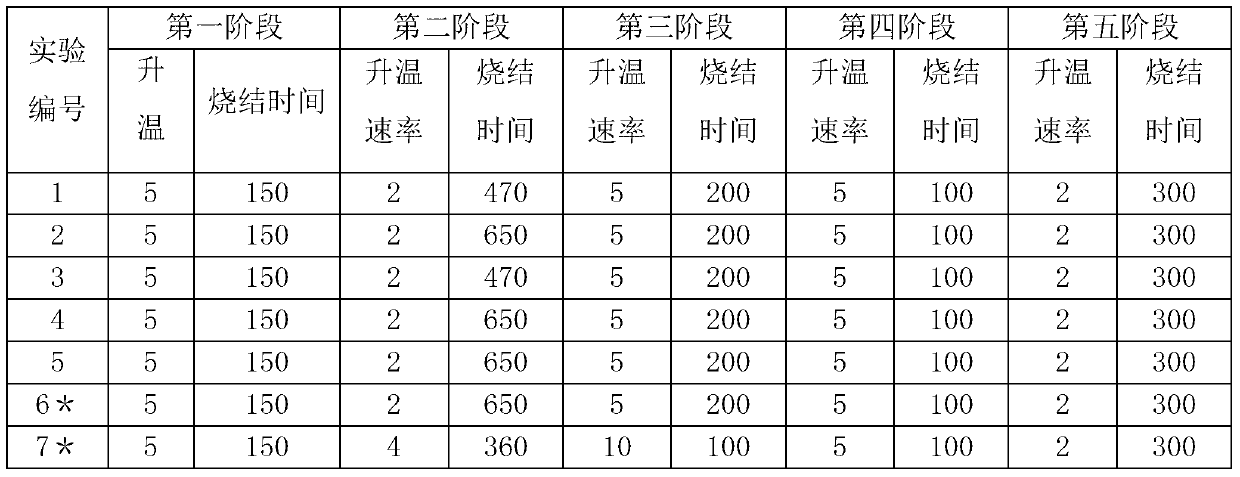
[0030] The sintering system of Experimental Example 8 is relatively simple, specifically, the sintering temperature is gradually increased from room temperature to 1300°C, the heating rate is controlled at 15°C / min, and the total sintering time is 180 minutes.
experiment example 9
[0031] The sintering system of Experimental Example 9 is divided into four stages, in which the first stage is to gradually increase the sintering temperature from room temperature to 150 ° C, the heating rate is controlled at 3 ° C / min, and then keep the temperature for 30 minutes to complete the NH 4 HCO 3 The second stage is to gradually increase the sintering temperature from 150°C to 480°C, the heating rate is controlled at 8°C / min, and then keep the temperature for 120 minutes to complete the TiH 2 Dehydrogenation pore formation; the third stage is to gradually increase the sintering temperature from 480°C to 620°C, control the heating rate at 2°C / min, and then keep it for 240 minutes to complete the reaction pore formation of Ti and Si to generate Ti-Si binary Intermetallic compounds; the fourth stage is to gradually increase the sintering temperature from 620°C to 1300°C, control the heating rate at 5°C / min, and then keep it warm for 300 minutes to promote the reacti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com