Simple separation and identification method of human placenta myofibroblasts
A fibroblast and separation method technology, which is applied in the field of simple separation and identification of human placental myofibroblastic cells, can solve the problems of complicated experimental steps, waste of resources and the like, and achieves the advantages of convenient cell purification, short time-consuming and pollution reduction. effect of risk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1 Isolation and culture of placental myofibroblasts
[0045] Take fresh placental tissue (within 12 hours) from a normal delivery baby in a sterile biological safety cabinet, use a scalpel to take a tissue about 5 cm long and wide from the center of the placenta, wash it twice with 250 mL of normal saline, and squeeze the placental tissue vigorously. The blood in the tissue was fully washed out, and the blood transfusion tissue on the amniotic membrane and decidua was peeled off with tweezers and a scalpel; the fetal decidua tissue was collected, washed once with 250 mL of normal saline, and the fetal decidua tissue was removed with a scalpel. Cut into 1.5 cm in length and 0.5 cm in width; 75% alcohol was quickly cleaned and disinfected for 10 seconds, and then washed twice with 250 mL of normal saline; DMEM digestion solution containing 1% collagenase I equal to the volume of the tissue fragments was used to incubate at 37 °C Digest for 16-18 h, stop digestion ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2 Morphological identification of placental myofibroblasts
[0048] Cultivate the myofibroblasts isolated according to the method of Example 1. After 2 days of induction of adherence, scattered spindle-shaped adherent cells can be seen under the microscope. The culture supernatant is completely poured out, and the impurity cells that are not adhered to the wall are removed at the same time, and cultured for 5- After 7 days, radial monoclonal cells can be seen to form, and the monoclonal cells are scraped with a cell scraper and cultured in a 12-well plate until the number of cells reaches 5×10 6 When left or right, it is used for other follow-up identifications.
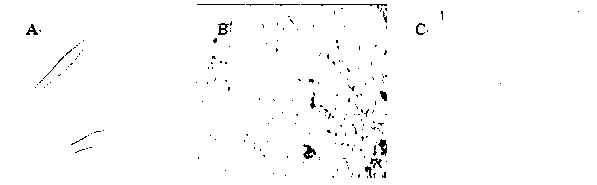
[0049] It can be seen under the microscope ( figure 1 ) The cells are spindle-shaped or spindle-shaped, have two poles, and are small in size. With the increase of culture time, the cells become larger and grow in fusion. These characteristics are in line with the growth characteristics and morphologica...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 Identification of surface markers of placental myofibroblasts
[0051] The 3rd passage cells cultured according to Example 1 from different placenta sources were collected respectively, and the cell surface markers were detected by flow cytometry, and the changes of the cell surface markers from different placenta sources were observed. Digest and collect cells, take 1×10 after counting 6 For each cell, wash once with PBS, centrifuge at 1500 rpm for 10 min; discard the supernatant, leave 200 uL, mix the cells by pipetting, add FITC-labeled CD90, CD45, APC-labeled CD29, HLA-DR and PE-labeled CD44 antibodies 10 each μL, and set 1 tube as a blank control, react at 4 °C in the dark for 30 min, wash once with PBS, centrifuge at 1500 rpm for 10 min, discard the supernatant, leave 200 uL, and test on the machine.
[0052] Flow test results figure 2 It shows that the expressions of CD90 (about 99%), CD44 (about 98%), and CD29 (about 97%) in different placental-deri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com