Zr-based bulk amorphous alloy containing Sn and Nb, and preparation method and application thereof
An amorphous alloy and bulk technology, which is applied to the application field of nuclear power plant fuel assemblies, can solve the problems of inability to meet the use requirements, poor plasticity of amorphous alloys, shortage of resources, etc., and achieve Zr saving, good plasticity and low comprehensive cost. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: Preparation of Zr-Cu-Fe-Al-Sn-Nb series amorphous alloy
[0032] The chemical composition of the zirconium-based alloy is Zr in atomic percent 61.5 Cu 21.5-x Fe 5 Al 11 sn 1 Nb x , x=0, 1, 2, the above formula is used for batching. Among them, Zr has a purity of 99.9wt%, Cu has a purity of 99.98wt%, Fe has a purity of 99.9wt%, Al has a purity of 99.99wt%, Sn has a purity of 99.99wt%, and Nb has a purity of 99.9wt%. The vacuum degree is 1×10 -3 The above master alloys were prepared in an electric arc furnace / water-cooled copper crucible in Pa; the melting atmosphere was high-purity argon (99.999%) that had undergone titanium melting and oxygen consumption, and each alloy ingot was repeatedly smelted 4 times to ensure uniform alloy composition.
[0033] The master alloy ingot was remelted in a vacuum electric arc furnace, and the vacuum degree was set to 1×10 -3 Pa. After it is completely melted, the above-mentioned compositional alloys are quickly ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Zr 61.5 Cu 19.5 Fe 5 Al 11 sn 1 Nb 2 Compressive Properties of Amorphous Alloys
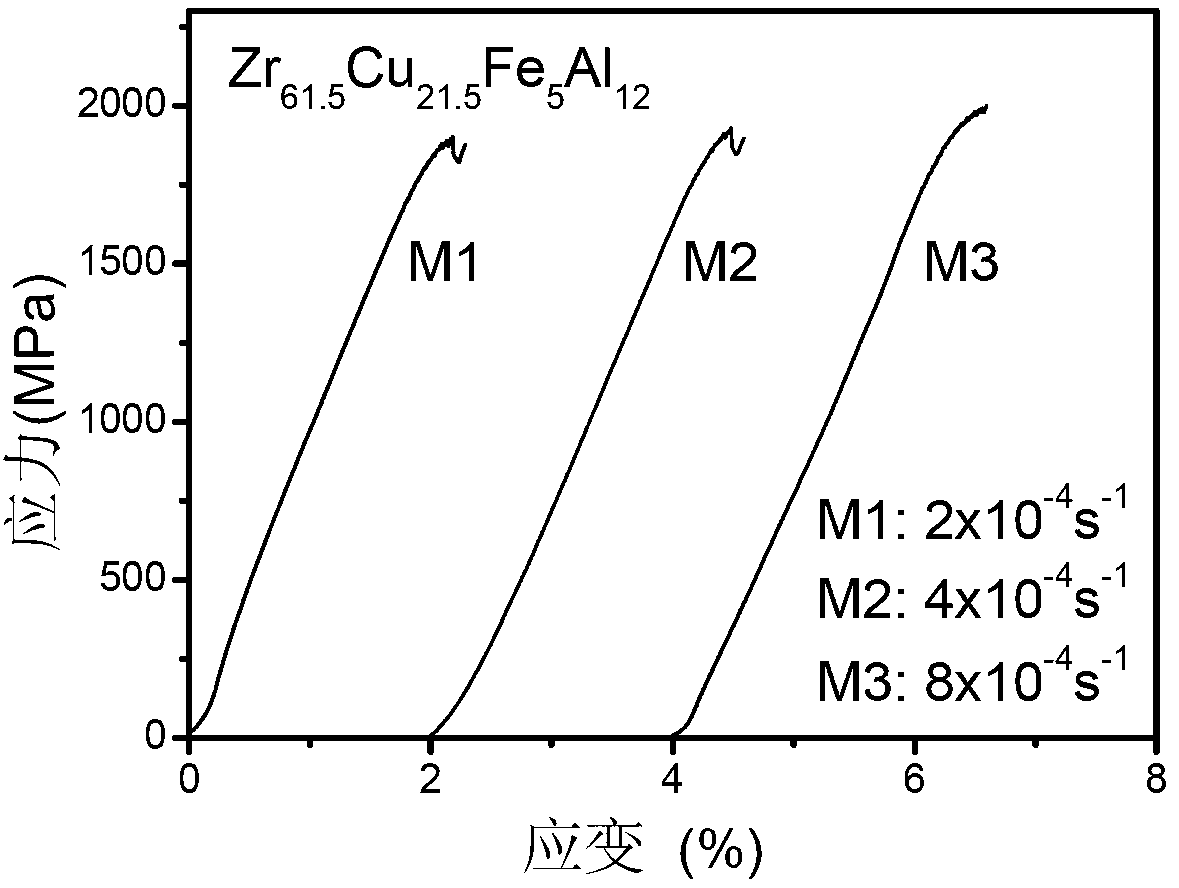
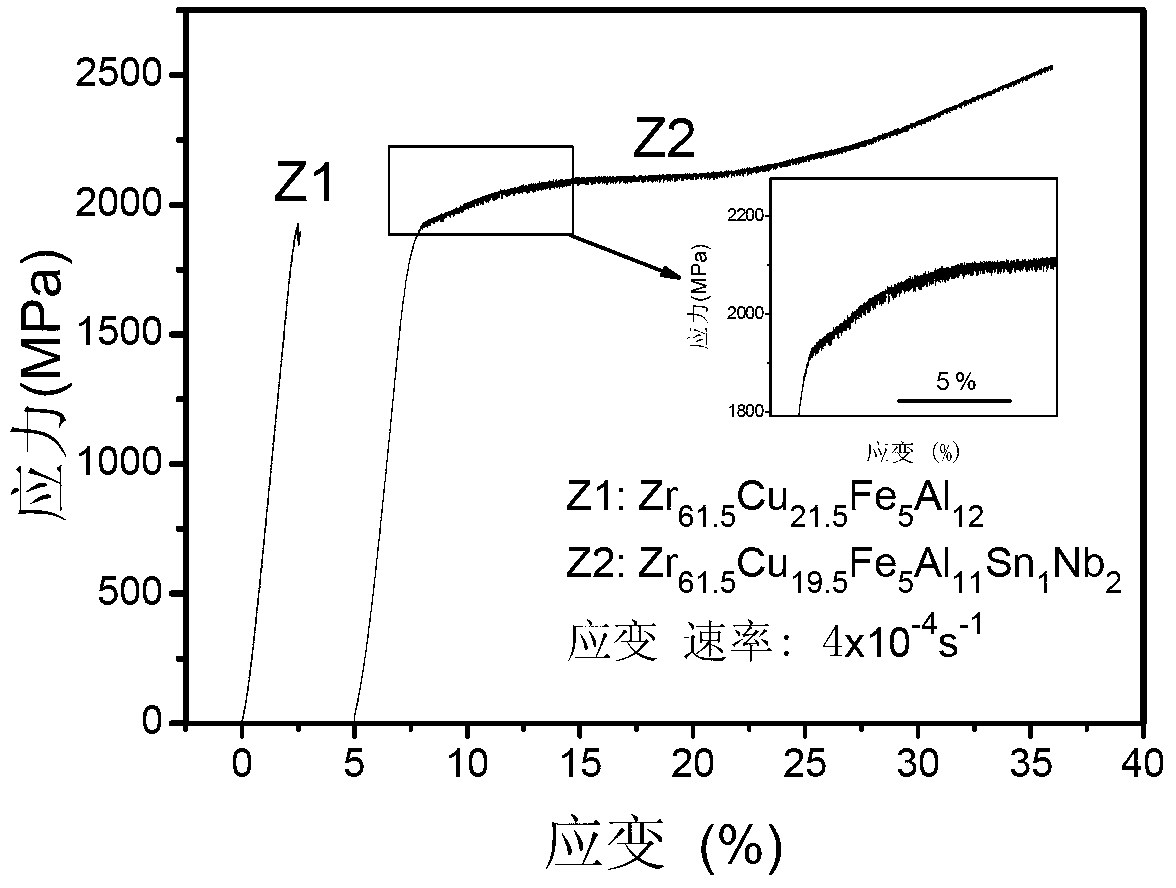
[0035] figure 1 for Zr 61.5 Cu 21.5 Fe 5 Al 12 Compressive stress-strain curves of amorphous alloys. It can be seen from the curve that the amorphous alloy exhibits typical brittle fracture behavior. Zr that the diameter of the present invention is 3mm 61.5 Cu 19.5 Fe 5 Al 11 sn 1 Nb 2 Amorphous rods were cut into compressive test specimens. image 3 Zr shown 61.5 Cu 19.5 Fe 5 Al 11 sn 1 Nb 2 and Zr 61.5 Cu 21.5 Fe 5 Al 12 Amorphous Alloy in 4×10 -4 the s -1 Compressive engineering stress-strain curves at strain rates. Table 1 shows the comparison results of the mechanical properties of the two materials, Zr 61.5 Cu 19.5 Fe 5 Al 11 sn 1 Nb 2 Maximum compressive stress σ of amorphous alloy max Higher than 2500MPa, compression plasticity higher than 15%, significantly higher than Zr 61.5 Cu 21.5 Fe 5 Al 12 Maximum compressive stress and com...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Zr 61.5 Cu 19.5 Fe 5 al 11 sn 1 Nb 2 Resistance to Ar Ion Irradiation of Amorphous Alloys
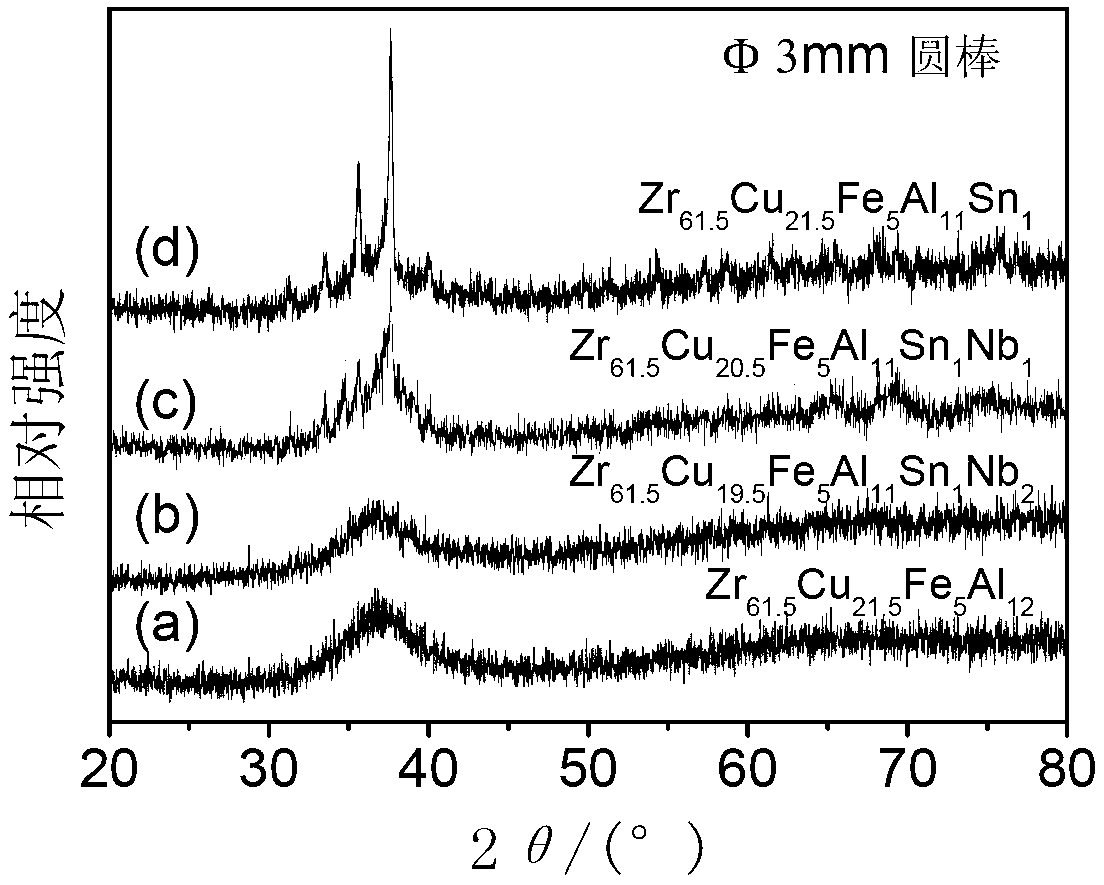
[0040] Zr with a diameter of 3mm prepared above 61.5 Cu 19.5 Fe 5 al 11 sn 1 Nb 2 Amorphous rods are cut into discs with a thickness of 0.6-1mm, polished with sandpaper, surface polished, cleaned with acetone and absolute alcohol, washed with deionized water, and then dried and preserved. With 300keV, the dose is 3×10 16 / cm 2 The Ar ions bombard the surface of the disc sample with a beam density of 0.531μA / cm 2 . like Figure 8 As shown, there is no obvious crystallization peak in the XRD diffraction curve of the sample after irradiation, indicating that the Zr 61.5 Cu 19.5 Fe 5 al 11 sn 1 Nb 2 The alloy still maintains an amorphous structure, which has excellent resistance to Ar ion irradiation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com