Process for improving age hardening effect of high-zinc deformed magnesium alloy
A technology for deforming magnesium alloy and process method, applied in the field of magnesium alloy processing, can solve the problems of reducing supersaturation, over-burning of alloy, coarse size, etc., and achieve the effect of improving deformability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
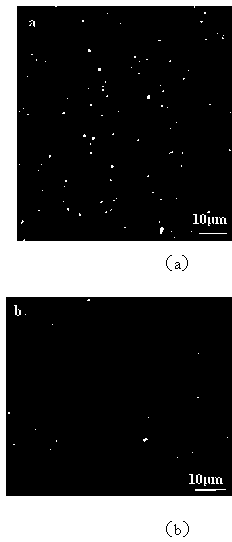
[0019] Example 1: A high-zinc-magnesium alloy ingot was prepared by semi-continuous casting (other casting methods are also applicable), the composition of which is Mg-7Zn-3Al-0.7%Er, and the ingot was homogenized at 325°C for 20h annealed and then cooled to room temperature. figure 1 is the metallographic microstructure of the Mg-7Zn-3Al-0.7%Er alloy before and after homogenization, determined by figure 1 It can be seen that there are a large number of non-equilibrium eutectic compounds in the as-cast structure ( figure 1 a), After homogenization annealing, some non-equilibrium eutectic compounds are dissolved, but there are still many undissolved compound phases in the alloy. Quantitative metallographic results show that the volume percentage of the homogenized compound is 4.7%. The homogenized ingot was face-milled, kept at 350°C for 120 minutes, and then hot-extruded on a horizontal extruder with an extrusion ratio of 25, and then air-cooled to room temperature after ext...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Example 2: A high-zinc-magnesium alloy ingot was prepared by a semi-continuous casting process, and its composition was Mg-10Zn-4Al-0.4%Y. The ingot was subjected to homogenization annealing at 320°C for 40 hours, and then cooled to room temperature with the furnace. The homogenized ingot was face-milled, kept at 340°C for 90 minutes, then hot-extruded on a horizontal extruder with an extrusion ratio of 16, and then air-cooled to room temperature after extrusion. The extruded deformed material is subjected to two-step gradual solution treatment. First, it is held at 315°C for 3 hours, then heated to 360°C at a heating rate of ~ 2K / min, and held at 0.5h, and then placed in warm water at 60°C. Water quenching. Compared with the conventional T6 solid solution treatment process, the compound quantity in the alloy is greatly reduced after the gradual solid solution treatment of the present invention. Finally, the quenched alloy was aged at 150°C for 35h. After the solid so...
Embodiment 3
[0021]Example 3: A high-zinc-magnesium alloy ingot was prepared by a semi-continuous casting process, and its composition was Mg-8Zn-3.5Al-0.4%Er. The ingot was subjected to homogenization annealing at 315°C for 50 hours, and then cooled to room temperature with the furnace . The homogenized ingot was face-milled, kept at 345°C for 60 minutes, then hot-extruded on a horizontal extruder with an extrusion ratio of 28, and then air-cooled to room temperature after extrusion. The extruded deformed material was subjected to two-step gradual solution treatment. First, it was kept at 320°C for 2h, then heated to 355°C at a heating rate of ~ 2K / min, and kept at 1h, and then watered in warm water at 50°C. Quenching. Compared with the conventional T6 solid solution treatment process, the compound quantity in the alloy is greatly reduced after the gradual solid solution treatment of the present invention. Finally, the quenched alloy was aged at 180°C for 20h. After the solid solution ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Vickers hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Vickers hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Vickers hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com