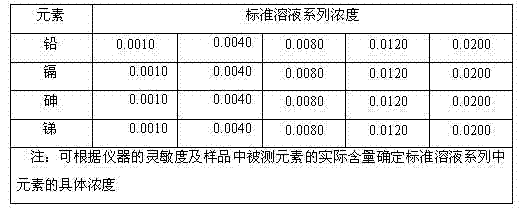
Detection method for determining migration quantity of trace lead, cadmium, arsenic and antimony in food contact material by sequential injection-HG-AFS method
A technology of HG-AFS and food contact materials, which is applied in the detection field of the migration of harmful elements in food contact materials, can solve the problems of cumbersome and time-consuming operations, low sensitivity, and cumbersome operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] A detailed description will be given below of specific embodiments of the present invention.
[0035] The method for detecting the migration of harmful elements in food contact materials by sequential injection-hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0036] 1. Sample pretreatment method
[0037] 1. Migration test
[0038] 1. 1 Tableware containers made of ceramics, enamel, and glass
[0039] Wash and dry the sample first, then add 4% acetic acid to boil to 1cm from the upper edge, add a glass cover, and place it at 22°C±2°C for 24h for migration test. After thorough mixing, take part of the migration test solution for analysis.
[0040] 1. 2 Stainless steel and aluminum tableware containers
[0041] Wash and dry the sample first, then add 4% acetic acid to 0.5cm from the upper edge, add a glass cover, boil on low heat for 30 minutes, take it off, add 4% acetic acid to the original volume, and p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com