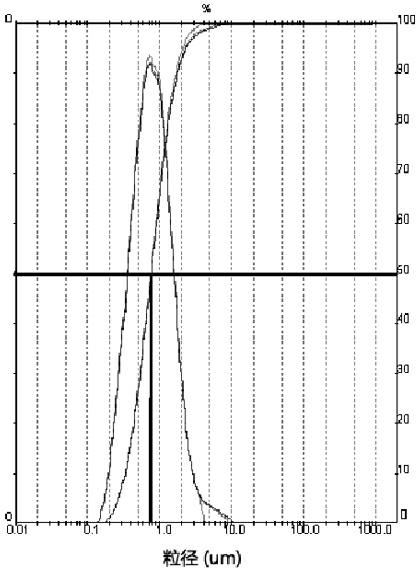
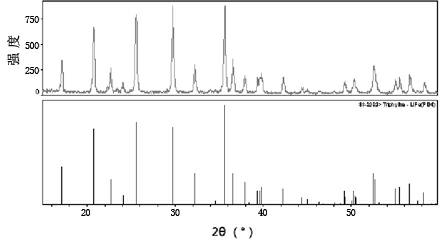
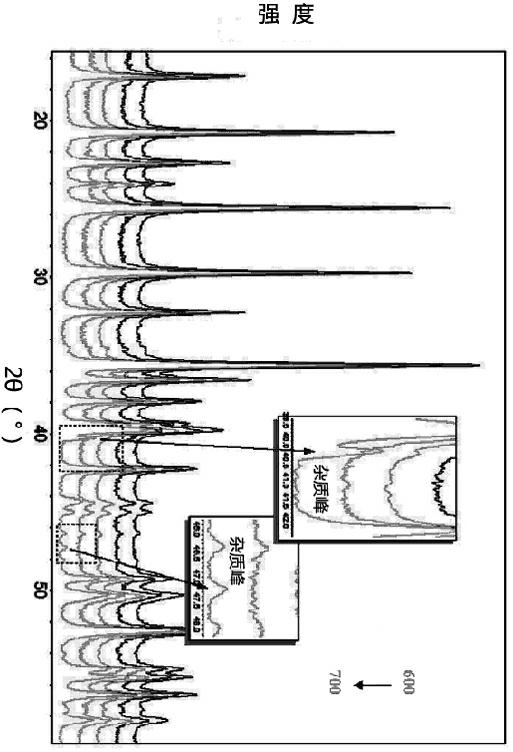
Low-temperature solid-phase synthesis method of nanoscale LiFePO4
A solid-phase synthesis, nano-technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of poor product performance consistency, poor safety performance, high price, etc., to improve output and performance consistency, good charge and discharge Performance, the effect of lowering the calcination temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] 1. Raw material weighing
[0030] Weigh 1250 g lithium salt, 5950 g iron salt, 3850 g phosphorus salt, 500 g carbon source, 100 kg grinding medium and 2 parts of ethanol respectively.
[0031] Wherein, the lithium salt can be at least any one of lithium hydroxide, lithium acetate, lithium carbonate, lithium fluoride, lithium nitrate or lithium dihydrogen phosphate
[0032] The iron salt may be at least any one of ferric oxide, ferric nitrate, ferric hydroxide, ferric chloride, ferrous acetate, ferrous oxide, ferrous oxalate or ferrous sulfate.
[0033] The phosphorus salt may be at least any one of phosphoric acid, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, diammonium hydrogen phosphate, phosphorus pentoxide, ammonium phosphate or lithium dihydrogen phosphate.
[0034] The carbon source can be graphite fine powder (natural or artificial), organic pyrolytic carbon (such as polyvinyl alcohol, carboxymethyl cellulose, polystyrene, rubber latex, polytetrafluoroethylene, polymethyl met...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com