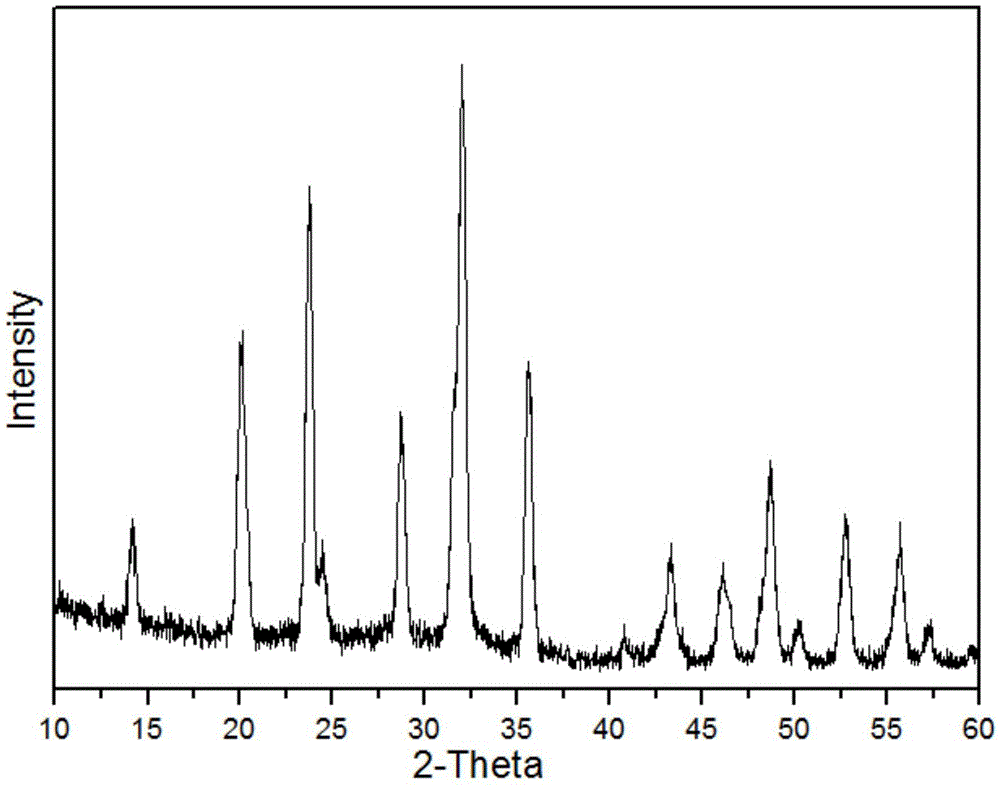
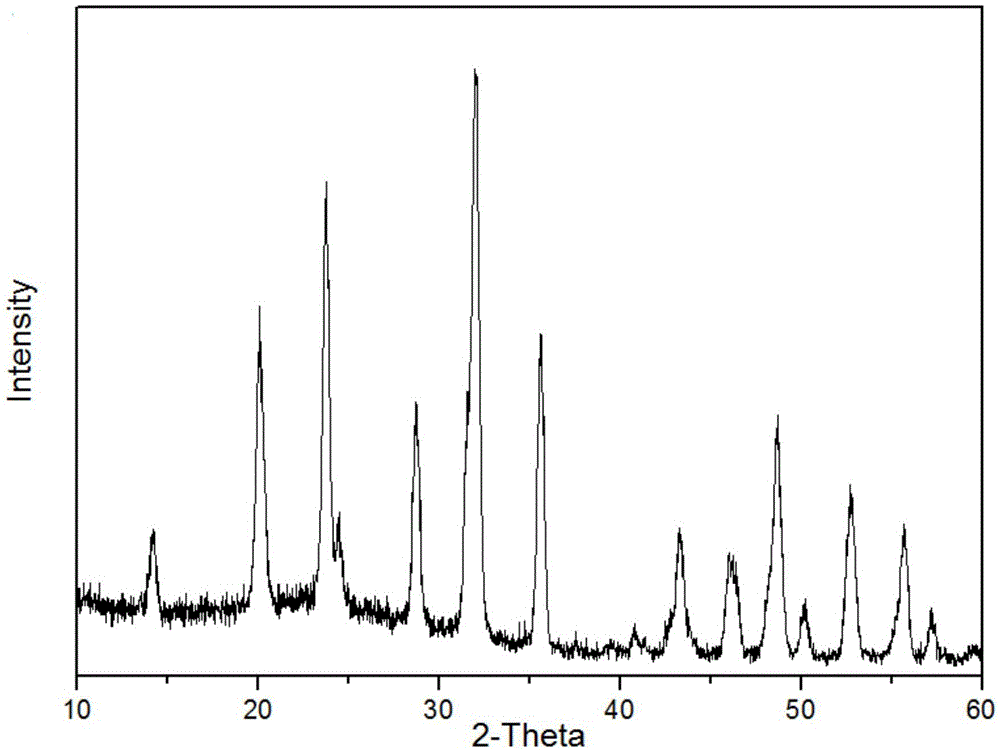
Sodium vanadium phosphate sodium ion battery positive electrode material and preparation method therefor
A sodium vanadium phosphate, ion battery technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to achieve theoretical capacity, poor electronic conductivity of phosphate, etc. The effect of improving electronic conductivity and excellent electrochemical performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0061] S1: Dissolve 0.5g of agarose in a flask filled with 50ml of boiling water, place the entire flask in a water bath environment and keep warm for 10min, the temperature of the water bath is 90°C, and stir at 440r / min throughout the process to make the agarose solution uniform;
[0062] S2: Add sodium acetate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and vanadium acetylacetonate in sequence to the agarose solution in step S1, the masses of sodium acetate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and vanadium acetylacetonate are 1.987g, 2.786g and 5.625g respectively , and close the mouth of the flask, and place it in a water bath environment to keep warm for 10 hours. The temperature of the water bath is 90°C, and the whole process is stirred at 440r / min.
[0063] The stoichiometric ratio of the sodium acetate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and vanadium acetylacetonate satisfies the following relationship: the molar ratio of Na:V:P is 3:2:3, and only when such a stoichiometric ratio relationship...
Embodiment 2
[0070] S1: Dissolve 0.5 g of agarose in a flask filled with 50 ml of boiling water, place the flask as a whole in a water bath for 20 minutes, the temperature of the water bath is 100°C, and stir at 440 r / min throughout the process to make the agarose solution uniform;
[0071] S2: Add sodium acetate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and vanadium acetylacetonate in sequence to the agarose solution in step S1, the masses of sodium acetate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and vanadium acetylacetonate are 1.987g, 2.786g and 5.625g respectively , and close the mouth of the flask, and place it in a water bath environment for insulation for 20 hours. The temperature of the water bath is 100°C, and the whole process is stirred at 440r / min.
[0072] The stoichiometric ratio of the sodium acetate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and vanadium acetylacetonate satisfies the following relationship: the molar ratio of Na:V:P is 3:2:3, and only when such a stoichiometric ratio relationship is satisf...
example 3
[0079] S1: Dissolve 0.5 g of agarose in a flask filled with 50 ml of boiling water, place the entire flask in a water bath environment and keep warm for 30 minutes, the temperature of the water bath is 95°C, and stir at 440 r / min throughout the process to make the agarose solution uniform;
[0080] S2: Add sodium acetate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and vanadium acetylacetonate in sequence to the agarose solution in step S1, the masses of sodium acetate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and vanadium acetylacetonate are 1.987g, 2.786g and 5.625g respectively , and close the mouth of the flask, and place it in a water bath environment to keep warm for 14 hours. The temperature of the water bath is 95°C, and the whole process is stirred at 440r / min.
[0081] The stoichiometric ratio of the sodium acetate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and vanadium acetylacetonate satisfies the following relationship: the molar ratio of Na:V:P is 3:2:3, and only when such a stoichiometric ratio rela...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com